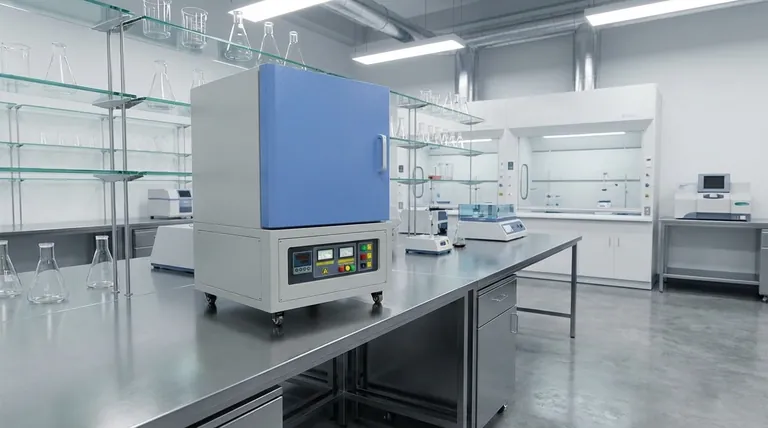
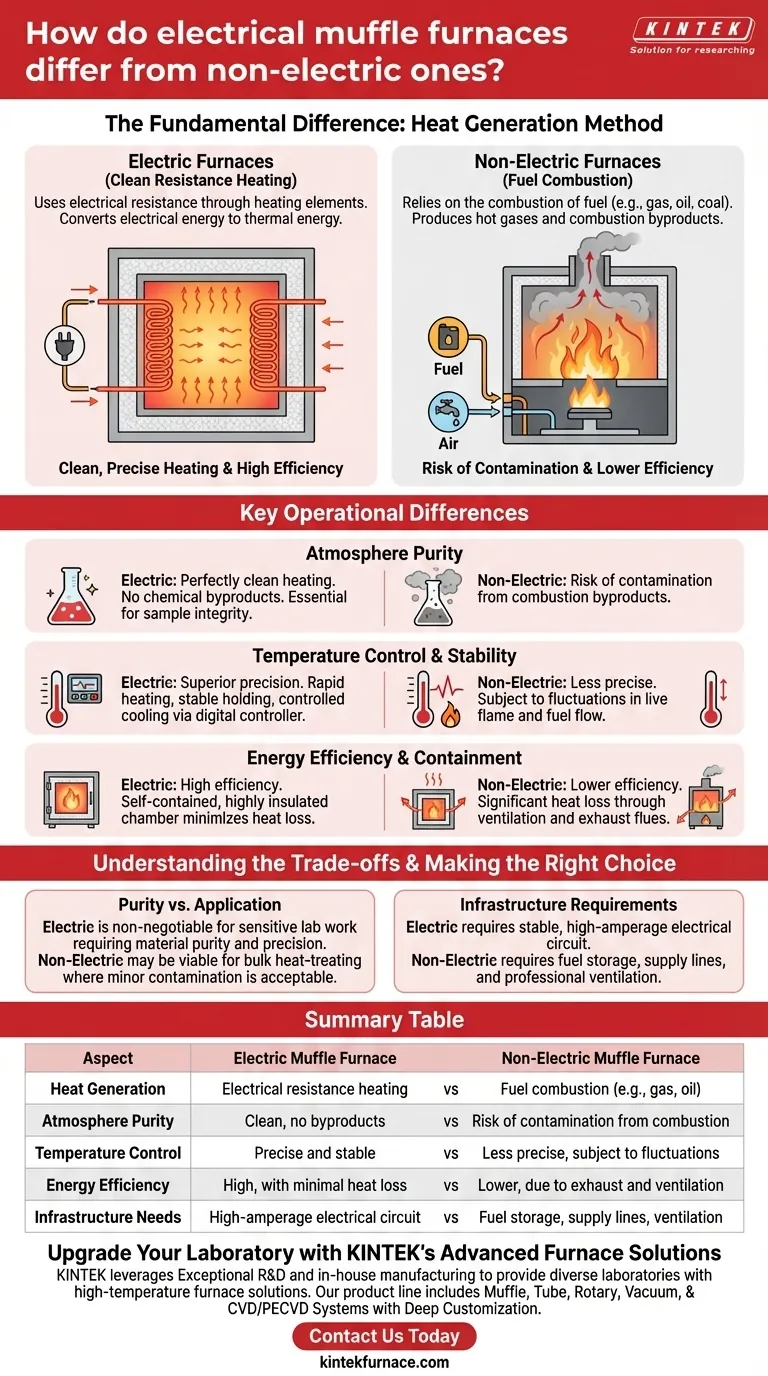
The fundamental difference between electric and non-electric muffle furnaces lies in their method of generating heat. An electric furnace uses electrical resistance through heating elements for clean, precise heating, while a non-electric furnace relies on the combustion of fuel. This core distinction dictates everything from the purity of the heating environment to the level of temperature control possible.
The choice between an electric and non-electric muffle furnace is fundamentally a decision about process control. Electric models offer superior purity and precision, while combustion-based systems operate on different principles that inherently introduce variables electric versions eliminate.

The Core Mechanism: How Heat is Generated
The method of heat generation is the primary point of divergence and the source of all other operational differences.
Electric Furnaces: Clean Resistance Heating
Modern electric muffle furnaces generate heat by passing a current through a high-temperature heating coil. This process, known as resistance heating, converts electrical energy directly into thermal energy.
These coils, often made of durable iron-chrome alloys, use radiation or convection to transfer heat into the chamber. The entire system is housed within heavily insulated material, minimizing heat loss and maximizing energy efficiency.
Non-Electric Furnaces: Fuel Combustion
Non-electric furnaces generate heat by burning a fuel source, such as gas, oil, or coal. This combustion process produces hot gases that heat the furnace chamber.
While effective for reaching high temperatures, this method inherently creates combustion byproducts. These contaminants can interact with the materials being heated inside the furnace.
Key Operational Differences
The contrast in heating methods leads to significant differences in performance, purity, and control.
Purity of the Atmosphere
This is the most critical distinction for many technical applications. Electric furnaces provide a perfectly clean heating environment.
Because there is no combustion, there are no chemical byproducts to contaminate the sample. This is essential for processes like ashing, chemical analysis, or materials science where sample integrity is paramount.
Temperature Control and Stability
Electric furnaces offer far superior temperature control and recovery. The energy input from the heating coil can be regulated with high precision by a digital controller.
This allows for rapid heating to a setpoint, stable temperature holding, and controlled cooling. Non-electric systems are subject to the fluctuations inherent in managing a live flame and fuel flow.
Energy Efficiency and Containment
Electric muffle furnaces are designed as self-contained, energy-efficient cabinets. The insulation is highly effective at keeping thermal energy within the chamber, reducing wasted energy and keeping the exterior cool.
Combustion furnaces, by contrast, require ventilation and exhaust systems (flues) to remove harmful gases, which also results in significant heat loss.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace requires acknowledging the trade-offs inherent in each design.
The Purity vs. Application Dynamic
The unparalleled purity of an electric furnace is a requirement for sensitive lab work but may be unnecessary for some industrial applications.
For large-scale, bulk heat-treating or smelting where minor surface contamination from combustion is not a concern, a fuel-fired furnace may be a viable option.
Infrastructure Requirements
An electric furnace requires access to a stable and often high-amperage electrical circuit. The power draw can be substantial, especially for larger models.
A non-electric furnace requires a completely different infrastructure, including secure fuel storage, supply lines, and professionally installed ventilation to safely manage exhaust fumes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The best furnace is the one that aligns with your specific technical and operational goals.
- If your primary focus is material purity and precision: The clean, highly controllable environment of an electric muffle furnace is non-negotiable for sensitive lab and research work.
- If your primary focus is repeatable, automated processes: The digital controls and thermal stability of a modern electric furnace provide unmatched consistency and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is bulk heating where contamination is not a factor: A combustion-based furnace could be considered, but you must account for the required ventilation and fuel infrastructure.
By understanding that the heating method dictates the furnace's core capabilities, you can confidently select the right tool for your specific technical goal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Electric Muffle Furnace | Non-Electric Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Generation | Electrical resistance heating | Fuel combustion (e.g., gas, oil) |
| Atmosphere Purity | Clean, no byproducts | Risk of contamination from combustion |
| Temperature Control | Precise and stable | Less precise, subject to fluctuations |
| Energy Efficiency | High, with minimal heat loss | Lower, due to exhaust and ventilation |
| Infrastructure Needs | High-amperage electrical circuit | Fuel storage, supply lines, ventilation |
Upgrade Your Laboratory with KINTEK's Advanced Furnace Solutions
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Whether you need the purity and precision of an electric muffle furnace or have specific industrial demands, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why are precision stirring and drying equipment necessary for photocatalytic materials? Master Microstructure Control
- What is the primary role of a muffle furnace in the annealing process of AlCrTiVNbx alloys? Enhance Alloy Strength
- What role does a muffle furnace play in g-C3N4 synthesis? Mastering Thermal Polycondensation for Semiconductors
- Why is a muffle furnace used to determine the ash content of biochar? Master Your Material Purity Analysis
- What role does a muffle furnace play in analyzing the combustion residues? Optimize Your Composite Char Analysis



















