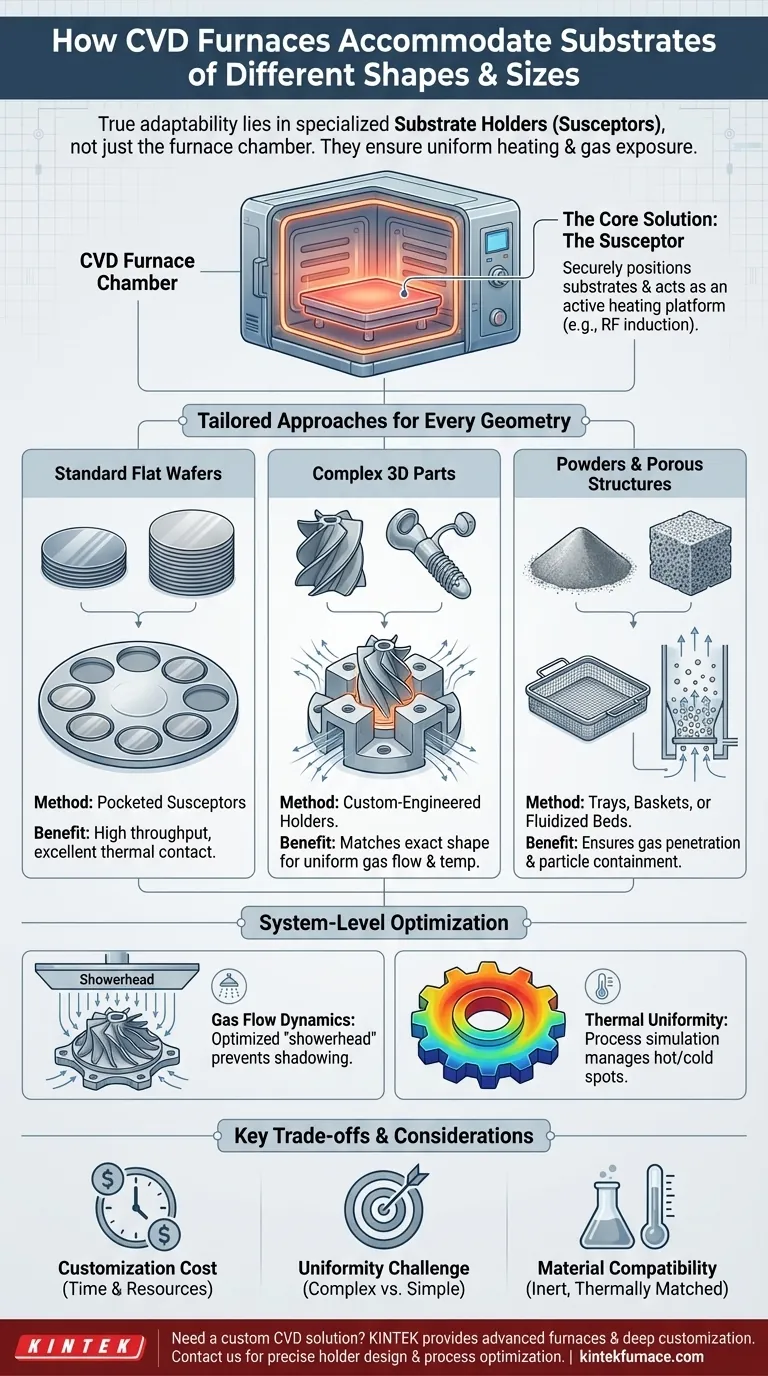
At its core, a CVD furnace's adaptability doesn't come from the furnace chamber itself, but from the highly specialized substrate holders (or susceptors) designed to fit within it. These components are custom-engineered to securely position substrates of virtually any geometry—from flat wafers to complex 3D parts. This ensures the two most critical factors for a successful coating: uniform heating and consistent exposure to precursor gases.
While the furnace provides the controlled environment of heat, vacuum, and gas, it is the internal fixturing—the substrate holder—that truly solves the challenge of geometry. True adaptability in a CVD process is achieved by designing or selecting a holder that precisely matches the substrate's shape and the process's requirements for uniformity.

The Central Role of the Substrate Holder
The flexibility of a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process hinges almost entirely on the design of the component that holds the part being coated. This is far more than a simple shelf.
What is a Susceptor?
A susceptor, or substrate holder, is a platform inside the CVD reactor chamber. It is responsible for physically securing the substrate.
Crucially, it is often an active part of the heating process. In many systems, the susceptor (typically made of graphite) is heated by radio-frequency (RF) induction, and it, in turn, heats the substrate through conduction.
Accommodating Standard Flat Substrates
For the most common applications, like semiconductor wafer processing, susceptors are designed for high throughput and perfect uniformity.
These are often large, circular graphite platters with precisely machined pockets. Each pocket holds a single wafer, ensuring excellent thermal contact and preventing any movement during the process.
Handling Curved and 3D Geometries
This is where custom engineering becomes critical. To coat a non-flat object, such as a turbine blade, medical implant, or optical lens, a standard holder is useless.
Engineers design and fabricate custom holders with cavities or clamps that match the object's exact shape. The goal is to expose all critical surfaces to the gas flow while maintaining stable, uniform temperatures across the entire part.
Managing Powders and Porous Structures
Coating porous materials like metal foams or batches of powder requires a different approach. The challenge is ensuring gas can penetrate the entire structure without the material being displaced by the gas flow.
Holders for these applications often resemble trays or mesh baskets made of a compatible material like molybdenum or graphite. In some advanced systems, a fluidized bed reactor is used, where gas flows up through the powder, causing it to behave like a fluid and ensuring each particle is coated.
Beyond the Holder: System-Level Adaptations
While the holder is the primary tool for accommodation, the rest of the CVD system must work in concert with it to achieve a quality coating on a complex shape.
Optimizing Gas Flow Dynamics
Simply holding a complex part is not enough. The precursor gases must flow uniformly over all surfaces to be coated.
This is managed by the gas injection system, often called a "showerhead." For complex parts, engineers may adjust the showerhead design or use multiple gas inlets to direct the flow around the part and prevent "shadowing," where one area of the substrate blocks gas from reaching another.
Ensuring Thermal Uniformity
Complex shapes have varied thicknesses and surface areas, creating hot and cold spots. A point on a sharp edge will heat up much faster than a thick, flat section.
Process engineers combat this by carefully designing the susceptor to distribute heat evenly and by modulating the furnace's heating elements. Process simulation is often used to predict and correct for these thermal gradients before a run.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Accommodating unique substrate geometries in a CVD process is powerful, but it comes with significant challenges that must be respected.
The Cost of Customization
Designing, simulating, and fabricating a custom susceptor for a novel 3D part is a significant investment in time and resources. It is a dedicated engineering project, not a simple adjustment.
The Uniformity Challenge
The more complex the substrate's geometry, the more difficult it is to achieve a perfectly uniform coating. Sharp corners tend to have higher growth rates, while recessed cavities may be starved of precursor gas, resulting in a thinner film.
Material Compatibility and Contamination
The holder material must be chosen carefully. It must withstand extreme temperatures, be chemically inert to the precursor gases, and have a thermal expansion coefficient that is compatible with the substrate to avoid stress. Any outgassing from the holder can contaminate the final film.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine the feasibility and approach for your application, consider the nature of your substrate and your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is standard planar substrates (e.g., wafers): You can rely on off-the-shelf, high-throughput systems with standardized pocketed susceptors for predictable results.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, three-dimensional parts: Budget for significant R&D, including the design and fabrication of custom susceptors and extensive process optimization, likely involving simulation.
- If your primary focus is coating porous materials or powders: Your main challenge is containment and gas penetration; look for specialized reactor designs or systems with mesh-based holders.
Ultimately, mastering CVD for a specific geometry is a problem of mechanical and process engineering, not just a simple choice of furnace.
Summary Table:
| Substrate Type | Key Accommodation Method | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Flat Substrates | Pocketed susceptors for secure placement | High throughput, uniform heating |
| Curved and 3D Geometries | Custom holders matching exact shape | Uniform gas flow, thermal management |
| Powders and Porous Structures | Trays, mesh baskets, or fluidized beds | Gas penetration, material containment |
Need a CVD furnace tailored to your unique substrate requirements? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities. Our experts design precise substrate holders and optimize processes for uniform coatings on any shape or size—from flat wafers to complex 3D parts and powders. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's performance and achieve your specific experimental goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- Why is the tube design important in CVD furnaces? Ensure Uniform Deposition for High-Quality Films
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab



















