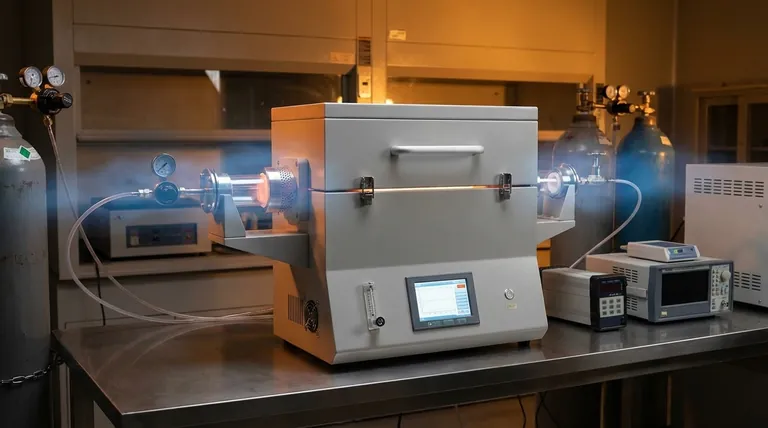
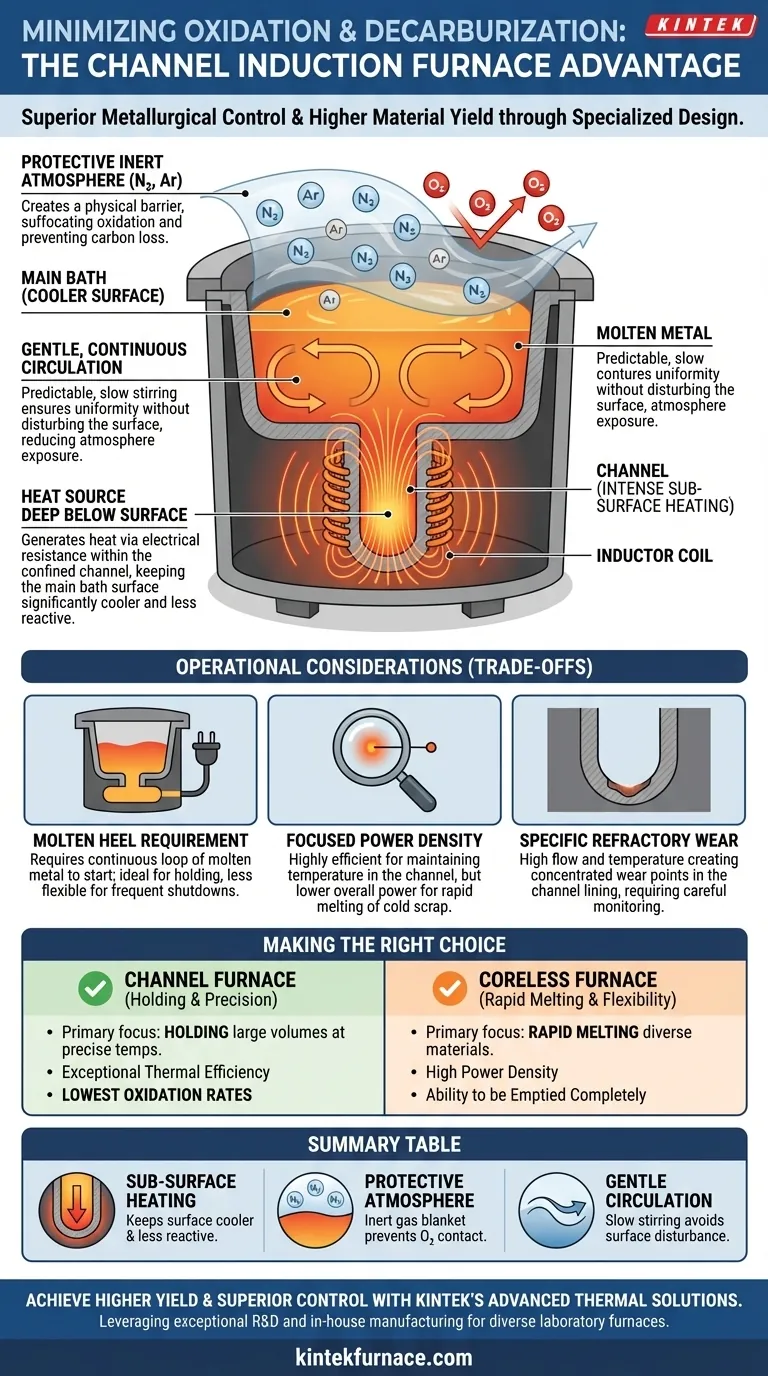
At its core, a channel induction furnace minimizes oxidation and decarburization through two primary mechanisms. First, it generates heat directly within a confined channel of molten metal beneath the main bath, which keeps the surface cooler and less reactive. Second, it facilitates the use of a protective, inert atmosphere over the melt surface, physically preventing contact with ambient oxygen.
The fundamental advantage of a channel furnace is its design, which inherently limits the two conditions necessary for oxidation and decarburization: high surface temperatures and direct exposure to atmospheric oxygen. This results in superior metallurgical control and higher material yield.

The Principle: How to Stop Unwanted Reactions
Oxidation is the reaction of metal with oxygen, forming slag and causing metal loss. Decarburization is the loss of carbon from the surface of steel, which can soften the material and compromise its specified properties. Both are driven by heat and exposure to oxygen.
Controlled Sub-Surface Heating
A channel furnace works like an electrical transformer where the secondary coil is a closed loop, or "channel," of molten metal. The inductor coil generates a powerful magnetic field, inducing a strong electrical current within this metal loop.
This process generates intense heat from electrical resistance inside the channel, deep below the surface of the main bath. The main bath is heated via the gentle circulation of this superheated metal from the channel.
Because the heat source is not an external flame or arc, the surface of the melt remains significantly cooler and calmer than in other furnace types. This lower surface temperature dramatically slows the rate of any potential chemical reactions like oxidation.
Maintaining a Protective Atmosphere
The furnace's enclosed design is perfectly suited for atmosphere control. The ambient air above the melt can be displaced and replaced with a blanket of protective, inert gas.
Gases like nitrogen or argon are commonly used. Because they are non-reactive, they form a physical barrier between the liquid metal surface and any residual oxygen, effectively suffocating the oxidation process. This is also critical for preventing carbon from reacting with oxygen and leaving the steel (decarburization).
Gentle, Continuous Circulation
The electromagnetic forces in the channel create a continuous, predictable, and gentle stirring motion throughout the bath.
This slow, constant movement ensures temperature uniformity without violently disturbing the surface. Unlike the vigorous stirring in some other furnace designs, this gentleness prevents new, hot metal from being constantly exposed to the atmosphere, further minimizing the opportunity for oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While exceptional for minimizing metal loss, the design of a channel furnace presents specific operational considerations that differ from other induction furnaces, such as the coreless type.
The "Molten Heel" Requirement
A channel furnace cannot be started from cold, solid material. It requires a continuous loop of molten metal—the "heel"—to complete the electrical circuit.
This makes it an ideal holding or duplexing furnace but less flexible for operations that require frequent complete shutdowns, startups, or rapid changes in alloy composition.
Focused Power Density
The heat is generated in a very small, concentrated area (the channel). This is highly efficient for maintaining temperature but means channel furnaces have a lower overall power density compared to coreless furnaces.
Consequently, they are not designed for rapid melting of large volumes of cold scrap. Their strength lies in superheating and holding already-molten metal with high thermal efficiency and precision.
Specific Refractory Wear
The high temperatures and constant metal flow are concentrated within the narrow channel. This creates a specific wear point on the refractory lining that must be carefully monitored and maintained, which differs from the more uniform wear patterns in a coreless furnace bath.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a channel furnace must be aligned with your specific metallurgical and operational objectives.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of metal at a precise temperature with minimal quality loss: The channel furnace is the superior choice due to its exceptional thermal efficiency and low oxidation rates.
- If your primary focus is rapid melting of diverse charge materials or frequent alloy changes: A coreless induction furnace may be more suitable due to its high power density and ability to be emptied completely.
Ultimately, the channel induction furnace is engineered to prioritize metallurgical stability and efficiency over raw melting speed.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | How It Minimizes Oxidation & Decarburization |
|---|---|
| Sub-Surface Heating | Heat is generated deep within a molten metal channel, keeping the surface cooler and less reactive. |
| Protective Atmosphere | An inert gas blanket (N₂, Ar) prevents contact with atmospheric oxygen. |
| Gentle Circulation | Predictable, slow stirring ensures temperature uniformity without violently disturbing the surface. |
Achieve higher material yield and superior metallurgical control with KINTEK's advanced thermal solutions.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements like minimizing oxidation.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a custom furnace solution can enhance your process efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















