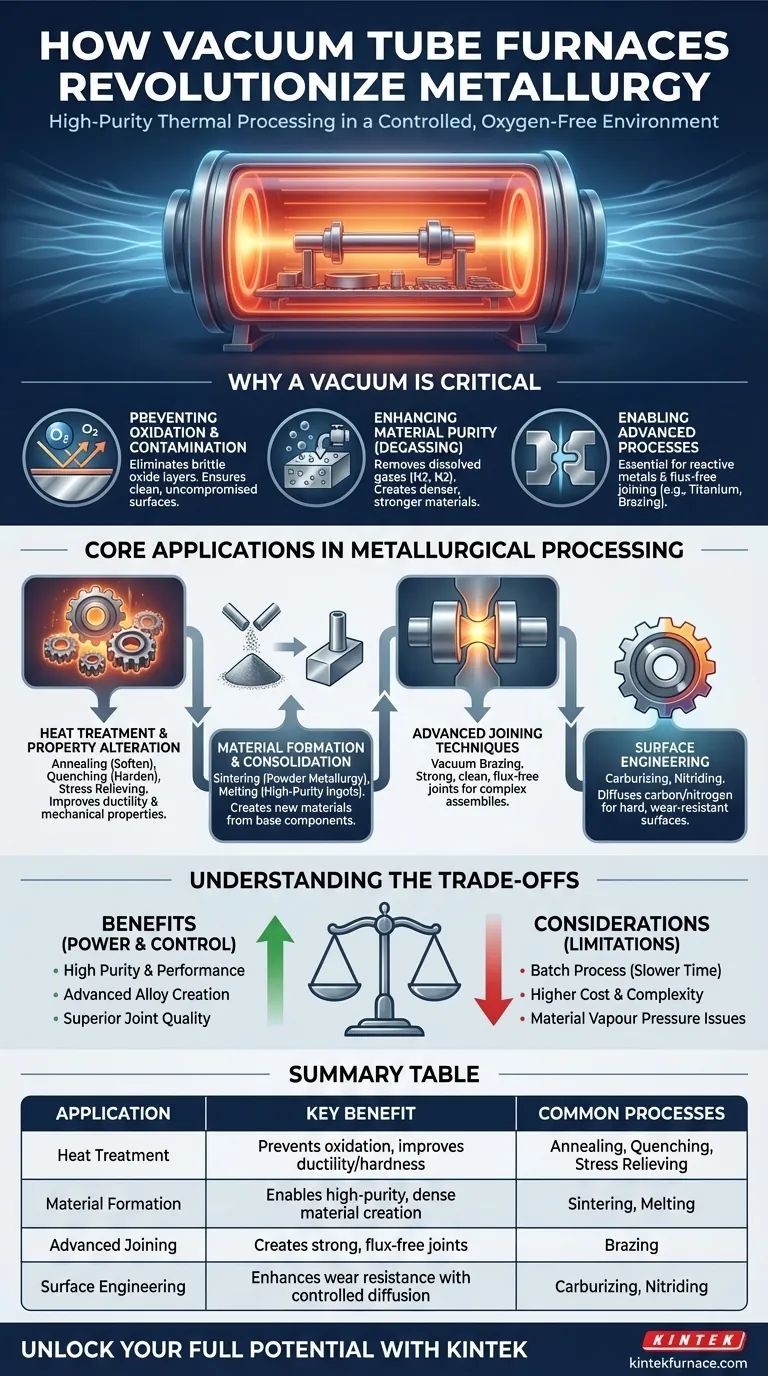
In modern metallurgy, vacuum tube furnaces are indispensable tools for high-purity thermal processing. They are used for a wide range of applications, including heat treatment (annealing, quenching), material formation (sintering, melting), and advanced joining (brazing), by creating a controlled, oxygen-free environment that prevents contamination and enhances the final properties of the metal.
The fundamental value of a vacuum furnace is not just its ability to heat materials, but its power to control the environment in which they are heated. By removing reactive gases like oxygen, these furnaces prevent undesirable chemical reactions, enabling the production of higher-quality, purer, and more advanced materials than is possible in a standard atmosphere.

Why a Vacuum is a Critical Metallurgical Tool
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven by the need for absolute control over a material's chemistry and microstructure during heating. This control directly translates to superior performance.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At high temperatures, most metals aggressively react with oxygen in the air. This reaction, oxidation, forms a brittle, flaky layer on the surface that compromises the material's strength, conductivity, and appearance.
A vacuum furnace works by pumping out the atmosphere from a sealed chamber before heating begins. This removal of oxygen and other reactive gases prevents oxidation, ensuring the metal's surface remains clean and its bulk properties are uncompromised.
Enhancing Material Purity
Many metals contain dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen, which are introduced during initial melting and casting. These trapped gases can create internal voids and cause embrittlement, significantly reducing the material's reliability.
The vacuum environment actively pulls these dissolved gases out of the metal in a process called degassing. This purification step results in a denser, more robust material with improved mechanical properties.
Enabling Advanced Processes
Certain advanced metallurgical processes are simply not possible in a conventional furnace. For example, sintering reactive metal powders (like titanium) or brazing sensitive electronic components requires a pristine environment.
The vacuum ensures that no unwanted reactions occur, allowing for the successful creation of high-performance alloys, near-net-shape parts via powder metallurgy, and strong, flux-free joints.
Core Applications in Metallurgical Processing
Vacuum furnaces are versatile tools applied across various stages of metal production and fabrication. Their use is defined by the desired outcome for the material.
Heat Treatment and Property Alteration
Heat treatment is the controlled heating and cooling of metals to change their physical and mechanical properties.
Key processes include vacuum annealing to soften metal and improve ductility, vacuum quenching to harden it, and stress relieving to remove internal stresses built up during manufacturing.
Material Formation and Consolidation
Vacuum furnaces are central to creating new materials from base components.
Vacuum sintering is used to fuse metal powders together into a solid, dense part, which is critical in powder metallurgy for components in aerospace and medical implants. Vacuum melting is used to produce high-purity ingots of specialty alloys.
Advanced Joining Techniques
Vacuum brazing is a high-tech method for joining two metal components. A filler metal with a lower melting point is placed between the parts, and the entire assembly is heated in a vacuum.
The vacuum ensures a perfectly clean surface, allowing the filler metal to flow and create an exceptionally strong, clean, and durable joint without the need for corrosive chemical fluxes.
Surface Engineering
These furnaces also enable case hardening processes like carburizing and nitriding. In these techniques, the vacuum is established first to clean the part, and then a specific carbon- or nitrogen-rich gas is introduced in precise amounts.
This controlled atmosphere allows carbon or nitrogen to diffuse into the surface of the steel, creating a hard, wear-resistant outer layer while maintaining a tougher core.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnace technology involves specific considerations that make it unsuitable for every application.
Process Time and Throughput
Vacuum processes are inherently batch processes, not continuous. The time required to pump the chamber down to the desired vacuum level before heating and to cool the parts before opening the chamber can significantly extend the total cycle time.
This generally results in lower throughput compared to continuous, open-air furnace systems, making it better suited for high-value components rather than bulk processing.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
A vacuum furnace is a complex system involving a sealed chamber, robust heating elements, and sophisticated vacuum pumps, seals, and control systems.
This complexity leads to higher initial investment, more intensive maintenance requirements, and higher operating costs compared to simpler atmospheric furnaces.
Material Limitations
Certain elements and alloys have a high vapor pressure, meaning they can begin to vaporize or "boil off" under vacuum at high temperatures.
This can be a problem if you want to retain those elements in an alloy (e.g., zinc in brass). This phenomenon, known as outgassing, must be carefully managed to prevent altering the material's composition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate thermal process depends entirely on the material you are working with and your end objective.
- If your primary focus is improving ductility and machinability: Vacuum annealing is the ideal process to soften materials while maintaining pristine surface quality.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, high-strength parts from powders: Vacuum sintering prevents oxidation between powder particles, leading to superior bonding and mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is joining complex or reactive metal components: Vacuum brazing provides exceptionally clean and strong joints without the need for corrosive fluxes.
- If your primary focus is developing cutting-edge materials: A vacuum furnace is essential for researching and producing reactive materials like titanium alloys and nickel-based superalloys.
Mastering processing within a vacuum unlocks a class of materials defined by purity, strength, and performance.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Common Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Prevents oxidation, improves ductility and hardness | Annealing, Quenching, Stress Relieving |
| Material Formation | Enables high-purity, dense material creation | Sintering, Melting |
| Advanced Joining | Creates strong, flux-free joints | Brazing |
| Surface Engineering | Enhances wear resistance with controlled diffusion | Carburizing, Nitriding |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Metallurgical Processes with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on heat treatment, sintering, brazing, or developing cutting-edge alloys, our vacuum tube furnaces deliver superior purity, performance, and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific needs and elevate your metallurgical outcomes! Get in touch now
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















