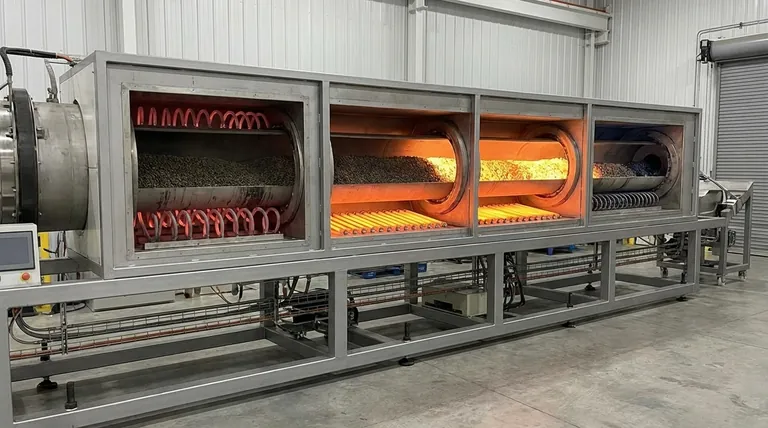
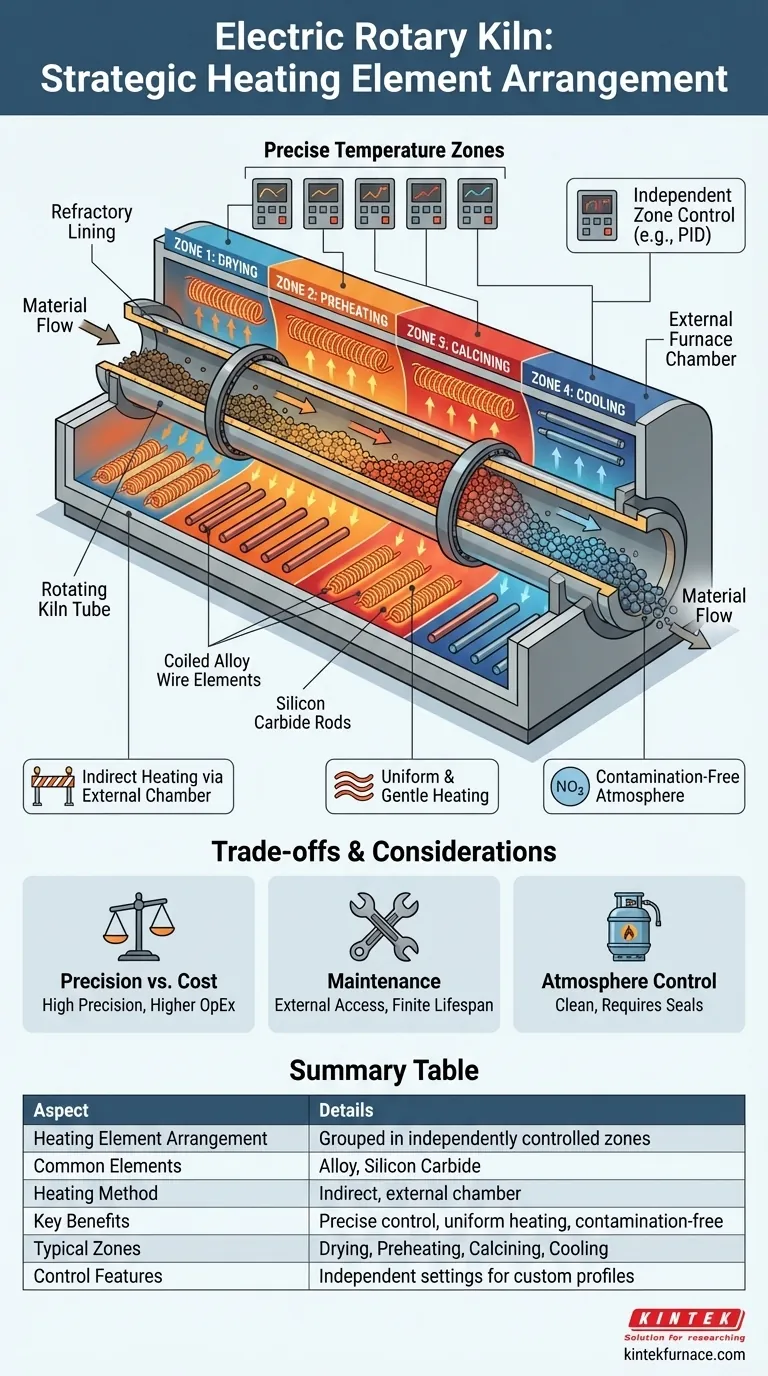
In an electric rotary kiln, the heating elements are not placed randomly. They are strategically arranged in distinct, independently controlled groups along the length of the kiln to create precise temperature zones. For example, a common configuration uses alloy heating elements grouped into four zones and rows of silicon carbide rods placed at the bottom of the furnace chamber.
The arrangement of heating elements is the core design feature enabling an electric rotary kiln to function. It transforms the kiln from a simple heated tube into a sophisticated instrument for executing a precise thermal profile, heating material gradually and controllably as it travels from inlet to outlet.

The Principle of Zoned Heating
The fundamental purpose of arranging heating elements in groups is to divide the kiln into functional zones. This allows for precise control over the temperature gradient that the material experiences as it moves through the kiln.
Creating a Thermal Profile
Each group of heating elements corresponds to a specific stage of the process, such as drying, preheating, calcining, or cooling. As material advances down the inclined, rotating tube, it enters successively hotter zones.
This methodical progression ensures the material is heated and cooled at the exact rate required for the desired chemical reaction or physical change.
The Role of Independent Control
Each zone's temperature is set and controlled separately. This is the primary advantage of an electric kiln.
An operator can program a precise "thermal profile" or recipe, ensuring that the material in the preheating zone is at one temperature while material in the calcining zone is at a higher, completely different temperature. This level of control is critical for sensitive or high-purity materials.
Physical Placement of Elements
The heating elements, such as silicon carbide rods or coiled alloy wire, are typically housed in an external, stationary furnace chamber that surrounds the rotating kiln cylinder.
They are often arranged in rows along the bottom or sides of this outer chamber. This configuration provides indirect heat, warming the kiln shell, which in turn radiates heat to the material tumbling inside.
Why Indirect Heating is Key
Electric rotary kilns almost always use an indirect heating method. This design choice has significant implications for material processing.
How Heat is Transferred
The electric elements heat the atmosphere and refractory surfaces within the outer furnace chamber. This energy is transferred to the rotating kiln shell, which becomes the primary heat source for the material inside.
This prevents any direct contact between the heating elements and the process material, which is crucial for preventing contamination. It also provides a more uniform, gentle heating compared to a direct flame.
The Importance of Refractory Linings
The rotating kiln tube is lined with a refractory material (insulation). This lining serves two purposes: it protects the external steel shell from the extreme internal temperatures and it helps maintain and stabilize the temperature of the material bed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the zoned electric design offers superior control, it comes with specific considerations that differ from traditional, direct-fired kilns.
Precision vs. Operating Cost
Electric heating provides unmatched temperature precision and repeatability. However, the operational cost of electricity can be significantly higher than that of natural gas, making it a critical factor for large-scale, bulk material processing.
Element Maintenance and Lifespan
Heating elements are consumable components with a finite lifespan. Their placement in an external furnace chamber facilitates easier inspection and replacement compared to internal elements, but it remains a recurring maintenance task.
Atmosphere Control
Because there is no combustion gas, an electric kiln offers a clean processing environment. This makes it easier to control the internal atmosphere, allowing for inert (nitrogen, argon) or reactive gas environments, but requires robust seals at the inlet and outlet to prevent air leakage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The strategic arrangement of heating elements directly supports specific process outcomes. Understanding this allows you to select the right technology for your application.
- If your primary focus is material purity: The indirect, zoned heating of an electric kiln is ideal, as it eliminates contamination from combustion byproducts.
- If your primary focus is a complex thermal profile: The independent, multi-zone control is a non-negotiable advantage for executing precise heating, soaking, and cooling ramps.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: The programmable and automated nature of electric heating zones ensures that every batch is processed under identical conditions.
Ultimately, the deliberate arrangement of heating elements is what empowers the electric rotary kiln to deliver unparalleled process control.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Heating Element Arrangement | Grouped into distinct, independently controlled zones along the kiln length |
| Common Elements Used | Alloy heating elements, silicon carbide rods |
| Heating Method | Indirect heating via external furnace chamber |
| Key Benefits | Precise temperature control, uniform heating, contamination-free processing |
| Typical Zones | Drying, preheating, calcining, cooling |
| Control Features | Independent zone temperature settings for custom thermal profiles |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with tailored high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced electric rotary kilns and other furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for superior material processing. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency



















