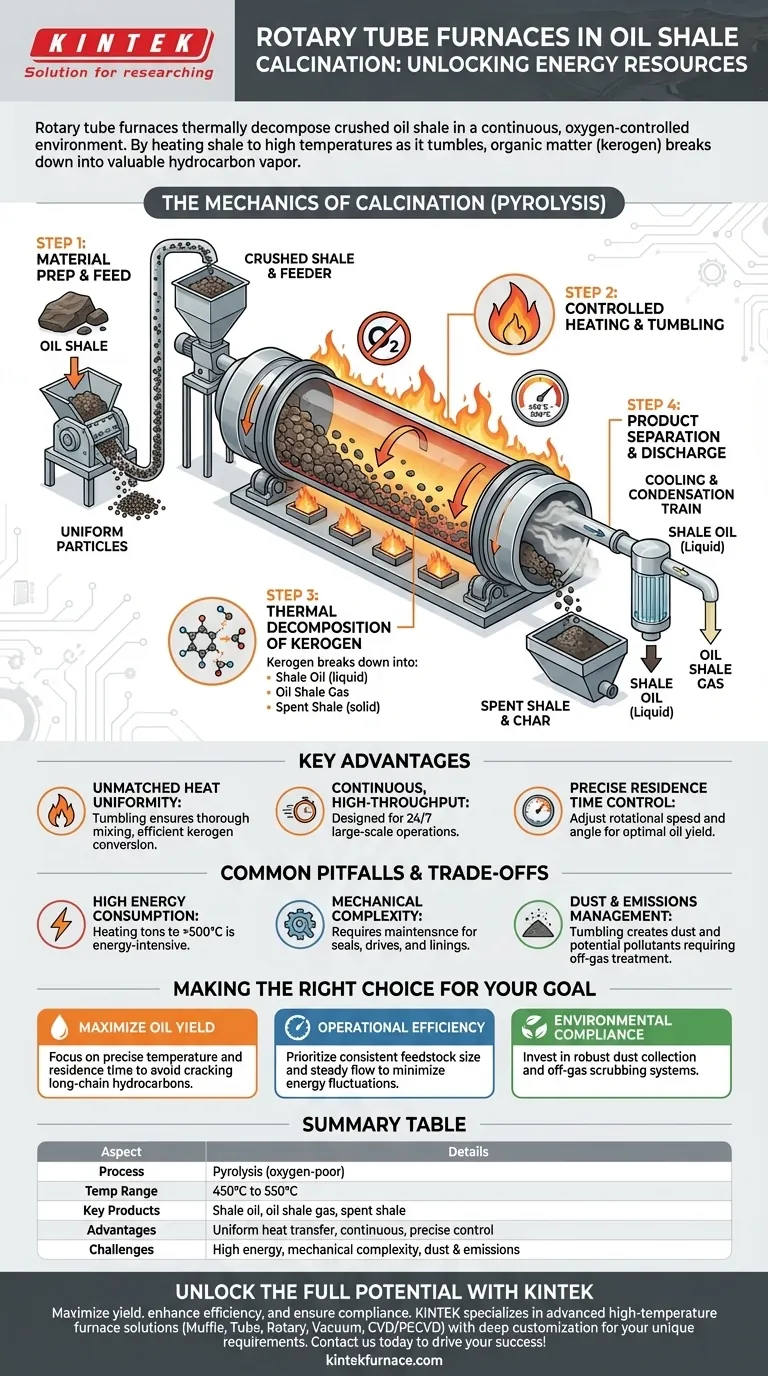
Rotary tube furnaces are used to thermally decompose crushed oil shale in a continuously moving, oxygen-controlled environment. By heating the shale to high temperatures as it tumbles through a rotating tube, the furnace efficiently breaks down the solid organic matter (kerogen) within the rock, releasing it as valuable hydrocarbon vapor for collection.
The core function of a rotary tube furnace in this context is to achieve uniform and controlled thermal decomposition at an industrial scale. The furnace’s rotation is the key, ensuring every particle of shale is heated evenly, which maximizes the release of shale oil and prevents the process from becoming inefficient combustion.
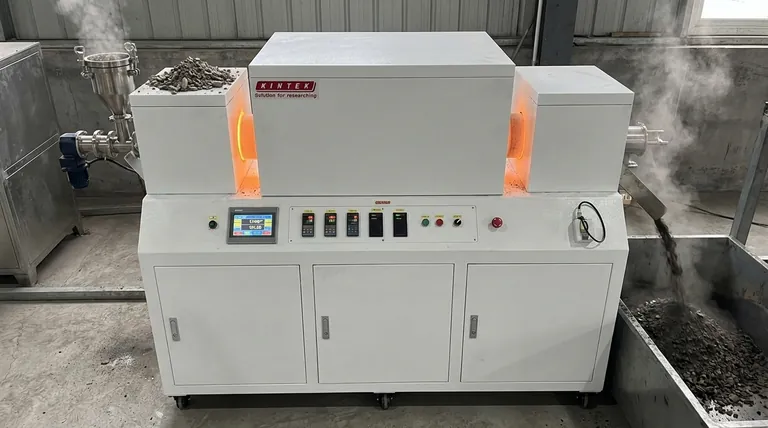

The Mechanics of Oil Shale Calcination
Calcination is a broad term for thermal decomposition. In the context of oil shale, the specific process is more accurately called pyrolysis—heating in the near-absence of oxygen. A rotary furnace is the ideal machine for conducting this process continuously.
Step 1: Material Preparation and Feed
Before entering the furnace, raw oil shale is crushed into a specific, relatively uniform particle size. This is critical because it ensures consistent heat absorption and reaction time for every particle inside the furnace. This prepared material is then continuously fed into the elevated end of the long, cylindrical furnace tube.
Step 2: The Controlled Heating Environment
The furnace tube is positioned at a slight angle and rotates slowly. This rotation causes the crushed shale to tumble and gradually move down the length of the tube toward the lower, discharge end. This tumbling action is the furnace's primary advantage, as it constantly exposes new surfaces to the heat, preventing hot spots and ensuring every particle is processed.
Step 3: Thermal Decomposition of Kerogen
As the shale travels through the heated zone, its temperature rises to the target range, typically between 450°C and 550°C. This heat breaks down the complex organic polymer, kerogen, into smaller, more valuable molecules:
- Shale Oil: A synthetic crude oil that condenses into a liquid upon cooling.
- Oil Shale Gas: Non-condensable hydrocarbon gases.
- Spent Shale: The remaining solid mineral rock and a carbonaceous residue called char.
Critically, this process is done in an oxygen-poor atmosphere to prevent the valuable hydrocarbons from burning.
Step 4: Product Separation and Discharge
The hydrocarbon vapors released during pyrolysis are drawn from the furnace. They are passed through a cooling and condensation train to separate the liquid shale oil from the non-condensable gases. The solid spent shale exits the lower end of the furnace, where it is cooled and removed for disposal or further use.
Understanding the Key Advantages
Rotary furnaces are the industry standard for this process not by accident, but because their design offers fundamental benefits for high-volume thermal processing.
Unmatched Heat Transfer Uniformity
The tumbling motion ensures that the material is mixed thoroughly as it's heated. This convective movement is far more effective than simple conduction, leading to highly uniform temperatures throughout the material bed and maximizing the efficiency of the kerogen conversion.
Continuous, High-Throughput Operation
Unlike batch ovens, rotary furnaces are designed for a continuous flow of material. This makes them exceptionally well-suited for the large-scale, 24/7 operations required to make oil shale processing economically viable.
Precise Control Over Residence Time
The time the shale spends inside the hot zone of the furnace is a critical variable. This residence time can be precisely controlled by adjusting the furnace's rotational speed and angle of inclination, allowing operators to fine-tune the process to maximize oil yield.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
While effective, employing rotary furnaces involves significant engineering and operational challenges that must be managed.
High Energy Consumption
Heating tons of rock to over 500°C is an extremely energy-intensive process. The overall economic feasibility of an oil shale operation often hinges on the cost of energy used for pyrolysis.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
Rotary furnaces are heavy-duty machines with complex rotating seals, large gear-and-pinion drives, and refractory linings that must withstand high temperatures and abrasion. These components require regular, specialized maintenance to prevent costly downtime.
Dust and Emissions Management
The tumbling of crushed rock creates significant dust, which must be captured and managed. Furthermore, the pyrolysis process can release sulfur compounds and other pollutants that require robust off-gas treatment systems to meet environmental regulations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When implementing or optimizing an oil shale calcination process, your primary objective will dictate your focus.
- If your primary focus is maximizing oil yield: Concentrate on precise temperature control and optimizing residence time to ensure complete kerogen conversion without thermally "cracking" the desired long-chain hydrocarbons into less valuable gas.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Prioritize a consistent feedstock particle size and a steady-state material flow to minimize energy fluctuations and reduce mechanical stress on the equipment.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: Invest heavily in robust systems for dust collection and the scrubbing of off-gases, treating them as integral parts of the process rather than afterthoughts.
By mastering the interplay between material properties, heat transfer, and residence time, you can effectively leverage rotary furnaces to convert raw oil shale into a valuable energy resource.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Pyrolysis (heating in oxygen-poor environment) |
| Temperature Range | 450°C to 550°C |
| Key Products | Shale oil, oil shale gas, spent shale |
| Advantages | Uniform heat transfer, continuous operation, precise residence time control |
| Challenges | High energy consumption, mechanical complexity, dust and emissions management |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Oil Shale Processing with KINTEK
Are you aiming to maximize oil yield, enhance operational efficiency, or ensure environmental compliance in your calcination processes? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratory and industrial needs. Our rotary tube furnaces, part of a comprehensive product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, are engineered for superior performance and reliability. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements, ensuring optimal heat transfer, continuous throughput, and precise control for your oil shale applications.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can drive your success and schedule a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput



















