At their core, rotary kilns serve environmental protection by using high-temperature thermal processes to safely destroy hazardous materials, convert waste into energy, and recover valuable resources from various waste streams. This technology transforms environmental liabilities into either harmless substances or valuable assets, making it a cornerstone of modern industrial recycling and waste management.
The true value of a rotary kiln in an environmental context is its ability to provide a highly controlled, high-temperature environment. This control allows for the complete destruction of pollutants and the precise chemical reactions needed to reclaim valuable materials from what would otherwise be landfill waste.

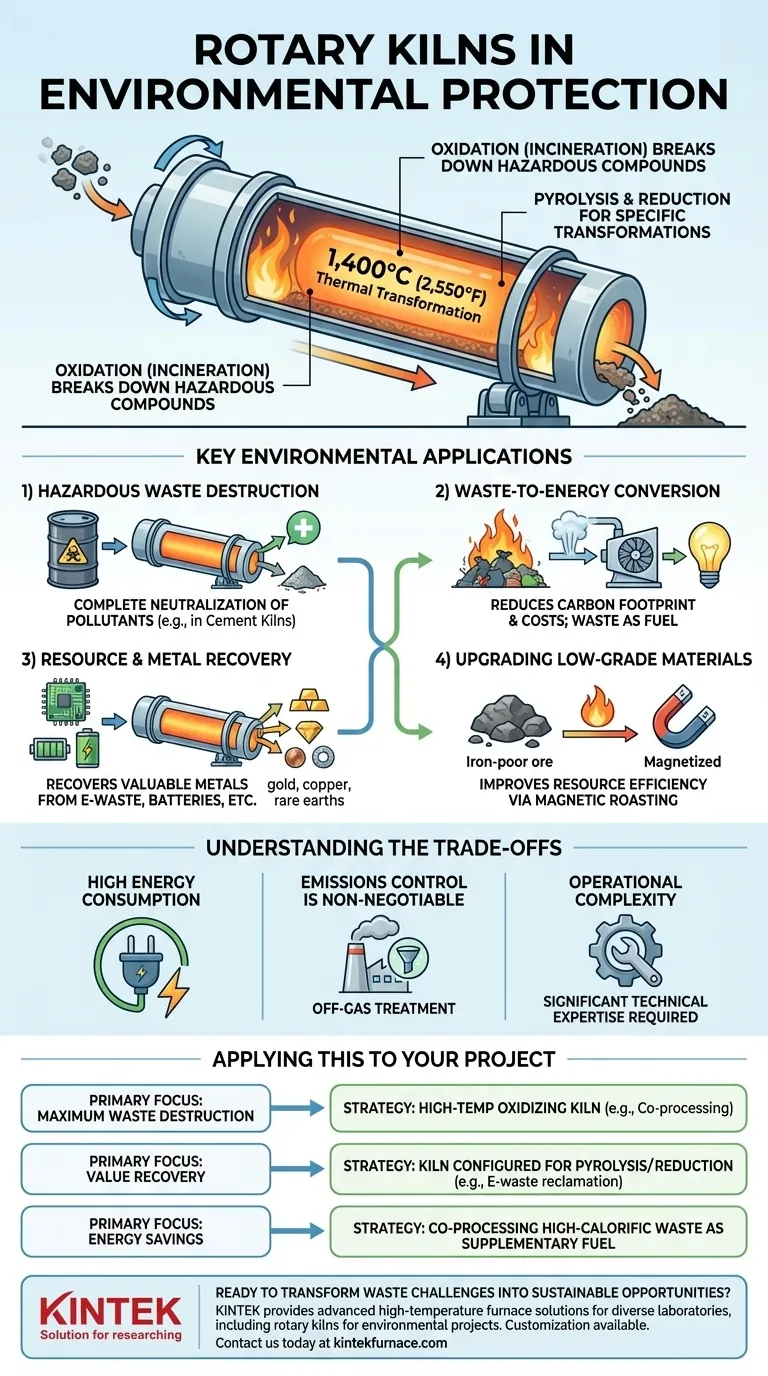
The Principle: Thermal Transformation
A rotary kiln is a large, rotating, and slightly inclined cylindrical furnace. Material is fed into the higher end and moves down toward the flame at the lower end due to the rotation and incline, ensuring uniform exposure to heat. This simple mechanism is powerful for environmental applications.
How High Temperatures Neutralize Waste
The extreme heat inside a kiln—often exceeding 1,400°C (2,550°F)—powers several key processes. Oxidation (incineration) breaks down complex hazardous organic compounds into simpler, safer molecules like carbon dioxide and water. Other processes like pyrolysis and reduction can be used to target specific chemical transformations.
A Controlled and Contained Process
Modern kilns are designed as closed systems. Advanced sealing devices prevent the escape of raw materials or harmful gases, while hydraulic mechanisms ensure steady and reliable operation. This containment is critical when processing volatile or hazardous waste.
Key Environmental Applications
The versatility of thermal processing allows rotary kilns to be deployed across a wide range of environmental challenges.
Hazardous Waste Destruction
For over two decades, industries like cement manufacturing have used their kilns to co-process hazardous waste. The sustained high temperatures and long residence time in a cement kiln guarantee the complete destruction of harmful organic pollutants, neutralizing their environmental threat.
Waste-to-Energy Conversion
The same process of burning waste in a kiln also serves as a fuel source. By using high-calorific waste materials as a partial substitute for fossil fuels like coal, facilities can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and operating costs, turning waste disposal into an energy-saving activity.
Resource and Metal Recovery
Rotary kilns are essential for the circular economy. They are used to recover valuable metals from a variety of sources that are difficult to process otherwise, including:
- E-waste and circuit boards
- Spent industrial catalysts and batteries
- Mining tailings and industrial by-products like red mud
The kiln provides the controlled environment needed to separate the valuable metals through processes like roasting or reduction.
Upgrading Low-Grade Materials
Kilns can also improve resource efficiency. For example, they are used to roast iron-poor ore, changing its magnetic properties. This magnetic roasting makes the ore suitable for magnetic separation, allowing for the profitable extraction of iron from what was previously considered waste rock.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, rotary kilns are not a universal solution. Their application requires careful consideration of the operational realities.
High Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining the high temperatures required for thermal treatment is an energy-intensive process. While some of this can be offset by using waste as fuel, the kiln itself is a major energy consumer. Electric rotary kilns offer an alternative to direct fossil fuel combustion, but their environmental benefit depends on the carbon footprint of the electrical grid.
Emissions Control is Non-Negotiable
Burning waste, especially complex industrial or municipal waste, generates process gases that can contain pollutants. A rotary kiln system is only environmentally sound if it is paired with a sophisticated off-gas treatment system to scrub and filter these emissions before they are released into the atmosphere.
Operational Complexity
Managing a rotary kiln requires significant technical expertise. Ensuring the correct temperature profile, feed rate, and atmospheric conditions is critical for achieving complete destruction of contaminants and preventing the formation of unwanted by-products.
Applying This to Your Project
When evaluating a rotary kiln for an environmental application, your primary goal will dictate the optimal strategy.
- If your primary focus is maximum waste destruction: A high-temperature oxidizing (incinerating) kiln, such as a cement kiln co-processing waste, is the most direct solution.
- If your primary focus is value recovery: A kiln configured for specific processes like pyrolysis or reduction is necessary to reclaim metals from e-waste, batteries, or catalysts.
- If your primary focus is energy savings: Co-processing high-calorific waste as a supplementary fuel in an existing industrial kiln offers a clear path to reducing fossil fuel dependence.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln is a proven and robust technology for transforming waste from a problem into a resource.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Hazardous Waste Destruction | Complete neutralization of pollutants |
| Waste-to-Energy Conversion | Reduces carbon footprint and costs |
| Resource and Metal Recovery | Recovers valuable metals from e-waste, batteries, etc. |
| Upgrading Low-Grade Materials | Improves resource efficiency via magnetic roasting |
Ready to transform your waste challenges into sustainable opportunities? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on hazardous waste destruction, energy recovery, or metal reclamation, our tailored solutions can enhance your environmental projects. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency



















