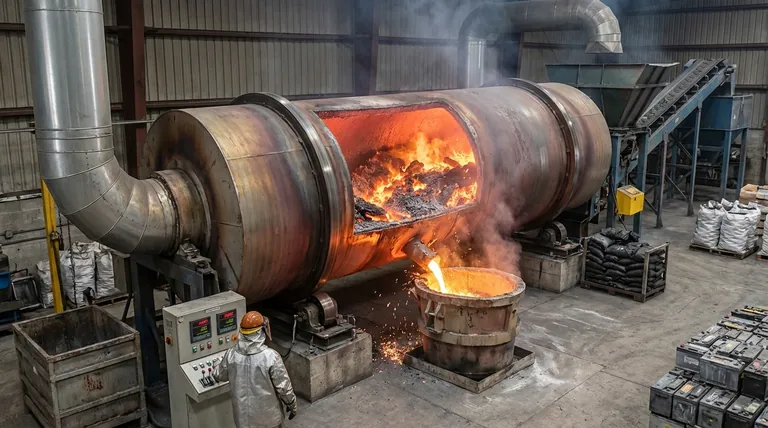
In industrial lead recycling, rotary furnaces serve as the primary vessel for melting lead-bearing materials, like battery scrap, and chemically converting lead compounds back into their pure, metallic form. The furnace's rotation is the key to this process, ensuring all materials are mixed thoroughly and heated uniformly, which is critical for an efficient chemical reaction.
The core function of a rotary furnace is to create a controlled, dynamic environment. Its value lies not just in melting the scrap but in using its uniform heat and constant motion to facilitate the chemical reduction of lead oxides and sulfates into valuable, reusable metallic lead.

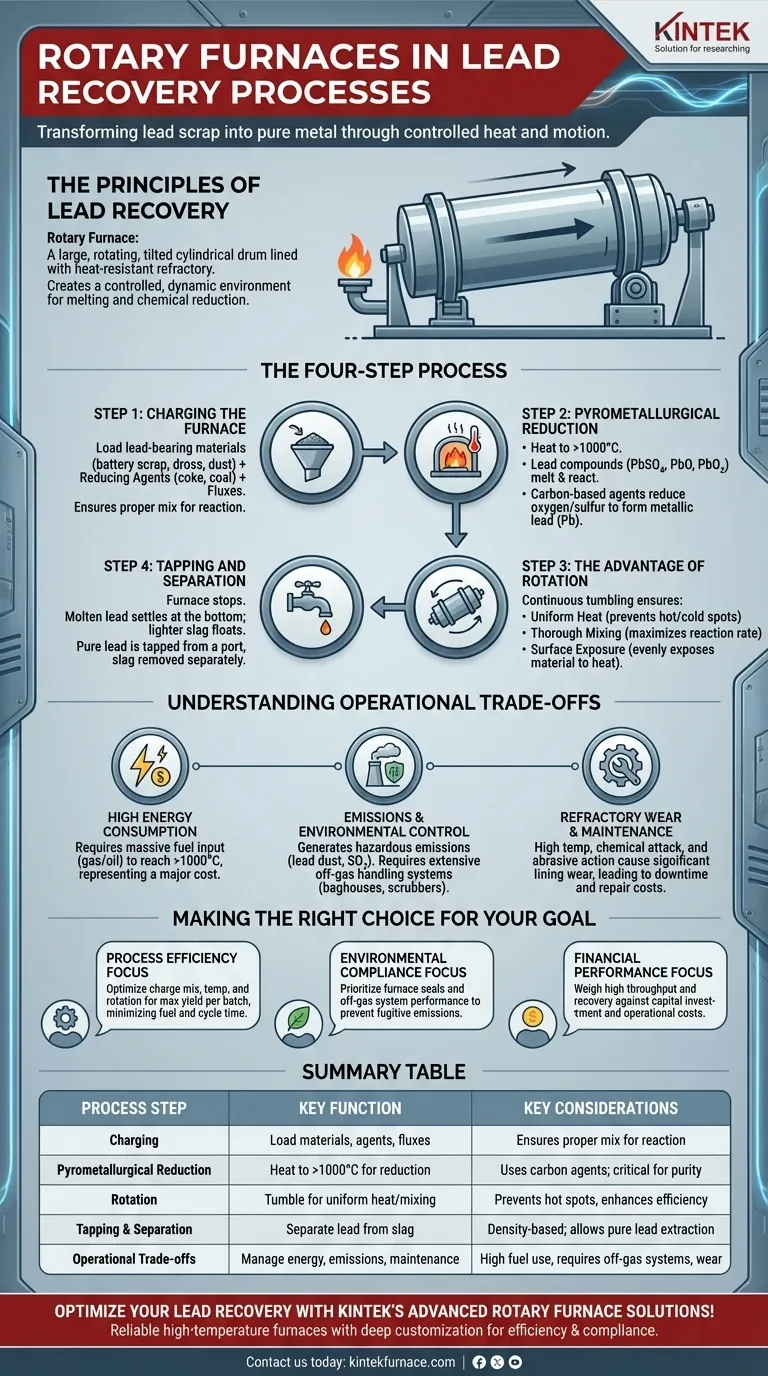
The Principles of Lead Recovery in a Rotary Furnace
A rotary furnace is essentially a large, rotating cylindrical drum lined with heat-resistant material (refractory). It's tilted at a slight angle to help material move through it, though in many lead recovery operations, it functions in a batch mode.
Step 1: Charging the Furnace
The process begins by loading a "charge" into the furnace. This charge typically consists of crushed lead-acid battery scrap, lead dross from other processes, and flue dust captured from previous cycles.
Critically, reducing agents and fluxes are also added. The most common reducing agent is a form of carbon, such as coke or coal, which performs the essential chemical work.
Step 2: Pyrometallurgical Reduction
This is the core chemical process. As the furnace heats up to temperatures often exceeding 1000°C, two things happen: the lead-bearing material melts, and the chemical reactions begin.
The lead in battery scrap exists mostly as lead sulfate (PbSO₄) and lead oxides (PbO, PbO₂). The goal is to strip the oxygen and sulfur atoms away to leave pure lead (Pb). The carbon-based reducing agent facilitates this by reacting with the oxygen to form carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO₂).
Step 3: The Advantage of Rotation
The furnace's slow rotation is its most important feature. It continuously tumbles the molten material, ensuring several key outcomes:
- Uniform Heat: It prevents hot and cold spots, ensuring the entire batch reaches the optimal reaction temperature.
- Thorough Mixing: It constantly mixes the molten lead compounds with the reducing agents and fluxes, maximizing the rate and completeness of the chemical reduction.
- Surface Exposure: It continually exposes new material to the heat from the burner and the furnace interior.
Think of it like a highly specialized, industrial-scale clothes dryer, where the tumbling action ensures every item is evenly heated and exposed to the hot air.
Step 4: Tapping and Separation
Once the reduction is complete, the furnace is stopped. The contents separate into layers based on density. The heavy, molten metallic lead settles at the bottom.
A lighter layer of slag, containing the fluxes, ash from the reducing agents, and non-metallic impurities, floats on top. The molten lead is "tapped" from a port at the bottom, while the slag is removed separately.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
While highly effective, rotary furnaces are complex industrial systems with significant operational challenges that must be managed.
High Energy Consumption
Bringing a massive, rotating steel drum and its contents to over 1000°C is extremely energy-intensive. These furnaces consume large amounts of fuel, typically natural gas or oil, representing a major operational cost.
Emissions and Environmental Control
The high-temperature reduction of lead scrap generates hazardous emissions, including lead-containing dust, sulfur dioxide (SO₂), and other volatile compounds. Consequently, rotary furnace operations require extensive and costly off-gas handling systems, such as baghouses and scrubbers, to capture these pollutants before they are released into the atmosphere.
Refractory Wear and Maintenance
The combination of high temperatures, chemical attack from slag, and the abrasive action of the rotating charge causes significant wear on the furnace's internal refractory lining. This lining must be periodically repaired or completely replaced, leading to downtime and high maintenance costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The use of a rotary furnace is a calculated decision based on balancing productivity with operational costs and regulatory demands. Your focus will change depending on your role in the operation.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Your goal is to optimize the charge mix, temperature, and rotation speed to maximize lead yield per batch while minimizing fuel consumption and cycle time.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: Your attention must be on the absolute integrity of the furnace seals and the performance of the off-gas collection and treatment systems to prevent fugitive emissions.
- If your primary focus is financial performance: You must weigh the furnace's high throughput and recovery rates against the significant capital investment and the ongoing operational costs of energy, labor, and maintenance.
By mastering this dynamic physiochemical environment, operators can efficiently and safely transform hazardous waste into a valuable industrial commodity.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Key Function | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Charging | Load lead-bearing materials, reducing agents, and fluxes | Ensures proper mix for chemical reactions |
| Pyrometallurgical Reduction | Heat to >1000°C to reduce lead compounds to pure lead | Uses carbon-based agents; critical for metal purity |
| Rotation | Tumble materials for uniform heat and mixing | Prevents hot spots, enhances reaction efficiency |
| Tapping and Separation | Separate molten lead from slag layers | Based on density; allows for pure lead extraction |
| Operational Trade-offs | Manage energy, emissions, and maintenance | High fuel use, requires off-gas systems, refractory wear |
Optimize your lead recovery with KINTEK's advanced rotary furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories and industrial facilities with reliable high-temperature furnaces, including Rotary, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental and production needs, enhancing efficiency and compliance. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can transform your recycling processes and boost your operational performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing



















