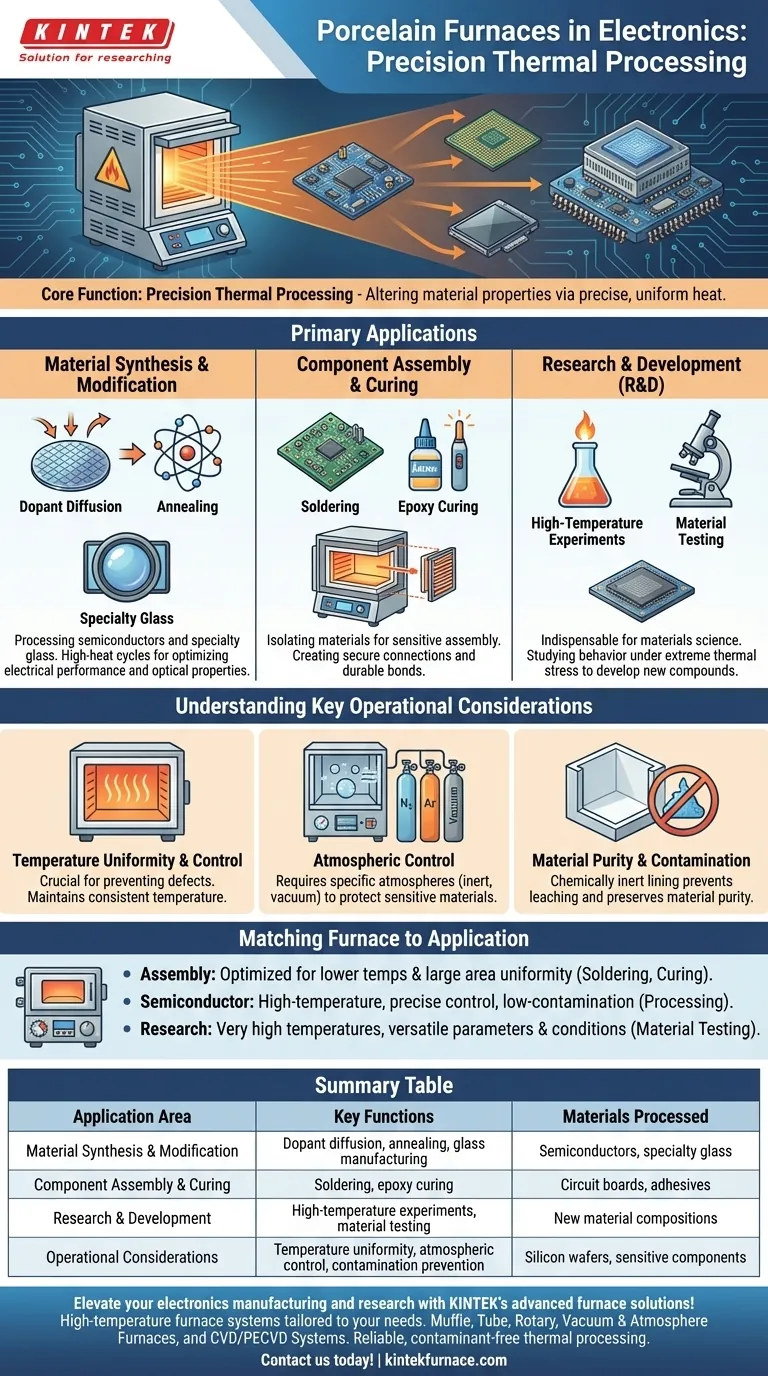
In the electronics industry, porcelain furnaces serve a critical, specialized role in the high-temperature processing of fundamental materials. Their primary applications include synthesizing or modifying semiconductors and specialized glass, as well as enabling controlled assembly processes like soldering and curing.
A porcelain furnace's value in electronics is not for building finished circuits, but for creating and refining the very materials that make them possible. They provide the controlled, high-heat, and contaminant-free environment required for manufacturing and testing next-generation components.
The Core Function: Precision Thermal Processing
The defining feature of a furnace in an electronics context is its ability to apply precise and uniform heat. This thermal energy is a tool used to deliberately alter the physical and chemical properties of materials.
Material Synthesis and Modification
Many advanced electronic materials only achieve their desired properties after being subjected to extreme temperatures. Porcelain furnaces provide the necessary environment for these transformations.
This includes processing semiconductors, where high-heat cycles are used to diffuse dopants into the silicon wafer or anneal crystal structures to repair damage and optimize electrical performance.
It also applies to the manufacturing of specialty glass used in displays and optics, where specific heating and cooling profiles are essential for achieving the right transparency, strength, and thermal expansion characteristics.
Component Assembly and Curing
Porcelain furnaces are a type of muffle furnace, which isolates the material being heated from direct contact with the heating elements. This design is ideal for sensitive assembly steps.
Furnaces are used for soldering complex components where other methods are impractical, creating secure and reliable electrical connections across a circuit board.
They are also used for curing epoxy resins and other adhesives. This process ensures these materials form strong, durable bonds that can withstand the operational stresses and temperatures of an electronic device.
Research and Development (R&D)
Beyond manufacturing, these furnaces are indispensable tools in materials science labs. Researchers use them to conduct high-temperature experiments on new material compositions.
By studying how materials behave under extreme thermal stress, engineers can determine their operational limits and develop advanced compounds with specific electrical, thermal, or structural properties for future electronic applications.
Understanding Key Operational Considerations
While powerful, the effective use of a porcelain furnace in electronics hinges on several critical factors. Mismanaging these can lead to component failure and inconsistent results.
Temperature Uniformity and Control
The most critical factor is the ability to maintain a uniform temperature throughout the chamber. Even minor variations can cause inconsistencies in a batch of semiconductors or create stress points in a glass substrate, leading to defects.
Atmospheric Control
Many electronic processes require a specific atmosphere within the furnace. This can mean a vacuum to prevent oxidation or the introduction of an inert gas (like nitrogen or argon) to protect sensitive materials. In other cases, a reactive gas is introduced to intentionally create an oxide layer.
Material Purity and Contamination
The ceramic or porcelain lining of the furnace is crucial because it is chemically inert at high temperatures. This prevents the furnace materials themselves from leaching contaminants into the highly pure silicon wafers or other sensitive components, which could ruin their electrical properties.
Matching the Furnace to the Electronic Application
To apply this knowledge, you must align the furnace's capabilities with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is component assembly: You need a furnace optimized for lower temperatures (for soldering and curing) with excellent thermal uniformity across a large area to process entire boards or trays of parts at once.
- If your primary focus is semiconductor processing: You require a high-temperature furnace with extremely precise process control, sophisticated atmospheric management, and a certified low-contamination chamber.
- If your primary focus is materials research: You need a versatile furnace that can reach very high temperatures and allows for easy modification of cycle parameters and atmospheric conditions to test a wide range of variables.
Ultimately, the porcelain furnace is a foundational tool that enables the very existence of high-performance electronic materials.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Functions | Materials Processed |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis & Modification | Dopant diffusion, annealing, glass manufacturing | Semiconductors, specialty glass |
| Component Assembly & Curing | Soldering, epoxy curing | Circuit boards, adhesives |
| Research & Development | High-temperature experiments, material testing | New material compositions |
| Operational Considerations | Temperature uniformity, atmospheric control, contamination prevention | Silicon wafers, sensitive components |
Elevate your electronics manufacturing and research with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems tailored to your needs. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're processing semiconductors, assembling components, or pioneering new materials, KINTEK delivers reliable, contaminant-free thermal processing. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your operations and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in ZnO-SP preparation? Master Nanoscale Synthesis Control
- How does high-temperature heating facilitate the conversion of rice husks into inorganic precursors for silica extraction?
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace used for Ni-BN powder preheating? Achieve defect-free coating density.
- What is the critical role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in converting biomass into Fe-N-BC?
- What is the core function of a muffle furnace in biomass activation? Optimize Carbonization & Pore Development



















