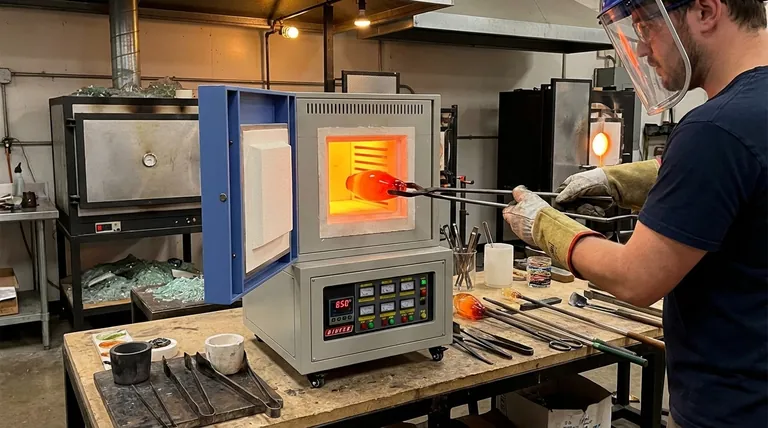
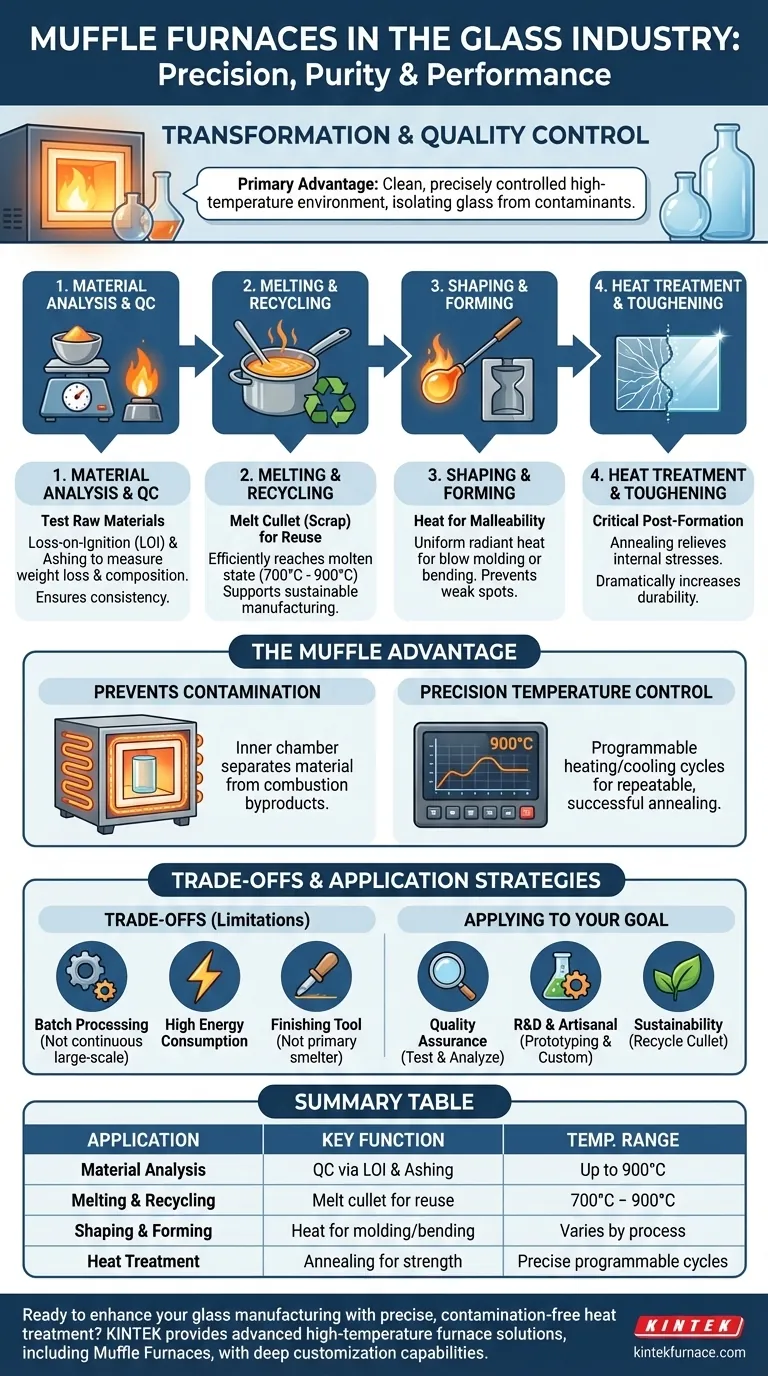
In the glass industry, muffle furnaces are essential tools for transformation and quality control. They are used to melt glass for recycling, heat it for shaping and molding, strengthen the final product through precise heat treatment, and analyze the chemical properties of raw materials. Electric muffle furnaces are particularly valued for their ability to reliably reach the high temperatures required for these processes.
A muffle furnace's primary advantage in the glass industry is its ability to provide a clean, precisely controlled high-temperature environment. This isolates the glass from fuel byproducts and direct flame, which is critical for achieving the desired structural properties, clarity, and strength.

The Core Functions in Glass Production
A muffle furnace is not typically used for the initial, large-scale melting of sand and other raw materials in mass production. Instead, it serves several critical, specialized roles throughout the manufacturing lifecycle.
Material Analysis and Quality Control
Before production begins, a muffle furnace is used to test the raw materials. Processes like loss-on-ignition (LOI) and ashing involve heating a sample to measure weight loss, revealing its composition and the presence of volatile components. This data is crucial for predicting how the glass will behave when melted and for ensuring consistent quality.
Melting and Recycling
The furnace is ideal for melting down cullet (scrap or waste glass) as part of a recycling process. It can efficiently bring the glass to its molten state, typically in the range of 700°C to 900°C, so it can be re-formed into new products. This makes it a key tool for sustainable manufacturing practices.
Shaping and Forming
To shape glass, it must be heated until it becomes malleable. A muffle furnace provides the uniform, radiant heat necessary for processes like blow molding or bending glass into specific forms. The consistent temperature throughout the chamber ensures the entire piece of glass is workable, preventing weak spots.
Heat Treatment and Toughening
Perhaps the most critical application is post-formation heat treatment. Processes like annealing involve heating the finished glass product to a specific temperature and then cooling it down slowly on a controlled schedule. This relieves the internal stresses created during forming, dramatically increasing the glass's durability and preventing it from cracking.
Why a Muffle Furnace Is the Right Tool
The unique design of a muffle furnace makes it uniquely suited for the delicate work of glass manufacturing, distinguishing it from other high-temperature equipment.
The 'Muffle' Advantage: Preventing Contamination
The name "muffle furnace" comes from the muffle, an inner chamber that separates the material being heated from the heating elements or flame. This is non-negotiable for glass production, where direct exposure to combustion byproducts could introduce impurities that affect the material's color, clarity, and structural integrity.
Precision Temperature Control
Modern electric muffle furnaces offer exceptional temperature stability and programmable heating cycles. Glassmakers can define precise heating rates, holding times, and cooling ramps. This level of control is essential for repeatable and successful annealing, where a deviation of even a few degrees can ruin the product.
Versatility Across the Workflow
The same type of furnace can be used for multiple tasks. A laboratory can use a muffle furnace for R&D and material analysis, while a small-scale production facility can use a larger version for annealing or custom shaping. This versatility makes it a valuable asset for a wide range of operational scales.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, muffle furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to using them correctly.
Scale and Throughput
Muffle furnaces are best suited for batch processing, not continuous, large-scale production. For melting tons of raw sand for float glass manufacturing, industries use massive, continuously fed tank furnaces. Muffle furnaces are for specialized, smaller-volume tasks.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of 900°C requires a significant amount of electrical energy. For any operation, this energy consumption is a primary cost factor that must be managed.
A Tool for Finishing, Not Primary Melting
It is helpful to think of a muffle furnace as a finishing or specialized processing tool rather than a primary smelter. Its strength lies in the precision it brings to heat treatment, recycling, and quality testing, not in raw production volume.
Applying This to Your Goal
Applying a muffle furnace effectively depends on matching its capabilities to your specific objective in the glass lifecycle.
- If your primary focus is quality assurance: Use the furnace for loss-on-ignition tests on raw materials and for analyzing the structural properties of finished samples.
- If your primary focus is product development or artisanal work: Leverage its precise temperature control for prototyping new shapes, creating custom pieces, and executing complex annealing cycles.
- If your primary focus is sustainability and recycling: Employ the furnace for efficiently melting down cullet into a pure, usable form for new products.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace empowers glassmakers with the precise environmental control needed to test, shape, and perfect their materials.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Material Analysis | Quality control via LOI and ashing | Up to 900°C |
| Melting & Recycling | Melt cullet for sustainable reuse | 700°C to 900°C |
| Shaping & Forming | Heat for blow molding and bending | Varies by process |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing to relieve stresses and toughen glass | Precise programmable cycles |
Ready to enhance your glass manufacturing with precise, contamination-free heat treatment? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored muffle furnaces can improve your glass quality, efficiency, and sustainability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















