In short, medium frequency induction furnaces are used in forging and forming to rapidly and precisely heat a metal workpiece, such as a steel billet, to a specific temperature where it becomes malleable. This allows the metal to be easily shaped by a press or hammer. The technology's main advantage is its ability to generate heat directly within the metal, ensuring fast, uniform, and efficient heating that is critical for high-volume, high-quality production in industries like automotive and aerospace.
The central reason to use medium frequency induction for forging is not just to heat metal, but to achieve a level of speed, precision, and efficiency that traditional fuel-fired furnaces cannot match. This control translates directly into higher quality forged parts, reduced material waste, and a more streamlined manufacturing process.

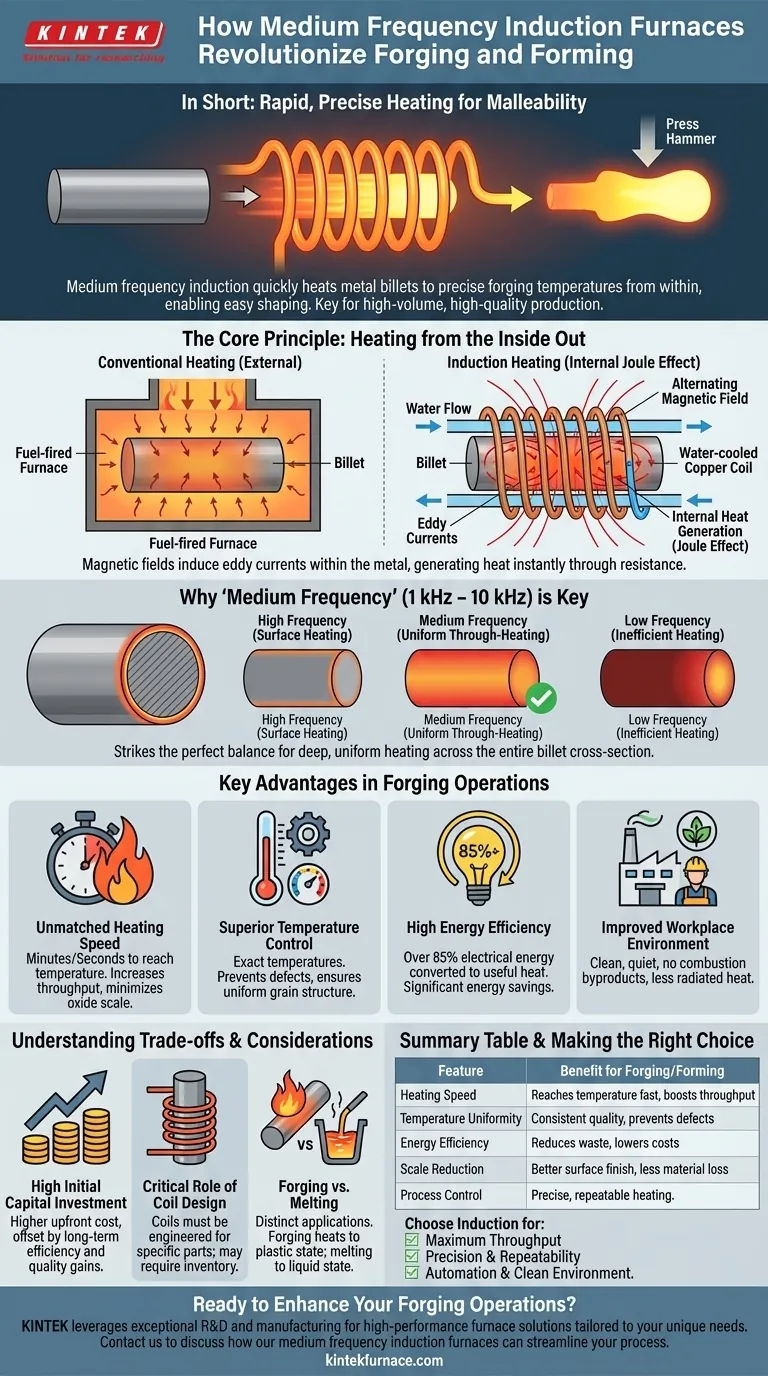
The Core Principle: Heating from the Inside Out
To understand its role in forging, you must first understand how induction works. It is fundamentally different from a conventional oven that heats from the outside.
How Electromagnetic Induction Generates Heat
An induction furnace uses a water-cooled copper coil to generate a powerful, alternating magnetic field. When a metal workpiece (which is electrically conductive) is placed inside this coil, the magnetic field induces electrical currents, known as eddy currents, within the metal itself.
The metal's natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents generates immense and immediate heat. This phenomenon, called the Joule effect, is the same principle that heats the element on an electric stove, but it is happening inside the material.
Why "Medium Frequency" is Key for Forging
The frequency of the alternating current is critical. Medium frequencies (typically 1 kHz to 10 kHz) are ideal for forging because they create a heating pattern that penetrates deep enough to uniformly heat the entire cross-section of a billet.
Too high a frequency would only heat the surface (case hardening), and too low a frequency would be less efficient. Medium frequency strikes the perfect balance for through-heating solid metal parts before they are shaped.
Key Advantages in Forging Operations
The choice to use induction heating is driven by several distinct operational advantages over traditional gas or coal-fired furnaces.
Unmatched Heating Speed
Because heat is generated internally, the metal reaches its target forging temperature in a matter of minutes, or even seconds, compared to hours in a conventional furnace. This drastically increases throughput.
This speed also minimizes the formation of oxide scale on the metal's surface. Less scale means a better surface finish on the final part and less material loss.
Superior Temperature Control and Uniformity
Induction systems offer incredibly precise temperature control. The power can be adjusted instantly, ensuring the billet is heated to the exact plastic deformation temperature required for the specific alloy.
This uniformity prevents hot or cold spots, which can lead to defects, inconsistent grain structure, and tool damage during the forging process. The result is a more reliable and repeatable operation.
High Energy Efficiency
Induction heating is a highly efficient process, with over 85% of the electrical energy being converted directly into useful heat within the workpiece.
Conventional furnaces lose enormous amounts of heat to the surrounding environment and up the exhaust stack. Induction's targeted heating minimizes this waste, leading to significant energy savings.
Improved Workplace Environment
Induction furnaces are clean, quiet, and produce no combustion byproducts like smoke or CO2. They radiate far less ambient heat than a fuel-fired furnace, creating a safer and more comfortable environment for operators.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, induction heating is not the universal solution for every heating application. It comes with its own set of technical and economic considerations.
High Initial Capital Investment
The upfront cost of an induction heating system, including the power supply and custom coils, is typically higher than that of a simple gas-fired furnace. The return on investment is realized through higher efficiency, throughput, and quality over time.
The Critical Role of Coil Design
The induction coil is not a one-size-fits-all component. It must be carefully engineered to match the size, shape, and material of the workpiece for optimal efficiency and heating uniformity.
This means that a facility forging many different part geometries may need a corresponding inventory of coils, adding to the system's complexity and cost.
Forging vs. Melting Applications
While the same principle of induction is used for melting metals in foundries, the furnace design and frequency are different. Forging requires heating a solid billet to a plastic state, whereas melting requires taking it to a full liquid state. The user in the reference is correct that induction is used for melting, but it's a distinct application from forging.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating technology depends entirely on your production priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput and part quality: Medium frequency induction is the definitive choice for its speed, precision, and repeatability, especially in automated, high-volume production lines.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial capital cost for low-volume work: A conventional fuel-fired furnace may be a more economical starting point, though it comes at the cost of lower efficiency and control.
- If your primary focus is process automation and a cleaner work environment: Induction heating systems integrate seamlessly into modern, automated manufacturing cells and offer significant environmental and safety benefits.
Ultimately, adopting induction heating for forging is a strategic decision to prioritize control and efficiency in your manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for Forging/Forming |
|---|---|
| Heating Speed | Reaches forging temperature in minutes/seconds, increasing throughput |
| Temperature Uniformity | Prevents defects and tool damage, ensures consistent part quality |
| Energy Efficiency | Over 85% electrical energy converted to heat, reducing waste |
| Scale Reduction | Minimizes surface oxidation, improves finish and reduces material loss |
| Process Control | Precise, repeatable heating for specific alloys and geometries |
Ready to enhance your forging and forming operations with advanced heating technology?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing capabilities to provide high-performance furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our expertise in Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, combined with strong deep customization capabilities, ensures we can deliver the precise heating solution your laboratory or production facility requires.
Contact us today to discuss how our medium frequency induction furnaces can streamline your process, improve part quality, and boost your manufacturing efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of ceramic/metal composites produced using a vacuum press? Achieve Superior Strength and Durability
- What are the main applications of vacuum hot pressing? Create Dense, Pure Materials for Demanding Industries
- How does induction heating ensure precision in manufacturing processes? Achieve Superior Thermal Control & Repeatability
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density
- What other types of furnaces are related to hot pressing? Explore Key Thermal Processing Technologies



















