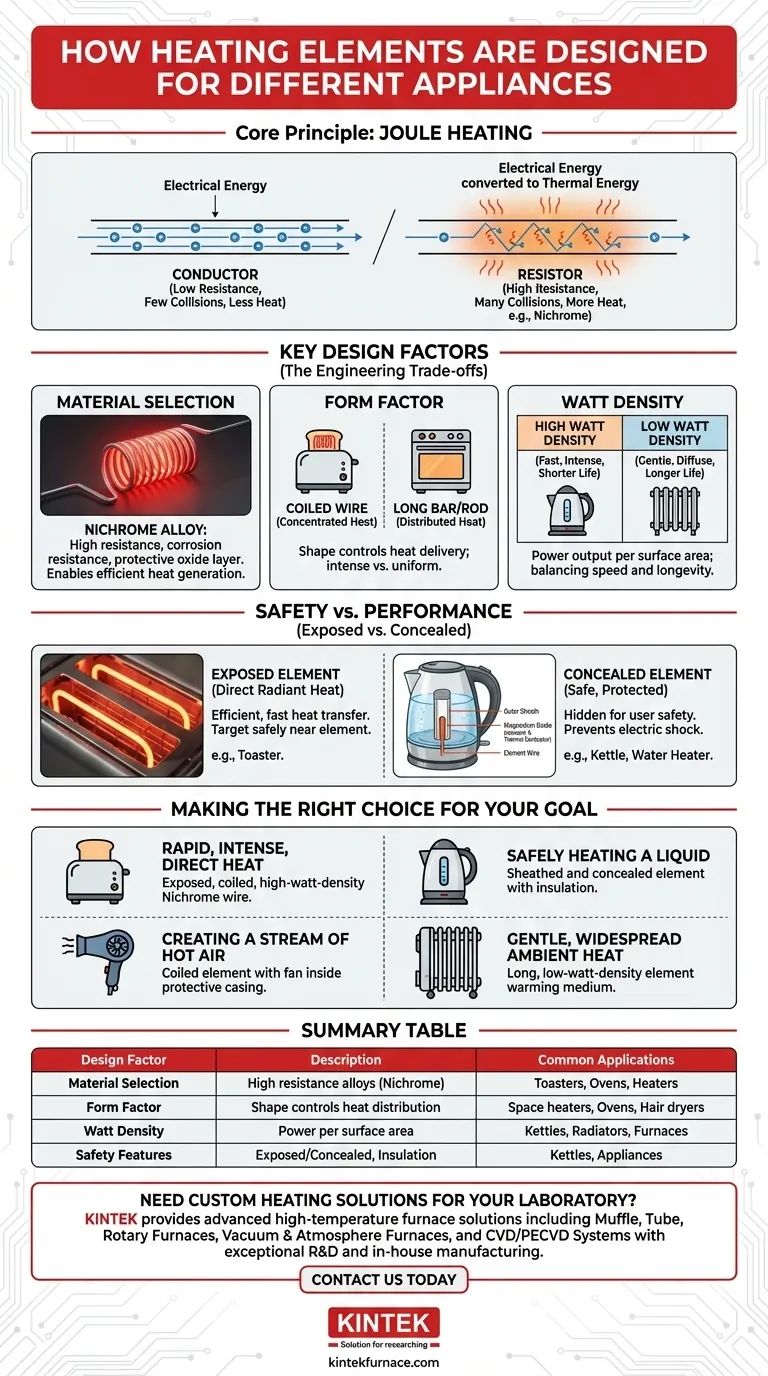
At their core, all heating elements operate on the same principle: they are designed to resist the flow of electricity, converting electrical energy into heat. However, their physical design—specifically their material, shape, and enclosure—is meticulously engineered to match the unique demands of each appliance, from the intense, focused heat of a toaster to the gentle, widespread warmth of a room heater.
The design of a heating element is never arbitrary. It is a deliberate compromise between four key factors: the required heating speed and intensity, the physical space available, the lifespan of the material, and, most critically, user safety.

The Universal Principle: Joule Heating
Every appliance that generates heat from electricity, whether it's a kettle, oven, or hair dryer, relies on a phenomenon known as Joule heating.
The Science of Resistance
When an electric current passes through a material, the electrons in the current collide with the atoms of that material. In a good conductor like copper, electrons flow easily with few collisions.
In a resistor, however, the material is specifically chosen to impede this flow. These frequent collisions cause the atoms to vibrate, which we perceive as heat. This is the fundamental conversion of electrical energy to thermal energy.
Key Design Factors for Any Heating Element
While the principle is universal, engineers manipulate three primary variables to tailor an element for a specific task: material, form factor, and power density.
Material Selection: The Heart of the Element
The most common material used for high-temperature heating elements is an alloy called Nichrome (nickel-chromium).
This alloy is dominant for two reasons. First, it has a high electrical resistance, meaning it generates significant heat efficiently. Second, when heated, it forms a stable, protective outer layer of chromium oxide that prevents it from corroding and breaking down, ensuring a long operational life.
Form Factor: Shaping the Heat Output
The physical shape of the element is the most obvious design choice and directly controls how heat is delivered.
-
Coiled Wires: Tightly winding the element into a coil concentrates a long wire into a small space. This creates a source of intense, radiant heat, perfect for applications like toasters or space heaters where the goal is to quickly heat a surface or the air directly in front of it.
-
Long Bars or Rods: Straight, elongated elements are used when the goal is to distribute heat evenly over a larger area. You see this design in ovens, where the element needs to bake food uniformly, or in baseboard heaters that warm a room.
Watt Density: Balancing Power and Lifespan
Watt density is the amount of power output per square inch of the element's surface area. This is a critical engineering trade-off.
A high watt density provides very fast, intense heating but also puts more stress on the material, potentially shortening its lifespan. A low watt density is gentler on the element, leading to longer life and more diffuse, even heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Safety vs. Performance
The final design consideration is often the most important: how to deliver heat effectively without creating a hazard. This is managed by choosing whether to expose or conceal the element.
Exposed vs. Concealed Elements
An exposed element, like the glowing wires in a toaster, allows for direct, efficient radiant heat transfer. This is ideal when the target (a piece of bread) can be placed safely near the element.
A concealed element is hidden from the user for safety. In an electric kettle, the element is sheathed in metal to prevent electric shock from contact with water. In a hair dryer, it is enclosed within the barrel to prevent contact and to allow a fan to blow air over it, creating a stream of hot air.
The Role of Sheathing and Insulation
Concealed elements are not simply hidden; they are typically encased in a protective metal sheath. The space between the element wire and the sheath is filled with a powder, often magnesium oxide.
This powder is an excellent electrical insulator but a good thermal conductor. It prevents electricity from reaching the outer sheath while allowing heat to transfer through it efficiently and safely. This design is fundamental to appliances like water heaters, ovens, and coffee makers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
By understanding these core principles, you can deconstruct the design of nearly any heating appliance and understand the engineering choices behind it.
- If the primary focus is rapid, intense, and direct heat: The design will favor an exposed, coiled, high-watt-density Nichrome wire, as seen in a toaster.
- If the primary focus is safely heating a liquid: The design will use a sheathed and concealed element to prevent any interaction between electricity and water, as in a kettle.
- If the primary focus is creating a stream of hot air: The design will pair a coiled element with a fan inside a protective casing, as in a hair dryer or fan heater.
- If the primary focus is gentle, widespread ambient heat: The design will use a long, low-watt-density element to warm a medium like oil or air over a large surface area, as in an oil-filled radiator.
Ultimately, every heating element is an elegant solution to a specific thermal problem, perfectly balanced for its intended purpose.
Summary Table:
| Design Factor | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | Uses alloys like Nichrome for high resistance and corrosion resistance. | Toasters, ovens, heaters |
| Form Factor | Shape (e.g., coiled wires or long bars) controls heat distribution and intensity. | Space heaters, ovens, hair dryers |
| Watt Density | Power per surface area; high for fast heating, low for longevity. | Kettles, radiators, industrial furnaces |
| Safety Features | Exposed or concealed elements with insulation for user protection. | Electric kettles, water heaters, appliances |
Need custom heating solutions for your laboratory? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















