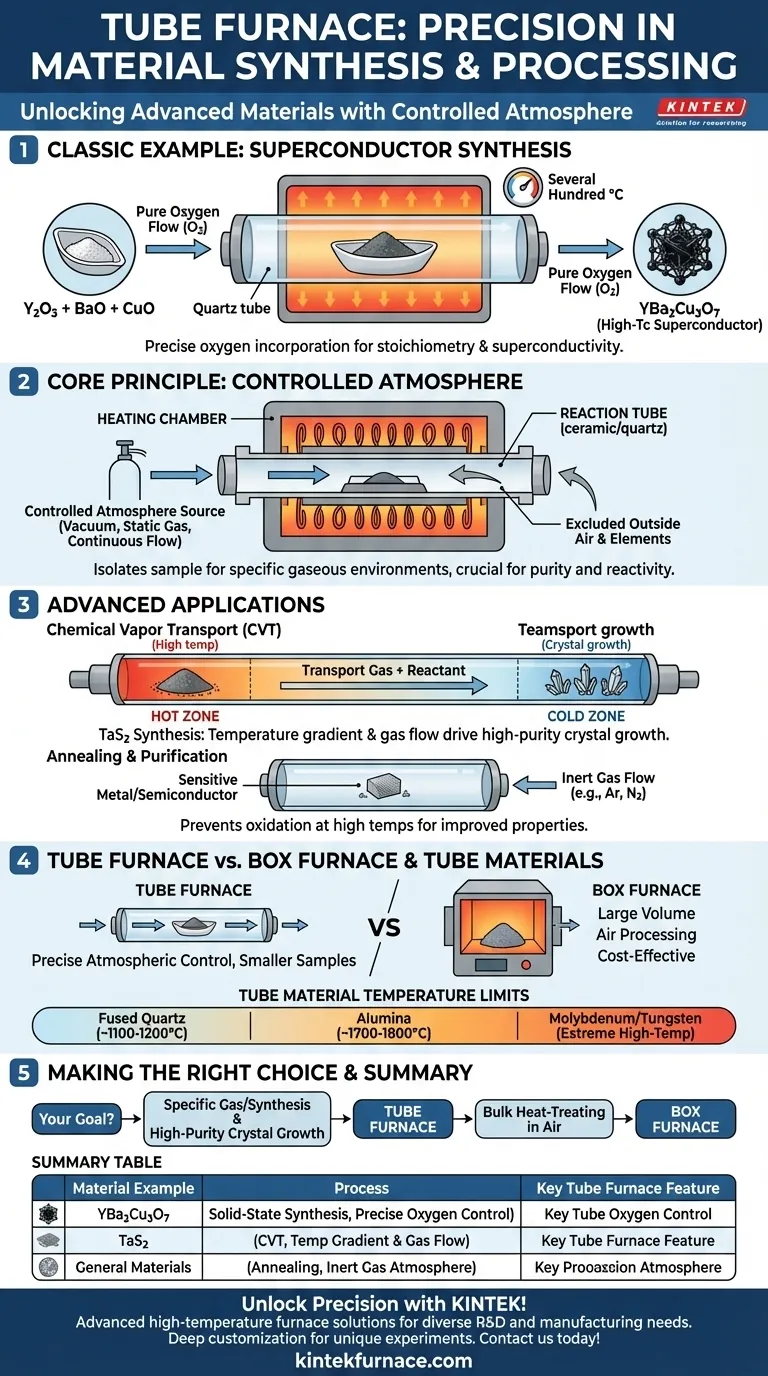
A classic example of a material prepared in a tube furnace is the high-temperature superconductor YBa₂Cu₃O₇. This synthesis involves heating a finely powdered mixture of yttrium oxide, barium oxide, and copper oxide within a ceramic boat. The entire process is conducted at several hundred degrees Celsius under a continuous flow of pure oxygen, a precise atmospheric control that is the hallmark of a tube furnace.
The defining capability of a tube furnace is not just its ability to generate high temperatures, but its power to precisely control the gaseous atmosphere around a sample. This control is what enables advanced material synthesis and processing that would be impossible in a standard oven or box furnace.

What Defines a Tube Furnace?
A tube furnace's unique design is central to its function. It consists of a cylindrical heating chamber into which a separate reaction tube, typically made of ceramic or quartz, is placed. This design is the key to its specialized applications.
The Core Principle: A Controlled Atmosphere
The tube isolates the sample from the outside air and the furnace's heating elements. This isolation allows a researcher to create a highly specific, controlled environment inside the tube.
This atmosphere can be a vacuum, a static gas, or, most commonly, a continuous flow of a specific gas or gas mixture. This is essential for reactions where the surrounding gas is a key reactant or must be excluded to prevent contamination.
Material Synthesis in Practice
The synthesis of the superconductor YBa₂Cu₃O₇ is a perfect illustration. The reaction requires a specific amount of oxygen to be incorporated into the material's crystal structure.
By heating the precursor powders while flowing pure oxygen through the tube, the furnace ensures the final product achieves the correct stoichiometry and its desired superconducting properties.
Advanced Tube Furnace Applications
While simple solid-state reactions are common, the design of a tube furnace unlocks more complex material preparation techniques.
Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT)
The synthesis of materials like Tantalum Disulfide (TaS₂) often uses a tube furnace for a process called chemical vapor transport.
In this technique, a source material at one end of the tube (the hot zone) reacts with a transport gas. This gaseous compound then diffuses to the other end of the tube (the cold zone), where it decomposes and deposits as a high-purity crystal.
Annealing and Purification
Tube furnaces are also critical for annealing, a heat treatment process that alters a material's microstructure to improve its properties.
Using an inert gas flow, like argon or nitrogen, prevents the material from oxidizing or reacting with air at high temperatures. This is crucial for processing sensitive metals, semiconductors, and other advanced materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A tube furnace is a specialized tool, not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Tube Furnace vs. Box Furnace
A box furnace is essentially a high-temperature oven with a large, accessible chamber. It is ideal for heat-treating large components or processing bulk powders in air.
A tube furnace, by contrast, is designed for smaller sample sizes where precise atmospheric control is the primary requirement. It sacrifices sample volume for environmental precision.
The Critical Role of the Tube Material
The furnace's performance is ultimately limited by the reaction tube itself.
- Fused Quartz: Common and cost-effective, but typically limited to around 1100-1200°C.
- Alumina: A high-purity ceramic that can withstand much higher temperatures, often up to 1700-1800°C.
- Molybdenum/Tungsten: Used for extremely high-temperature or corrosive applications where ceramics would fail.
The choice of tube material dictates the furnace's maximum operating temperature and its chemical compatibility with the process materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal processing tool depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing materials that require a specific gas environment: The tube furnace is the essential tool for processes like oxidation or reduction.
- If your primary focus is growing high-purity single crystals: The tube furnace is ideal for techniques like chemical vapor transport that rely on temperature gradients and a controlled atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is simply heat-treating large parts or bulk powders in air: A box furnace is almost always the more practical and cost-effective choice.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select the precise thermal tool required to achieve your material science objectives.
Summary Table:
| Material Example | Process | Key Tube Furnace Feature |
|---|---|---|
| YBa₂Cu₃O₇ (High-Temperature Superconductor) | Solid-State Synthesis | Precise Oxygen Atmosphere Control |
| TaS₂ (Tantalum Disulfide) | Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT) | Temperature Gradient and Gas Flow |
| General Materials | Annealing | Inert Gas Atmosphere for Protection |
Unlock Precision in Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK!
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're synthesizing superconductors or growing high-purity crystals, our tube furnaces offer the precise atmospheric control you need for superior results.
Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve your material science goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















