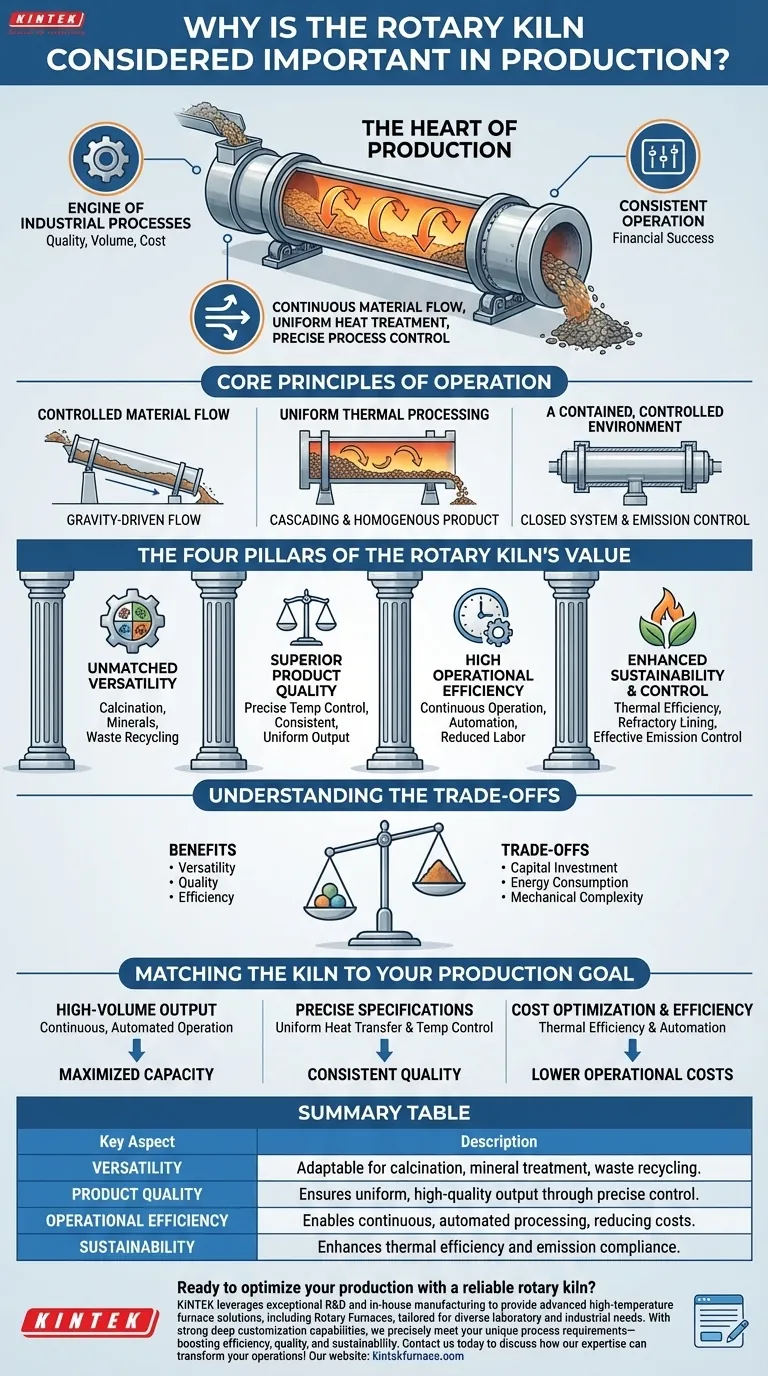
At its core, the rotary kiln is important because it is the engine of many industrial processes. Its performance and operational stability directly dictate the quality, volume, and cost of the final product. For this reason, it is often called the "heart of production," a central piece of equipment whose consistent operation is critical to the financial success of the entire enterprise.
The true importance of the rotary kiln lies not in a single feature, but in its unique combination of continuous material flow, uniform heat treatment, and precise process control. This synergy makes it an indispensable and highly efficient workhorse for thermal processing across numerous industries.

The Core Principles of Operation
To understand the kiln's value, we must first understand how it works. Its design is simple in concept but powerful in application.
Controlled Material Flow
A rotary kiln is a large, rotating cylindrical drum positioned at a slight incline. Raw material is fed into the higher end of the drum.
As the kiln slowly rotates, the material tumbles and gradually moves down toward the lower, discharge end due to gravity. This provides a continuous, controlled, and predictable flow through the system.
Uniform Thermal Processing
The tumbling motion, known as cascading, is the key to product quality. It constantly mixes the material, ensuring every particle is evenly exposed to the heat source.
This prevents hot spots and guarantees a homogenous final product, where all material has undergone the same physical change or chemical reaction.
A Contained, Controlled Environment
The kiln operates as a closed system. This allows for precise control over the internal atmosphere, temperature, and pressure.
This containment also prevents dust and pollutants from escaping, making it easier to manage emissions and maintain a safer working environment.
The Four Pillars of the Rotary Kiln's Value
The kiln's operational principles translate directly into four key business advantages that cement its importance.
Pillar 1: Unmatched Versatility
The kiln's design is not limited to one material or process. It is used for calcination of limestone to produce cement, thermal treatment of minerals and ores, and even the safe disposal and recycling of industrial waste.
This design flexibility allows it to be adapted for a wide range of particle sizes, moisture content, and required chemical reactions.
Pillar 2: Superior Product Quality
The combination of uniform heat transfer and a high degree of automation allows for exceptionally precise temperature control.
This leads to a highly consistent and uniform final product that meets strict quality specifications, batch after batch.
Pillar 3: High Operational Efficiency
Rotary kilns are designed for continuous operation, which eliminates the downtime associated with batch processing and maximizes plant output.
Furthermore, a high degree of automation reduces the need for manual labor, lowering operational costs and minimizing the potential for human error.
Pillar 4: Enhanced Sustainability and Control
Modern kilns are engineered for thermal efficiency, using refractory linings and internal heat exchangers to minimize heat loss and reduce fuel consumption.
The enclosed nature of the kiln, combined with filtration and gas control systems, allows for effective emission control, helping plants meet stringent environmental regulations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable, the rotary kiln is a significant piece of industrial machinery with inherent complexities.
Significant Capital Investment
A rotary kiln represents a major upfront cost. Its large scale, robust steel construction, and complex mechanical systems require a substantial initial investment.
High Energy Consumption
Heating a massive, rotating drum to extremely high temperatures is an energy-intensive process. Whether powered by fuel combustion or electricity, energy costs are a primary operational expense.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
The combination of high temperatures, constant rotation, and abrasive materials places significant stress on components. The refractory lining, support rollers, and drive gear all require regular inspection and skilled maintenance to prevent costly unplanned downtime.
Matching the Kiln to Your Production Goal
The rotary kiln's value is best understood by aligning its capabilities with your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is consistent, high-volume output: The kiln's capacity for continuous, automated operation is its most critical advantage.
- If your primary focus is precise product specifications: Leverage the uniform heat transfer from the tumbling action and the system's precise temperature control.
- If your primary focus is cost optimization and efficiency: Concentrate on features that improve thermal efficiency and the labor-saving benefits of automation.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln remains a cornerstone of modern industry because it reliably solves the fundamental challenge of processing bulk materials at scale with remarkable consistency and control.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Versatility | Adaptable for calcination, mineral treatment, and waste recycling across industries. |
| Product Quality | Ensures uniform, high-quality output through precise temperature control and mixing. |
| Operational Efficiency | Enables continuous, automated processing to maximize output and reduce labor costs. |
| Sustainability | Enhances thermal efficiency and emission control for environmental compliance. |
Ready to optimize your production with a reliable rotary kiln? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, tailored for diverse laboratory and industrial needs. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique process requirements—boosting efficiency, quality, and sustainability. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can transform your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing



















