At its core, the compact design of a channel induction furnace is advantageous because it simplifies installation in space-constrained facilities and inherently improves energy efficiency. This smaller footprint allows for seamless integration into existing production lines without major structural overhauls, while the reduced surface area minimizes thermal loss, directly lowering energy consumption and operational costs.
The true value of the compact design extends beyond just saving floor space. It is a fundamental characteristic that directly enables lower energy costs, faster integration, and a more controlled, efficient melting or holding process for modern industrial operations.
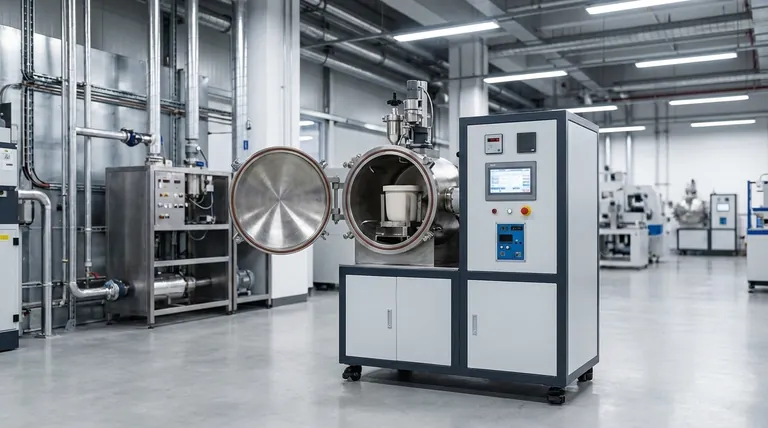

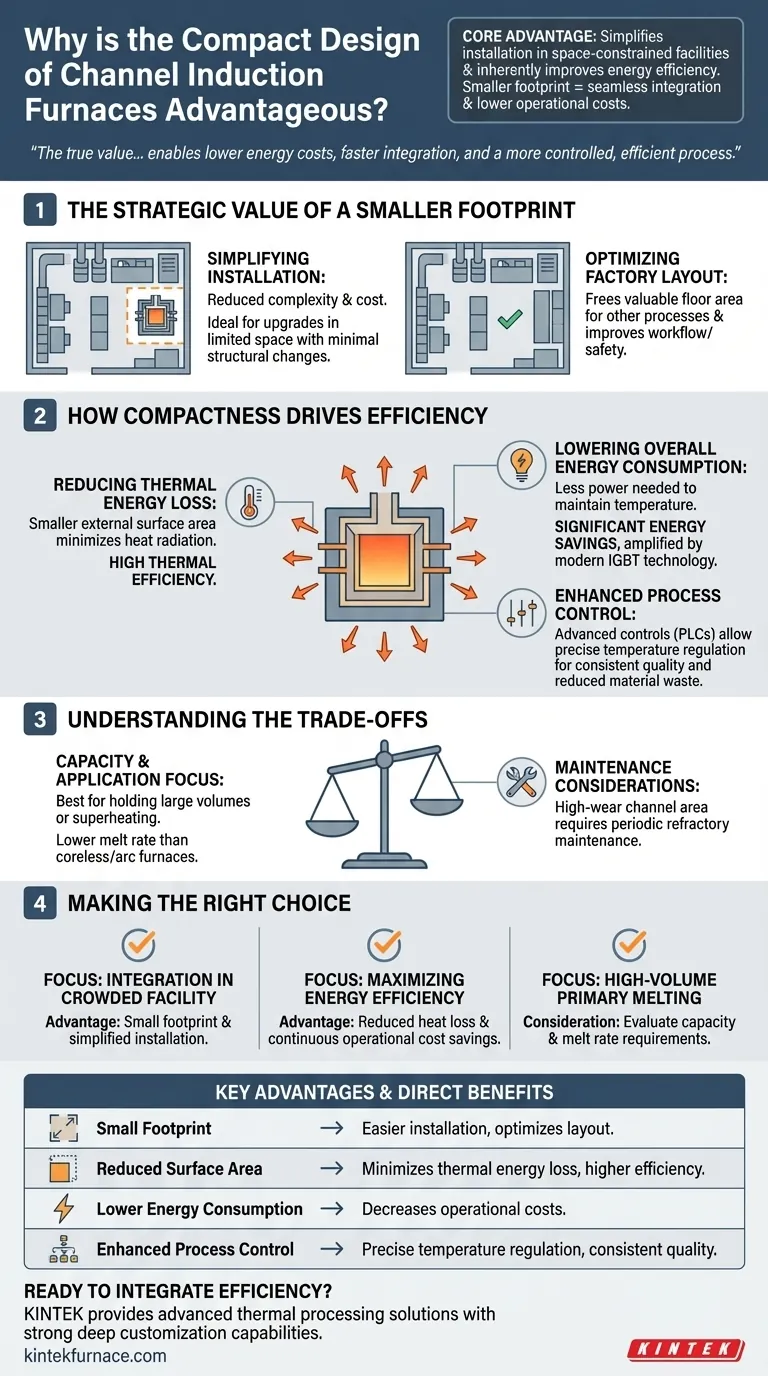
The Strategic Value of a Smaller Footprint
A furnace's physical size has direct and significant impacts on factory layout, installation complexity, and overall workflow. The compact nature of a channel induction furnace provides a clear operational advantage.
Simplifying Installation and Integration
The compact and relatively lightweight design dramatically reduces the complexity and cost of installation. These furnaces can often be placed into existing facilities with minimal modification to the building structure.
This makes them ideal for upgrading or expanding production lines where space is a premium and major construction is not feasible.
Optimizing Factory Floor Layout
By occupying less space, these furnaces free up valuable floor area for other critical processes, material handling, or maintenance access. This allows for a more logical and efficient factory workflow.
A well-organized layout not only improves productivity but also enhances safety for operators moving around the equipment.
How Compactness Drives Efficiency
The physical design of the furnace is intrinsically linked to its performance. A smaller, well-engineered body is not just about saving space; it is a key factor in achieving high levels of thermal and electrical efficiency.
Reducing Thermal Energy Loss
A core principle of thermodynamics is that heat radiates from an object's surface. A furnace with a smaller external surface area has less area from which to lose heat to the surrounding environment.
This design feature directly contributes to the high thermal efficiency of channel induction furnaces, as more of the generated heat is retained within the furnace and transferred to the metal.
Lowering Overall Energy Consumption
Because less energy is wasted as lost heat, less power is required to maintain the target temperature of the molten metal. This reduction in standby heat loss results in significant energy savings over the furnace's lifetime.
This inherent efficiency is often amplified by modern IGBT power supply technology, which provides precise control over energy input, further minimizing waste and reducing operational costs.
Enhancing Process Control
The compact design, combined with advanced controls like PLCs, allows for extremely precise temperature regulation. Maintaining a stable temperature is crucial for achieving specific metal properties and ensuring final product quality.
This level of control minimizes material waste from overheating and ensures consistent, repeatable results from batch to batch.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the compact design offers clear benefits, it is essential to understand its context and limitations to make an informed decision. No single technology is optimal for every application.
Capacity and Application Focus
Channel induction furnaces, partly due to their compact and efficient design, are often optimized for holding large volumes of already-molten metal at a specific temperature or for superheating.
While they can be used for melting, their melt rate may be lower than that of larger, coreless induction furnaces or electric arc furnaces, which are often preferred for primary melting of large quantities of cold scrap.
Maintenance Considerations
The "channel" or "loop" where induction occurs is a high-wear area that requires periodic refractory maintenance or replacement.
While the overall design is robust, the specific nature of the channel means maintenance can be more specialized compared to the open crucible of a coreless furnace. This is a critical factor to consider in your operational and maintenance planning.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace technology requires aligning its specific advantages with your primary operational objectives.
- If your primary focus is integrating into an existing, crowded facility: The furnace's small footprint and simplified installation are decisive advantages that minimize disruption and cost.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency for holding metal: The reduced heat loss from the compact design offers significant, continuous savings on operational costs.
- If your primary focus is high-volume primary melting from cold scrap: You must carefully evaluate whether the channel furnace's capacity and melt rate meet your throughput demands compared to larger furnace types.
Ultimately, understanding how a compact design influences both physical logistics and thermal efficiency empowers you to select the most effective tool for your specific production needs.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Direct Benefit |
|---|---|
| Small Footprint | Easier installation in space-constrained facilities; optimizes factory layout. |
| Reduced Surface Area | Minimizes thermal energy loss, leading to higher efficiency. |
| Lower Energy Consumption | Decreases operational costs due to reduced standby heat loss. |
| Enhanced Process Control | Enables precise temperature regulation for consistent product quality. |
Ready to Integrate Efficiency into Your Operation?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse industrial facilities with advanced thermal processing solutions. Our product line, including high-temperature furnaces and custom systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique production requirements.
Let us help you achieve superior energy savings and seamless integration. Contact our experts today to discuss how a compact, high-efficiency furnace can transform your metal holding or melting process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















