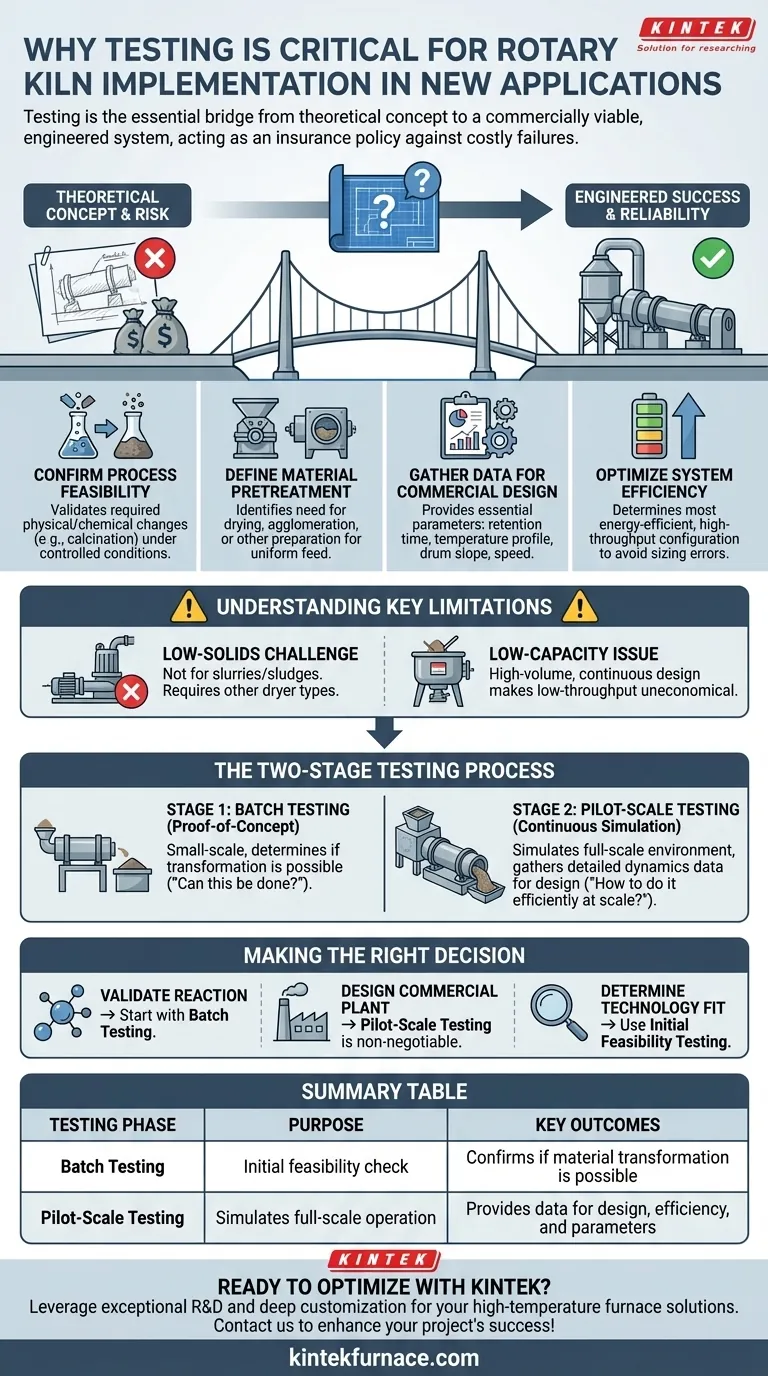
In short, testing is the critical step that validates whether a rotary kiln can successfully and economically process your material for a new application. It provides the essential data needed to move from a theoretical concept to an engineered, commercially viable system, preventing costly design errors and operational failures.
Before committing to a major capital investment, process testing acts as an insurance policy. It confirms technical feasibility, defines critical operating parameters, and gathers the precise data needed to design an efficient and reliable full-scale rotary kiln.

Why You Cannot Skip the Testing Phase
Investing in a rotary kiln without prior testing is a significant financial risk. The testing phase is not an added cost; it is an integral part of the engineering process that ensures the final system will meet your performance and business objectives.
Confirming Process Feasibility
The first and most fundamental question is whether the kiln can achieve the desired outcome. Testing confirms if the required physical change or chemical reaction—such as calcination, thermal desorption, or reduction—can be successfully induced in your specific material under controlled conditions.
Defining Material Pretreatment
Many materials cannot be fed directly into a kiln. Testing will reveal if your feedstock requires pretreatment, such as drying to a specific moisture content or agglomeration (pelletizing) to ensure uniform size and flow through the drum.
Gathering Data for Commercial Design
A pilot-scale test provides the hard data engineers need to design the full-scale unit. This includes critical parameters like required retention time, optimal temperature profile, drum slope, rotational speed, and necessary off-gas handling systems. Without this data, the design is based on guesswork.
Optimizing System Efficiency
Testing allows for the optimization of the process. By experimenting with different variables in a controlled environment, you can determine the most energy-efficient and high-throughput configuration, ensuring your commercial plant is not over- or under-sized.
Understanding the Key Limitations
While incredibly versatile, a rotary kiln is not the universal solution for all thermal processing needs. Feasibility testing is crucial for identifying when an alternative technology might be a better fit.
The Challenge of Low-Solids Materials
Rotary kilns are designed to process bulk solids. They are generally not suitable for materials with very low solids content, such as slurries or sludges, which may require a different type of dryer or thermal processing technology.
The Issue of Low-Capacity Needs
The robust engineering and high thermal capacity of a rotary kiln mean they are best suited for continuous, high-volume operations. For applications with very low throughput requirements, the capital and operational costs of a kiln may be prohibitive compared to batch-based alternatives.
The Two-Stage Testing Process
Professional testing typically occurs in two distinct phases, moving from initial validation to continuous process simulation.
Stage 1: Batch Testing
This is a small-scale, proof-of-concept test. A sample of your material is processed in a batch kiln to determine if the desired transformation is possible. It answers the basic question: "Can this even be done?"
Stage 2: Pilot-Scale Testing
Once feasibility is confirmed, pilot testing uses a small, continuous rotary kiln that simulates the full-scale production environment. This phase gathers the detailed data on process dynamics and equipment requirements needed for final system design. It answers the question: "How do we do this efficiently at scale?"
Making the Right Decision for Your Project
The goal of testing is to provide clarity and mitigate risk. Your approach should be guided by your project's specific objective.
- If your primary focus is validating a new chemical reaction: Begin with batch testing to confirm the fundamental chemistry works before investing in more extensive pilot trials.
- If your primary focus is designing a full-scale commercial plant: Pilot-scale testing is non-negotiable to gather the essential engineering data required for an efficient and reliable design.
- If your primary focus is determining technology fit: Use initial feasibility testing to quickly assess if a rotary kiln is appropriate for your material, especially if it has low solids or your capacity needs are small.
Ultimately, comprehensive testing transforms a speculative industrial project into a predictable and engineered asset.
Summary Table:
| Testing Phase | Purpose | Key Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Batch Testing | Initial feasibility check | Confirms if material transformation is possible |
| Pilot-Scale Testing | Simulates full-scale operation | Provides data for design, efficiency, and parameters |
Ready to optimize your thermal processing with a reliable rotary kiln? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored high-temperature furnace solutions can enhance your project's efficiency and success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency



















