When selecting a muffle furnace, the temperature range is the single most important specification because it dictates whether the furnace can successfully perform your specific application. A furnace that cannot reach or sustain the required process temperature will fail, while one that significantly exceeds your needs introduces unnecessary cost and potential inefficiencies.
The core challenge isn't just finding a furnace that can hit a peak temperature. It's about selecting a unit where your required working temperature falls comfortably within its continuous operating range to ensure process accuracy, equipment longevity, and operational safety.

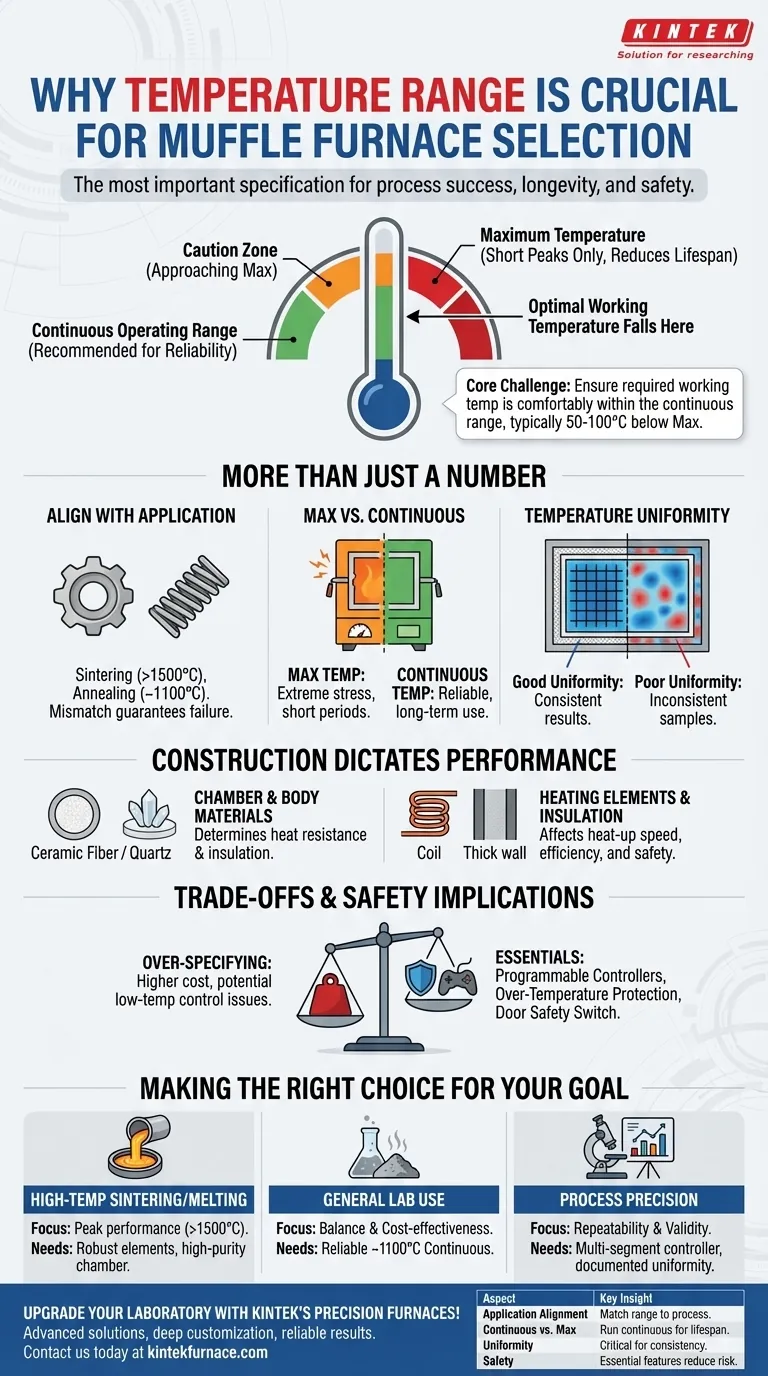
Why Temperature Range is More Than Just a Number
Understanding the nuances of a furnace's temperature specifications is critical for making an informed decision. The listed maximum temperature is only part of the story.
Aligning with Your Specific Application
The first step is always to define your process needs. Different applications have fundamentally different thermal requirements.
For example, sintering ceramics or metals requires very high temperatures, often exceeding 1500°C. In contrast, processes like annealing or general heat treatment may only require a lower range, perhaps up to 1100°C. Choosing a range that doesn't match your process guarantees failure.
Maximum vs. Continuous Operating Temperature
A furnace's maximum temperature is the absolute peak it can reach for short periods. Consistently running a furnace at its maximum limit places extreme stress on its heating elements and insulation, drastically reducing its lifespan.
The more important figure is the continuous operating temperature, which is typically 50°C to 100°C lower than the maximum. For reliable, long-term use, your standard process temperature should never exceed this continuous rating.
The Importance of Temperature Uniformity
A stated temperature is useless if it only applies to one spot in the chamber. Temperature uniformity describes how consistent the temperature is throughout the entire chamber volume.
Poor uniformity can lead to inconsistent results, where samples in different locations are processed incorrectly. This is directly influenced by the quality and placement of heating elements and insulation.
How Furnace Construction Dictates Performance
The temperature range a furnace can achieve is a direct result of its engineering and material science.
Chamber and Body Materials
The materials used for the furnace chamber and body determine its heat resistance and insulation properties.
Ceramic fiber bodies offer excellent insulation and are common in furnaces up to 1200°C. For higher-temperature experiments, chambers made of quartz or high-purity alumina are often used due to their superior heat and corrosion resistance.
Heating Elements and Insulation
The type and quality of the heating elements determine how quickly and efficiently the furnace heats up. The quality of the surrounding insulation dictates how well it holds that temperature and how much energy it consumes.
Poor insulation means the furnace will struggle to maintain its setpoint and the exterior will become dangerously hot.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Implications
Choosing a furnace involves balancing capability with cost and safety. Over-specifying can be as problematic as under-specifying.
The Pitfall of "More is Better"
It is a common mistake to purchase a furnace with a much higher temperature range than required, assuming it provides a buffer.
High-temperature furnaces are significantly more expensive to purchase and operate. Furthermore, they may not offer the same level of control or uniformity at lower temperatures, potentially compromising less demanding processes.
The Role of Temperature Controllers
The controller is the brain of the furnace. A basic controller may only hold a single setpoint, while an advanced programmable controller allows for complex profiles with multiple heating ramps and dwell times (soaks).
Precision work demands a high-quality controller that can prevent temperature overshoots and maintain stability.
Essential Safety Protections
Managing high temperatures carries inherent risks. A quality furnace must include safety features tied to its thermal system.
Look for over-temperature protection, which automatically shuts the furnace down if it exceeds a safe limit, and a door safety switch that cuts power to the heating elements when the door is opened.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select a furnace based on a clear understanding of your primary operational needs.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sintering or melting: You must select a furnace with a maximum temperature that safely exceeds your process needs, likely featuring robust silicon carbide elements and a high-purity ceramic chamber.
- If your primary focus is general lab use like ashing or heat treating: A reliable furnace with a continuous operating temperature around 1100°C offers the best balance of performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is process precision and repeatability: Prioritize a furnace with a multi-segment programmable controller and documented temperature uniformity specifications to ensure your results are valid and repeatable.
Ultimately, choosing the right temperature range ensures the integrity of your work and the longevity of your investment.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Application Alignment | Match furnace range to process needs (e.g., sintering >1500°C, annealing ~1100°C) to avoid failure. |
| Continuous vs. Max Temperature | Continuous operating temp (50-100°C below max) ensures reliability and extends furnace lifespan. |
| Temperature Uniformity | Consistency across the chamber prevents inconsistent results and improves accuracy. |
| Safety and Efficiency | Proper range selection reduces energy costs and risks, with features like over-temperature protection. |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's precision high-temperature furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your unique experimental requirements are met with accuracy and efficiency. Don't let temperature limitations hold back your research—contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your processes and deliver reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















