In short, oxidation resistance is the single most critical factor for a heating element's longevity and reliability. At the high temperatures required for heating, most metals react rapidly with oxygen in the air, causing them to degrade, become brittle, and ultimately fail. True oxidation resistance isn't about preventing oxidation entirely; it’s about using materials that form a stable, protective oxide layer on their surface that shields the underlying material from further attack.
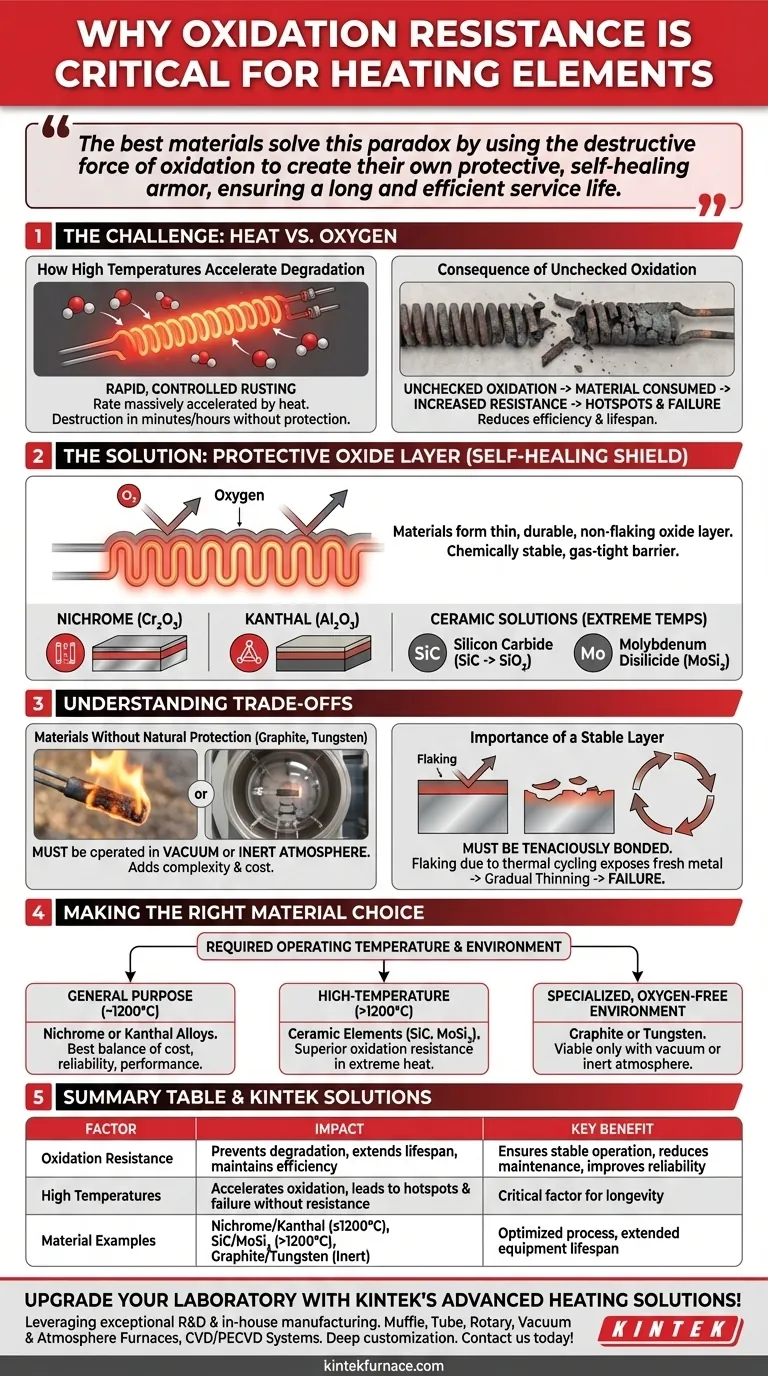
The core challenge of a heating element is surviving its own operational environment. The best materials solve this paradox by using the destructive force of oxidation to create their own protective, self-healing armor, ensuring a long and efficient service life.
The Fundamental Challenge: Heat vs. Oxygen
High-temperature operation creates an aggressive environment where the laws of chemistry work against the integrity of the heating element. Understanding this conflict is key to appreciating material choice.
How High Temperatures Accelerate Degradation
Oxidation is a chemical reaction, and like most reactions, its rate is massively accelerated by heat. Think of it as a form of rapid, controlled rusting.
An element that works perfectly at room temperature can be completely destroyed in minutes or hours when heated to its operating temperature in the presence of air.
The Consequence of Unchecked Oxidation
When an element oxidizes without a protective layer, the material is consumed. This reduces its cross-sectional area, which increases its electrical resistance unpredictably.
This change leads to hotspots, uneven heating, and eventually, a point where the element becomes so thin it simply burns out and breaks the circuit. This degradation also reduces the element's overall efficiency and operational lifespan.
The Protective Oxide Layer: A Self-Healing Shield
The solution is not to find a material that doesn't oxidize at all, but one that oxidizes in a very specific, beneficial way. This is the defining characteristic of all modern, high-performance heating element alloys.
How a Stable Oxide Layer Works
Materials like Nichrome (Nickel-Chromium) and Kanthal (Iron-Chromium-Aluminum) are designed to immediately form a thin, durable, and non-flaking oxide layer when first heated.
This layer—chromium oxide (Cr₂O₃) for Nichrome or aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) for Kanthal—is chemically stable and acts as a gas-tight barrier. It prevents oxygen from reaching the fresh metal underneath, effectively stopping further degradation.
Ceramic Solutions for Extreme Temperatures
Ceramic heating elements operate on the same principle but at even higher temperatures. Silicon Carbide (SiC) forms a protective layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂).
Materials like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) offer even more robust oxidation resistance, forming a protective glaze that allows them to maintain efficiency and last longer than SiC in very high-temperature applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect, and the choice of element depends on balancing performance against the specific operating environment. The absence of oxidation resistance imposes severe limitations.
Materials Without Natural Protection
Materials with excellent high-temperature properties but poor oxidation resistance, such as graphite or tungsten, are unusable in open air.
To prevent them from instantly burning away, they must be operated in a vacuum or an inert, protective atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen). This dramatically increases the complexity and cost of the heating system.
The Importance of a Stable Layer
The protective oxide layer must be tenaciously bonded to the parent material. If the layer were to flake off due to thermal cycling (expansion and contraction), it would expose fresh metal underneath.
This new surface would then oxidize, and the cycle would repeat, leading to a gradual "thinning" of the element and eventual failure. The stability of the oxide layer is just as important as its formation.
Making the Right Material Choice
Selecting a heating element material is a direct function of the required operating temperature and environment.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating (up to ~1200°C): Nichrome or Kanthal alloys offer the best balance of cost, reliability, and performance due to their stable protective oxide layers.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature industrial processes (>1200°C): Ceramic elements like Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) are necessary for their superior oxidation resistance in extreme heat.
- If you are operating in a specialized, oxygen-free environment: Materials like graphite or tungsten become viable options, but only if the system can maintain a vacuum or inert atmosphere.
Choosing a material with the right oxidation resistance for its environment is the most fundamental step in designing a durable and effective heating system.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Oxidation Resistance | Prevents material degradation, extends lifespan, and maintains efficiency by forming a protective oxide layer. |
| High Temperatures | Accelerate oxidation; without resistance, elements degrade quickly, leading to hotspots and failure. |
| Material Examples | Nichrome, Kanthal for up to 1200°C; SiC, MoSi₂ for higher temps; graphite/tungsten require inert atmospheres. |
| Key Benefit | Ensures stable operation, reduces maintenance costs, and improves reliability in heating applications. |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and durability. Contact us today to discuss how our oxidation-resistant heating elements can optimize your processes and extend equipment lifespan!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















