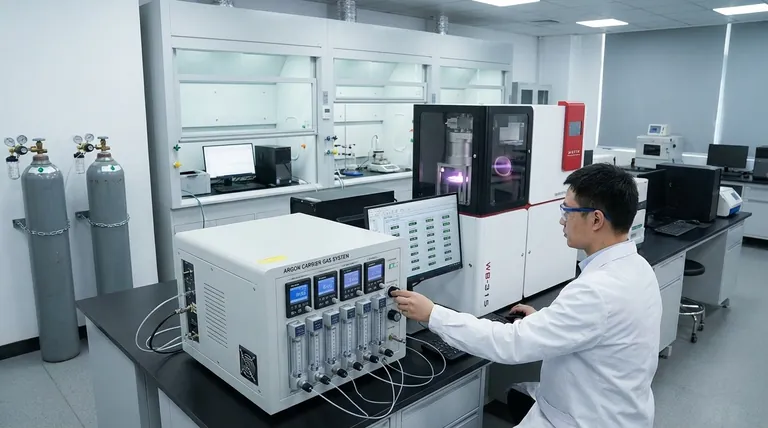
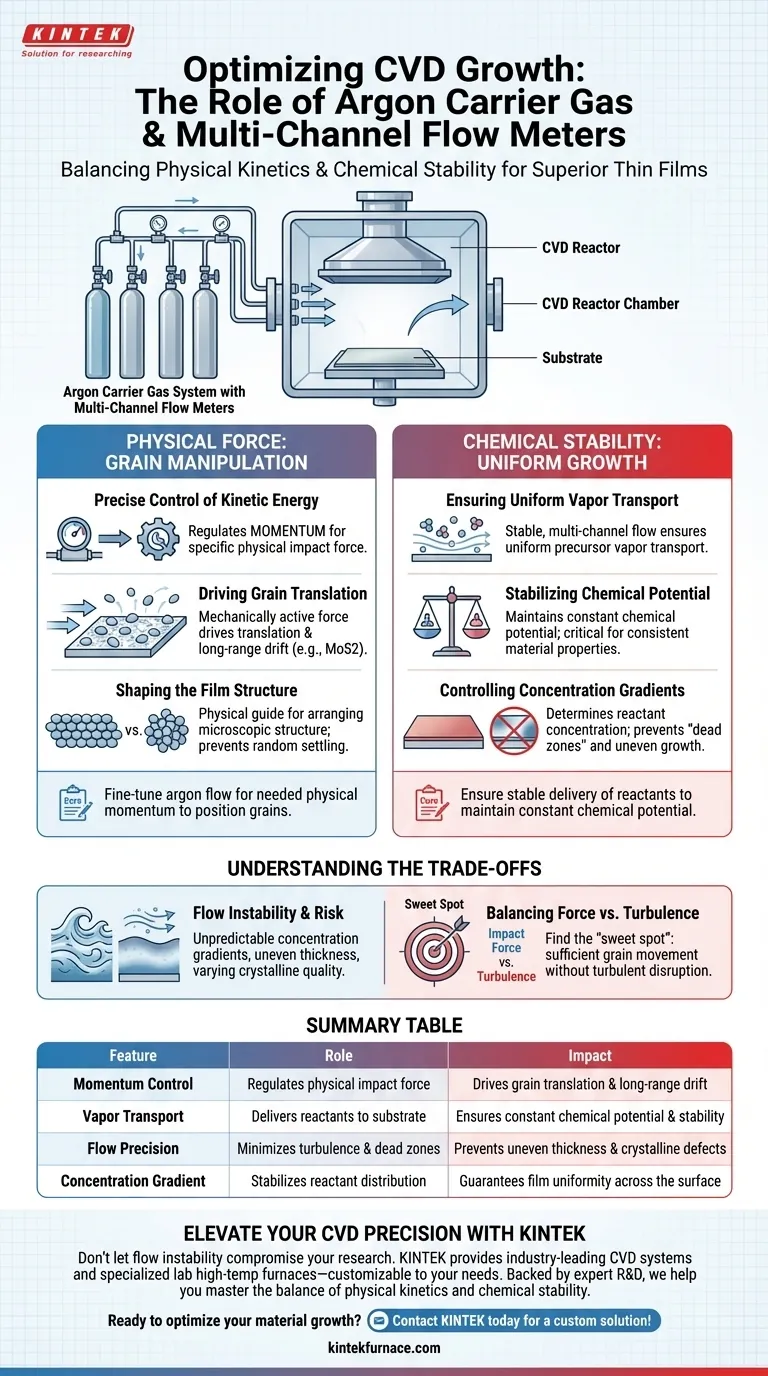
An argon carrier gas system equipped with multi-channel flow meters is essential for effectively governing both the physical kinetics and the chemical environment of the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process. This setup provides the rigorous control necessary to generate specific physical forces that manipulate grain movement while simultaneously maintaining the thermodynamic stability required for uniform material growth.
Core Takeaway: High-quality CVD growth requires decoupling physical transport from chemical reaction. Multi-channel meters allow you to fine-tune the argon flow to provide the physical momentum needed to position grains, while ensuring the stable delivery of reactants to maintain a constant chemical potential.

The Role of Physical Force in Grain Manipulation
Precise Control of Kinetic Energy
The primary function of the multi-channel flow meter is not simply to deliver gas, but to regulate momentum. By allowing for the precise control of flow rates, the system generates a specific physical impact force within the chamber.
Driving Grain Translation
This physical force is mechanically active on the substrate level. In specific applications, such as the growth of MoS2, this force is required to drive the translation and long-range drift of grains across the substrate surface.
Shaping the Film Structure
Without this controlled physical drift, grains may settle randomly or cluster inefficiently. The argon flow acts as a physical guide, helping to arrange the microscopic structure of the material as it deposits.
Maintaining Chemical Stability and Uniformity
Ensuring Uniform Vapor Transport
Beyond physical force, the argon system acts as the transport medium for reactants. A stable, multi-channel controlled flow ensures the uniform transport of precursor vapors (such as sulfur) from the source to the substrate.
Stabilizing Chemical Potential
Uniform transport is critical for maintaining a constant chemical potential throughout the reaction chamber. Fluctuations in flow can alter the local chemical environment, leading to inconsistent material properties.
Controlling Concentration Gradients
The stability of the argon flow directly determines the concentration gradient of reactants on the substrate. Precise metering prevents "dead zones" or areas of excessive concentration, ensuring the film grows evenly across the entire surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Flow Instability
If the carrier gas system lacks precise metering, flow instability becomes a major variable. This can lead to unpredictable concentration gradients, causing the resulting film to exhibit uneven thickness or varying crystalline quality.
Balancing Impact Force vs. Turbulence
While physical impact force is necessary for grain translation, excessive flow can introduce turbulence. You must use the multi-channel meters to find the "sweet spot" where the force is sufficient to move grains but stable enough to prevent turbulent disruption of the vapor cloud.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your CVD setup, tailor your flow strategy to your specific deposition targets:
- If your primary focus is Grain Alignment: Prioritize higher flow precision to maximize the physical impact force, ensuring grains drift and settle in the desired orientation.
- If your primary focus is Film Uniformity: Prioritize flow stability to maintain a constant chemical potential and eliminate concentration gradients across the substrate.
The precision of your flow meters ultimately dictates the structural integrity of your thin film.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in CVD Process | Impact on Material Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Momentum Control | Regulates physical impact force | Drives grain translation & long-range drift |
| Vapor Transport | Delivers reactants to substrate | Ensures constant chemical potential & stability |
| Flow Precision | Minimizes turbulence & dead zones | Prevents uneven thickness & crystalline defects |
| Concentration Gradient | Stabilizes reactant distribution | Guarantees film uniformity across the surface |
Elevate Your CVD Precision with KINTEK
Don't let flow instability compromise your research. KINTEK provides industry-leading CVD systems and specialized lab high-temp furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum systems—all customizable to your specific gas delivery needs. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we help you master the balance of physical kinetics and chemical stability.
Ready to optimize your material growth? Contact KINTEK today for a custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Jehyun Oh, Sang‐Yong Ju. Diffusion and Surface Effects on Sodium‐Promoted MoS <sub>2</sub> Growth Observed in <i>Operando</i>. DOI: 10.1002/smtd.202500813
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision mass flow controller essential for GaN thin films? Achieve High-Purity Semiconductor Growth
- What role does CVD play in nanotechnology? Essential for Precise Synthesis of Nanomaterials
- What role does a Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) system play in MoS2 thin films? Achieve Precise Atomic Layer Control
- What tasks do ultrasonic cleaning and ion sputtering systems perform in PVD? Achieve Atomic-Level Coating Adhesion
- What materials can be deposited using CVD? Unlock Versatile Thin Films for Your Applications
- What are the key characteristics and advantages of CVD coatings? Enhance Durability and Precision for Complex Parts
- What are the future trends in CVD technology? AI, Sustainability, and Advanced Materials
- What types of tools and components are CVD coatings applied to? Boost Durability and Performance in Your Applications









