In short, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are preferred in kilns because they deliver the high temperatures, uniform heat, and long-term durability essential for producing high-quality, consistent pottery. Unlike standard metallic elements, SiC provides superior performance under the demanding conditions of ceramic firing, directly impacting the success and finish of the final product.
The core reason for choosing silicon carbide is not just its ability to get hot, but its capacity to provide stable, evenly distributed heat cycle after cycle. This reliability is the foundation for achieving predictable and professional results in ceramics.

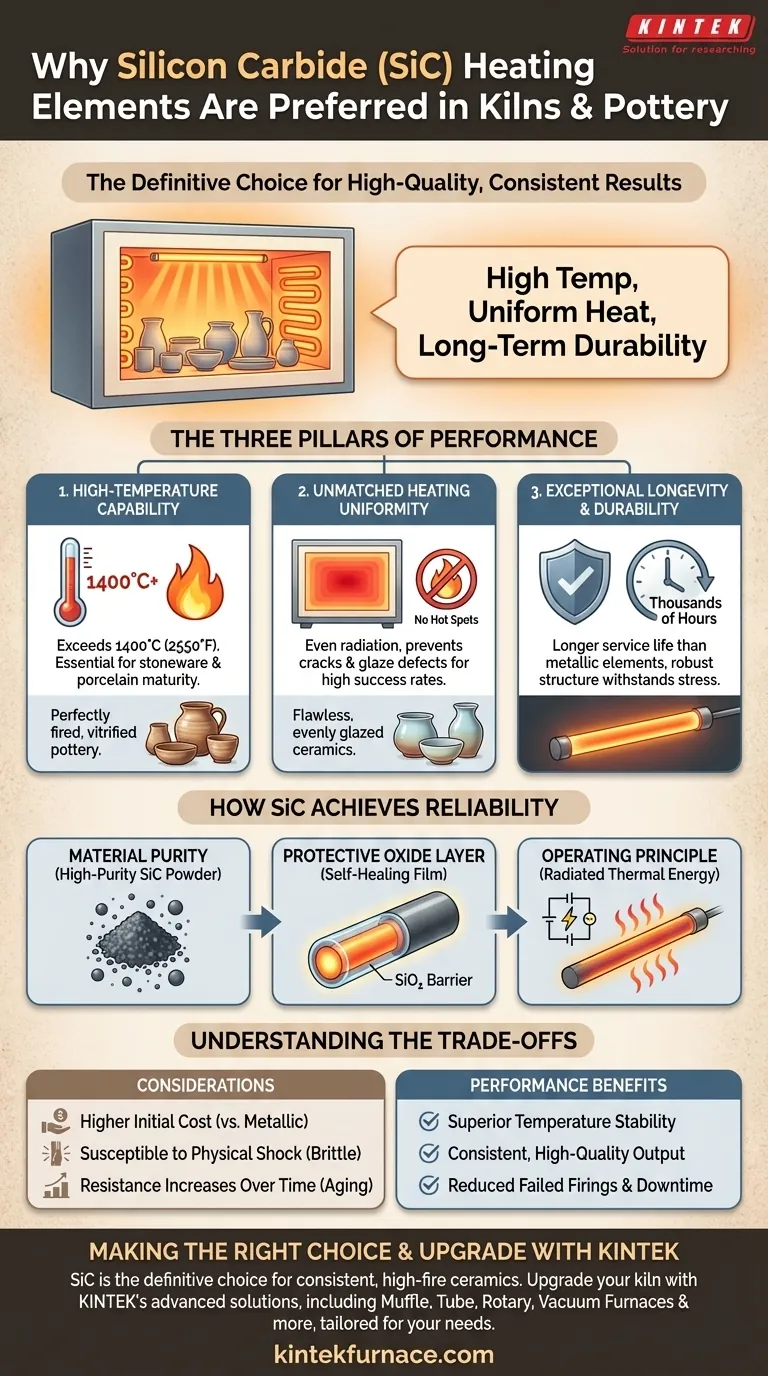
The Three Pillars of SiC Performance in Kilns
To understand why SiC is a superior material for this application, we must look at three distinct advantages it holds over other heating technologies.
1. High-Temperature Capability
Pottery, and especially high-fire stoneware and porcelain, requires extreme temperatures to mature the clay body and melt glazes correctly.
Silicon carbide elements are engineered to operate comfortably and efficiently at these high temperatures, often exceeding 1400°C (2550°F). This capability is crucial for achieving the desired hardness, vitrification, and aesthetic properties in advanced ceramic work.
2. Unmatched Heating Uniformity
Inconsistent heating is a primary cause of failure in a kiln firing. Hot spots can cause glazes to blister or run, while cold spots can leave clay under-fired and glazes dull.
SiC elements radiate heat very evenly throughout the kiln chamber. This uniform heating ensures that every piece in the load, regardless of its position, receives the same thermal treatment. This consistency is vital for preventing cracks, dunting, and glaze defects, leading to a much higher success rate.
3. Exceptional Longevity and Durability
Kiln elements are subjected to intense thermal stress. Longevity is a major factor in the operational cost and reliability of a kiln.
SiC elements have a significantly longer service life compared to traditional metallic wire elements. Their robust physical structure, derived from high-purity materials, is designed to withstand thousands of hours of operation without significant degradation.
How SiC Elements Achieve This Reliability
The performance of SiC is not accidental; it is a direct result of its material science and how it behaves at high temperatures.
The Role of Material Purity
The process begins with high-purity green silicon carbide powder. When formed into elements, this purity ensures a dense, uniform structure. This density is key to its strength and consistent electrical resistance, which translates to stable heat output.
The Protective Oxide Layer
The true genius of SiC lies in its self-protecting nature. As the element heats in the presence of oxygen, a thin, transparent layer of silicon dioxide (essentially glass) forms on its surface.
This protective film is highly resistant to further oxidation. It acts as a barrier that shields the core silicon carbide from burnout, dramatically enhancing its antioxidant properties and extending its operational life at extreme temperatures.
The Operating Principle
The mechanism is simple and effective. An electric current is passed through the SiC element. Due to its natural electrical resistance, the element heats up and radiates thermal energy into the kiln chamber. The temperature is precisely managed by adjusting the voltage or current supplied to the elements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While superior in performance, SiC elements are not without considerations. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging the trade-offs.
Higher Initial Cost
Silicon carbide elements typically have a higher upfront cost compared to standard Kanthal (FeCrAl) wire elements. This initial investment must be weighed against their longer lifespan and the reduced cost of failed firings.
Susceptibility to Physical Shock
Like many ceramic materials, SiC elements are strong under heat but can be brittle. They must be handled with care during installation and kiln loading to avoid physical shock, which can cause them to crack.
Resistance Change Over Time
Over their long life, SiC elements slowly "age," which causes their electrical resistance to gradually increase. Modern kiln controllers can often compensate for this, but it means the elements will eventually draw less power and require replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Studio
Ultimately, the choice of heating element depends on your specific goals, the type of work you do, and your budget.
- If your primary focus is consistent, high-quality results for high-fire ceramics: SiC is the definitive choice for its temperature stability, heating uniformity, and long-term reliability.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront cost for low-fire or hobbyist work: Traditional metallic elements can be a more economical starting point, but expect a shorter service life and potentially less firing consistency.
Choosing the right heating element is an investment in the quality and predictability of your ceramic work.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Capability | Operates above 1400°C, ideal for high-fire ceramics like stoneware and porcelain. |
| Heating Uniformity | Radiates even heat to prevent defects like cracks and glaze issues, ensuring consistent results. |
| Longevity and Durability | Longer service life than metallic elements, reducing replacement costs and downtime. |
| Material Purity | Made from high-purity SiC for stable performance and reliable heat output. |
| Protective Oxide Layer | Forms a self-protecting barrier against oxidation, extending element life. |
Upgrade your kiln with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide silicon carbide heating elements and a full product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—tailored for ceramics and diverse laboratory needs. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for superior performance and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your pottery results and operational efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















