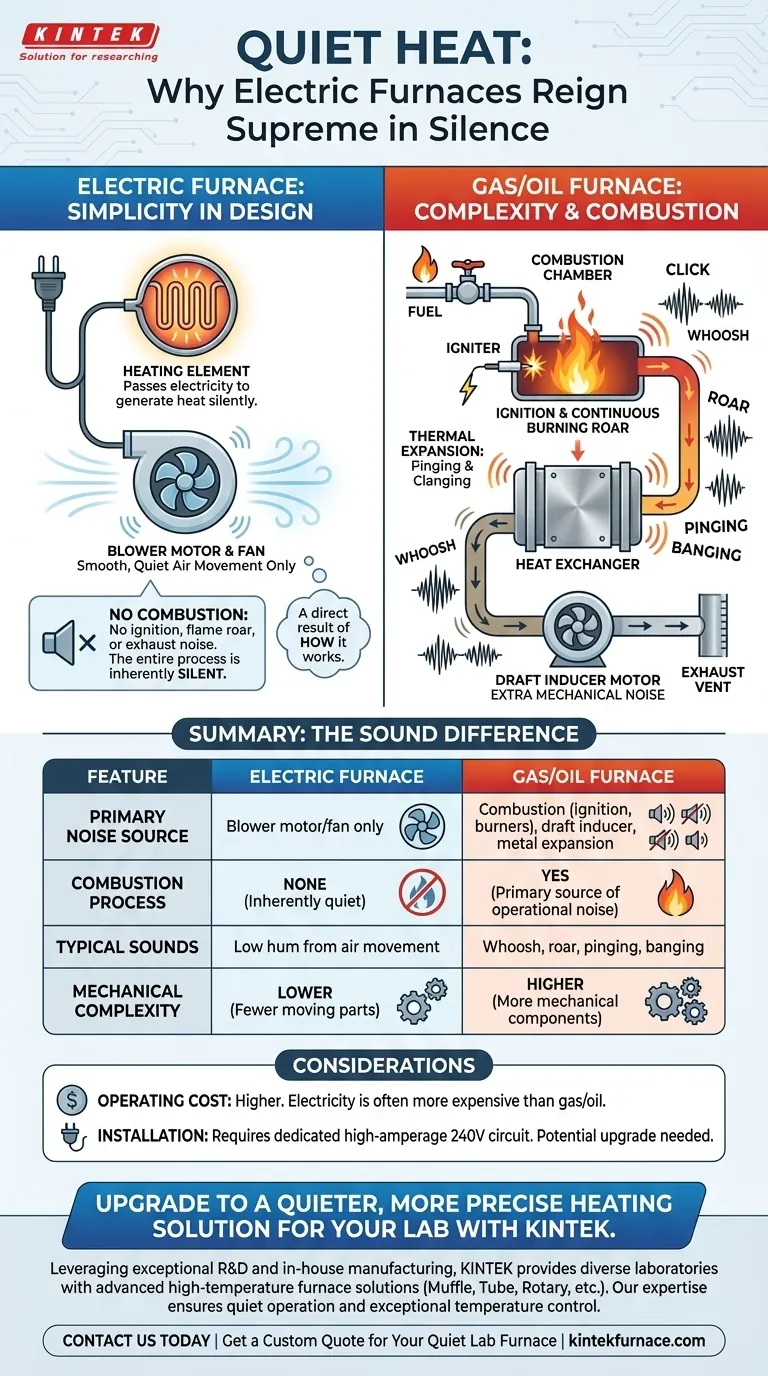
At their core, electric furnaces are quieter because their design is fundamentally simpler and lacks the noisy process of fuel combustion. Unlike gas or oil furnaces that rely on igniting a flame and managing exhaust, an electric furnace generates heat silently by passing electricity through heating elements, a process with no inherent noise beyond the movement of air.
The defining reason for an electric furnace's quiet operation is its lack of combustion. The noise associated with traditional furnaces—the ignition, the roar of burners, and the expansion of metal—is entirely absent in an electric system.

The Source of Quiet: Simplicity in Design
The quiet nature of an electric furnace isn't a feature that's added on; it's a direct result of how it works. The entire system is built around a single, silent principle.
How an Electric Furnace Works: The Heating Element
An electric furnace operates much like a large hairdryer or toaster. It draws in air from your home and passes it over a series of heating elements, which are metal coils that glow hot when electricity flows through them.
The only significant moving part in this process is the blower motor and fan, which circulates the newly heated air through your home's ductwork. Modern blower motors are designed for smooth, quiet operation.
No Combustion, No Combustion Noise
This is the critical difference. A gas or oil furnace is a complex machine that must safely burn fuel. The entire combustion process is a source of noise that simply doesn't exist in an electric furnace.
Understanding Noise in Other Furnaces
To appreciate the silence of an electric furnace, it helps to understand the sounds produced by its fuel-burning counterparts. These noises are normal operational sounds, not necessarily signs of a malfunction.
The Sound of Ignition and Burning
When a gas furnace cycles on, you hear a series of distinct sounds. First, a click from the gas valve opening, followed by the "whoosh" or low roar as the burners ignite. This continuous flame is the primary source of operational noise.
Mechanical Components and Metal Expansion
Fuel-burning furnaces also have more mechanical parts. A draft inducer motor is often used to vent exhaust gases, adding another layer of sound.
Furthermore, the intense heat of combustion causes the large metal heat exchanger to expand and contract. This thermal expansion often produces the "pinging," "banging," or "clanging" noises people associate with a furnace kicking on and off.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While an electric furnace is the champion of quiet operation, this benefit comes with important considerations. Objectivity requires acknowledging the complete picture.
The Cost of Quiet: Operational Expense
The primary trade-off is operating cost. In most regions, generating heat with electricity is significantly more expensive than using natural gas. While the furnace itself may be less expensive to purchase and install, the monthly utility bills will almost always be higher.
Installation and Infrastructure
An electric furnace requires a dedicated, high-amperage 240-volt circuit. If your home's electrical panel is not equipped to handle this load, a costly upgrade by an electrician will be necessary. Gas furnaces, conversely, use a standard 120-volt outlet.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your ideal heating system depends on whether you prioritize silence, running costs, or a balance of both.
- If your primary focus is minimal noise: An electric furnace is the undisputed winner, providing near-silent heat.
- If your primary focus is the lowest operating cost: A high-efficiency natural gas furnace is almost always the more economical choice over the long term, if gas service is available.
- If you seek a balance of modern efficiency and quiet operation: Consider a high-end, variable-speed gas furnace, which modulates its fan and burner to run more quietly and consistently than older, single-stage models.
Ultimately, understanding the mechanical reason for the noise—or lack thereof—empowers you to choose the system that best aligns with your home's needs and your personal priorities.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electric Furnace | Gas/Oil Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Noise Source | Blower motor/fan only | Combustion (ignition, burners), draft inducer, metal expansion |
| Combustion Process | None | Yes (primary source of operational noise) |
| Typical Sounds | Low hum from air movement | Whoosh of ignition, roar of burners, pinging/banging from heat exchanger |
| Mechanical Complexity | Lower (fewer moving parts) | Higher (more mechanical components) |
Upgrade to a Quieter, More Precise Heating Solution for Your Lab
If your research demands a stable, low-noise thermal environment, KINTEK's advanced electric furnaces are the ideal choice. Our expertise in high-temperature technology ensures not only quiet operation but also exceptional temperature uniformity and control—critical for sensitive experiments and material processing.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how a custom KINTEK electric furnace can enhance your lab's capabilities and productivity. Let our experts help you select or design the perfect heating solution for your specific application.
Get a Custom Quote for Your Quiet Lab Furnace
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What happens to convective and radiative heat transfer effects at high furnace gas temperatures? Radiation Dominates for Superior Heating
- What is a quartz tube furnace and what is its primary use? Essential for Controlled High-Temp Processing
- What is a Quartz Tube Furnace and what is its primary function? Essential for Real-Time Material Observation
- How should a quartz tube furnace be cleaned? Essential Steps for Safe, Contamination-Free Maintenance
- What is the difference between an alumina tube furnace and a quartz tube furnace? Choose the Right Tube Furnace for Your Lab



















