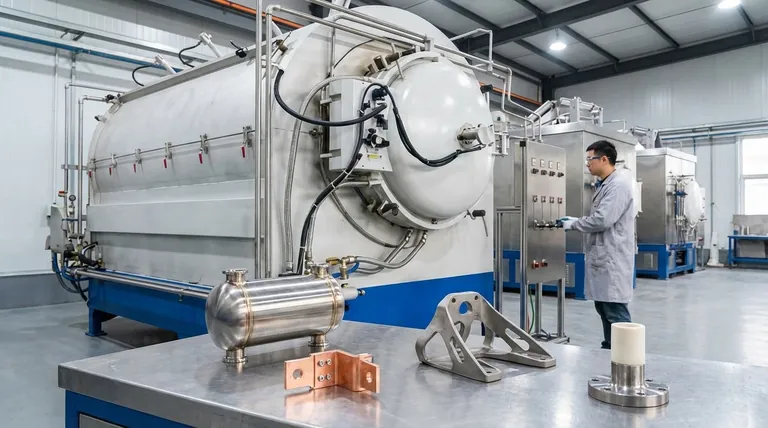
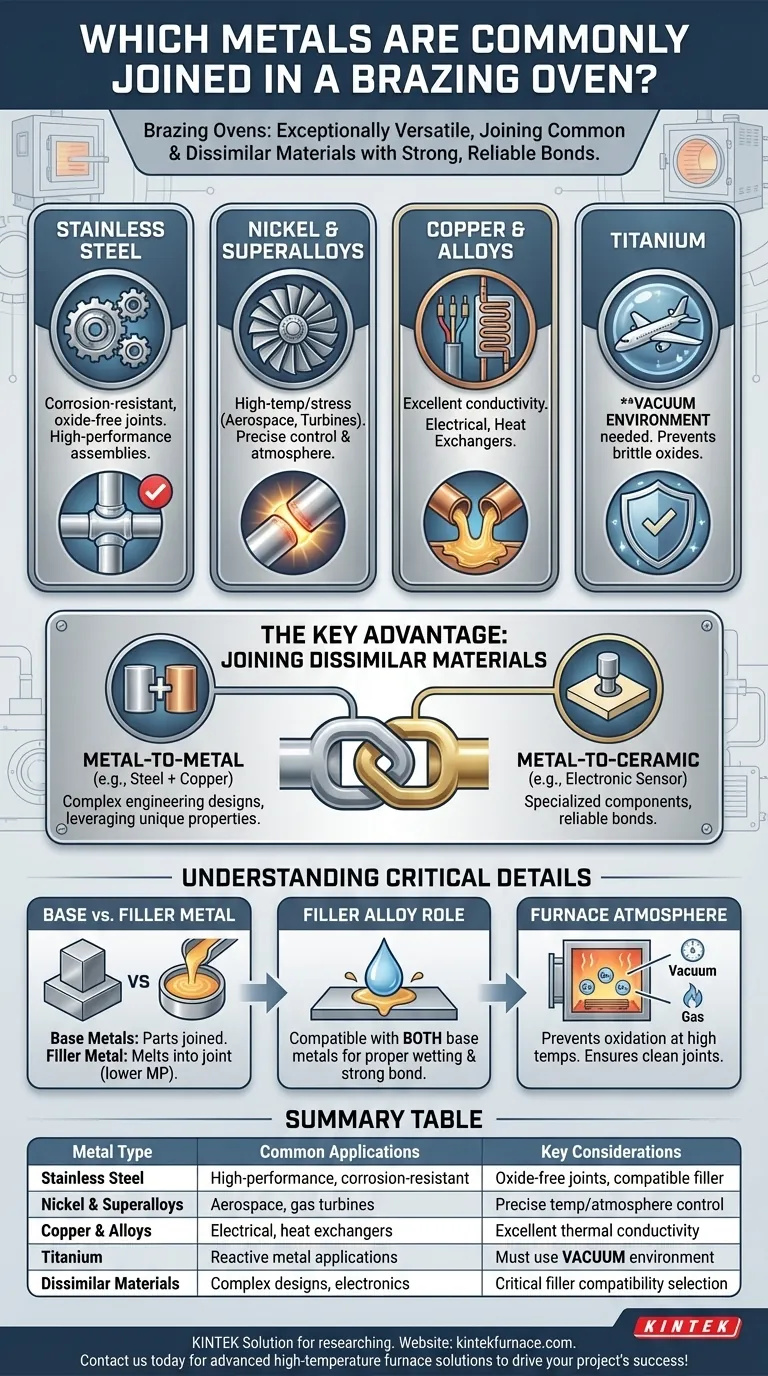
Brazing ovens are exceptionally versatile, capable of joining a wide range of common and advanced metals. The most frequently joined materials include stainless steel, nickel alloys, copper, and titanium, but the true strength of the process lies in its ability to join dissimilar materials that are otherwise difficult to connect.
The core capability of a brazing oven is not just joining individual metals, but creating strong, reliable bonds between dissimilar materials. This includes various combinations of metals and even joining metals to ceramics, all made possible by the careful selection of a filler alloy.

Common Base Metals for Brazing
Furnace brazing is a preferred method for creating clean, strong joints in high-performance and complex assemblies. The controlled environment of the oven makes it ideal for several key material groups.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is one of the most common materials joined in a brazing oven. The process allows for clean, oxide-free joints that maintain the corrosion-resistant properties of the base metal.
Nickel and Superalloys
For high-temperature and high-stress applications, such as in aerospace or gas turbines, nickel-based alloys are frequently brazed. The oven provides the precise temperature control and atmosphere needed for these demanding materials.
Copper and Copper Alloys
Copper is readily brazed due to its excellent thermal conductivity and compatibility with many filler metals. Brazing is used to create components for everything from electrical conductors to heat exchangers.
Titanium
Reactive metals like titanium can be successfully joined in a brazing oven, but this typically requires a vacuum environment. The vacuum prevents the formation of brittle oxides that would otherwise compromise the joint's integrity.
The Key Advantage: Joining Dissimilar Materials
The most significant benefit of furnace brazing is its ability to create metallurgical bonds between materials that cannot be welded together. This opens up possibilities for complex engineering designs.
Metal-to-Metal Combinations
Brazing allows for the joining of different metals, such as stainless steel to copper or steel to nickel alloys. This is critical for designs that must leverage the unique properties of multiple materials in a single component.
Metal-to-Ceramic Joining
In advanced applications, furnace brazing is one of the few methods capable of reliably joining metals to ceramics. This is essential for manufacturing specialized electronic components, sensors, and wear-resistant tools.
Understanding the Critical Details
Success in furnace brazing depends on more than just the base metals. A misunderstanding of the process components can lead to failed joints.
Base Metal vs. Filler Metal
It is crucial to distinguish between the base metals (the parts being joined) and the filler metal (the alloy that melts and flows into the joint). Metals like nickel, copper, and silver are often used as filler metals. The filler metal must have a lower melting point than the base metals it is joining.
The Role of the Filler Alloy
The selection of the correct filler alloy is paramount, especially when joining dissimilar materials. The filler must be chemically compatible with both base metals to ensure proper wetting, flow, and a strong final bond.
The Importance of the Furnace Atmosphere
The atmosphere inside the brazing oven prevents the base metals from oxidizing at high temperatures. Whether it's a vacuum for reactive metals like titanium or a specific gas for stainless steel, this controlled environment is what guarantees a clean, strong joint.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing the right approach depends entirely on the materials you need to join.
- If your primary focus is joining stainless steel or nickel alloys: Furnace brazing is a standard, highly effective method, but you must choose a filler metal compatible with your specific alloy grade.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals like copper to steel: The critical task is selecting a filler alloy that is metallurgically compatible with both base materials.
- If your primary focus is joining reactive metals like titanium: You must use a vacuum brazing oven to prevent oxygen contamination and ensure a ductile joint.
- If your primary focus is joining a metal to a ceramic: This is a specialized process that requires expert consultation to select the appropriate active filler metal and brazing cycle.
Ultimately, the versatility of furnace brazing makes it a powerful solution for a vast range of material joining challenges.
Summary Table:
| Metal Type | Common Applications | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High-performance assemblies, corrosion-resistant parts | Requires oxide-free joints; compatible filler metals |
| Nickel and Superalloys | Aerospace, gas turbines | Needs precise temperature control and atmosphere |
| Copper and Copper Alloys | Electrical conductors, heat exchangers | Excellent thermal conductivity; many filler options |
| Titanium | Reactive metal applications | Must use vacuum environment to prevent oxidation |
| Dissimilar Materials (e.g., steel to copper, metal to ceramic) | Complex engineering designs, electronics | Critical filler alloy selection for compatibility |
Ready to enhance your material joining processes with precision and reliability? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with stainless steel, nickel alloys, copper, titanium, or challenging dissimilar materials, our expertise ensures strong, clean joints for your high-performance applications. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored brazing solutions can drive your project's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- How do the radiant heating and controlled cooling functions of a vacuum brazing furnace benefit Kovar-to-SS joints?
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures
- How is vacuum heat treatment applied to elastic alloys? Unlock Peak Performance in Aerospace and Medical Devices
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density



















