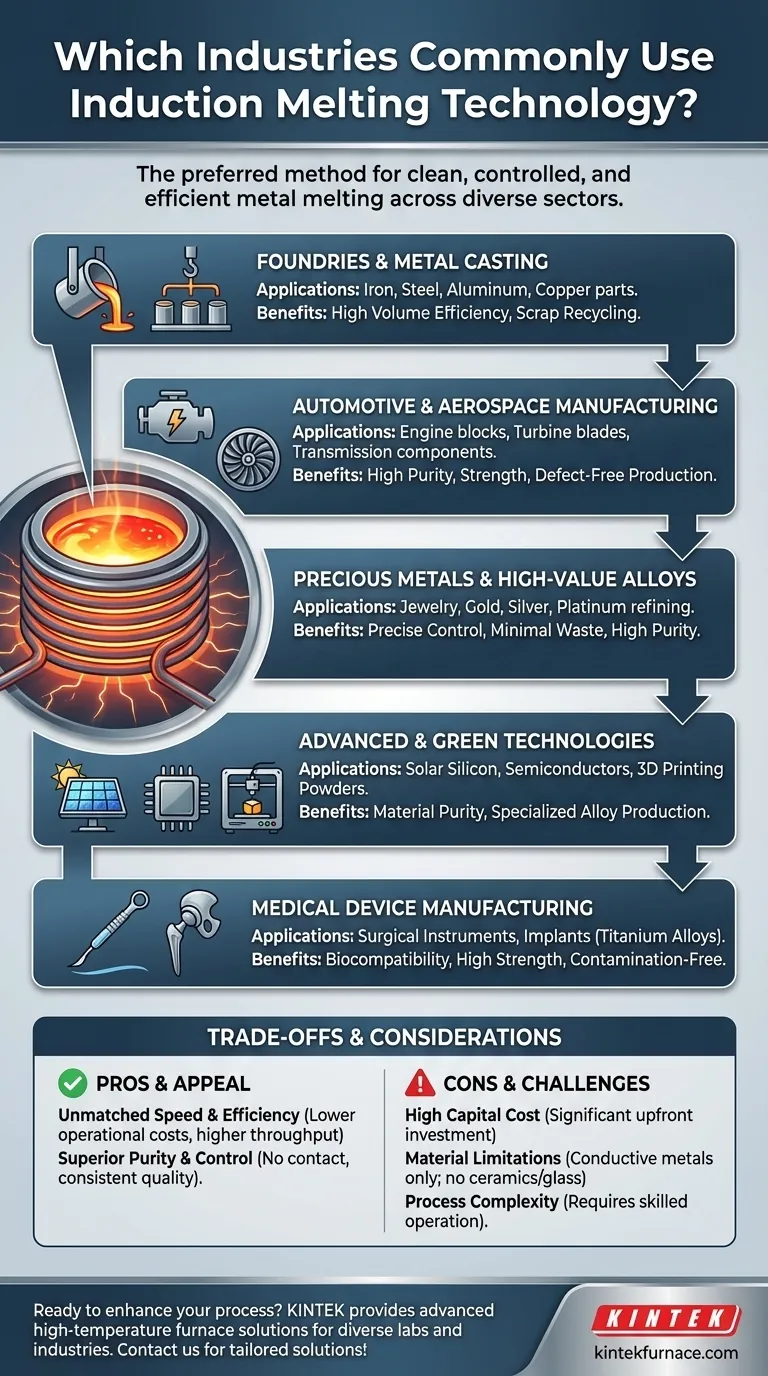
At its core, induction melting technology is the preferred method across any industry that requires clean, controlled, and efficient melting of metals. Its primary users include foundries, metal casting facilities, and the automotive, aerospace, and recycling sectors. Advanced fields like medical device manufacturing, electronics, and green energy also rely heavily on its precision.
Induction melting's value is not just in its ability to heat metal, but in its capacity for unmatched precision, speed, and purity. This control is why it has become an indispensable tool for industries ranging from high-volume manufacturing to high-purity advanced materials.

The Core Appeal of Induction Melting
Induction melting is an advanced process that uses electromagnetic induction to heat and melt conductive materials, primarily metals. Unlike traditional furnaces that use external heat sources, induction heating generates heat directly within the material itself.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
The direct heating method is exceptionally fast, significantly reducing melt times compared to conventional fuel-fired furnaces. This speed, combined with high energy efficiency, translates directly to lower operational costs and higher throughput.
Superior Purity and Control
Because there is no contact between the heating source and the metal, the risk of contamination is virtually eliminated. This makes induction melting ideal for producing high-purity alloys. Furthermore, the process offers extremely precise temperature control, ensuring consistent metallurgical quality batch after batch.
Key Industrial Applications
The unique benefits of induction melting make it a cornerstone technology in several critical industries, each leveraging its specific advantages.
Foundries and Metal Casting
This is the most traditional and widespread application. Foundries use induction furnaces to melt a vast range of metals, including iron, steel, aluminum, and copper, for casting into parts. Its ability to handle large volumes consistently and recycle scrap metal efficiently makes it the industry standard.
Automotive and Aerospace Manufacturing
Both industries demand high-performance components with zero tolerance for defects. Induction melting is used to produce critical parts like engine blocks, transmission components, and turbine blades. The process ensures the metallurgical integrity and strength required for these high-stress applications.
Precious Metals and High-Value Alloys
In jewelry making and precious metal refining, minimizing material loss is paramount. Induction melting provides the tight control over small, high-value batches of gold, silver, and platinum needed to prevent waste and ensure purity. It is also critical for producing the specialized superalloys used in aerospace and defense.
Advanced and Green Technologies
Modern industries rely on induction melting for cutting-edge materials. It is used to produce the high-purity silicon for solar panels and the specialized metals required for semiconductors and electronic components. It is also essential for producing fine metal powders for 3D printing (additive manufacturing) through processes like gas atomization.
Medical Device Manufacturing
The medical field requires materials that are both biocompatible and exceptionally strong. Induction melting, often performed in a vacuum, is used to create the high-purity titanium and stainless steel alloys for surgical instruments and medical implants like hip and knee replacements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction melting is not a universal solution. The primary considerations are its specialization and initial investment.
High Capital Cost
The equipment for induction melting represents a significant upfront capital investment compared to some simpler, fuel-fired furnace technologies. The decision to adopt it must be justified by the need for high quality, efficiency, or throughput.
Material Limitations
The technology works by inducing an electrical current within the material itself. Therefore, it is highly effective for conductive metals but is not suitable for melting non-conductive materials like ceramics or glass.
Process Complexity
Operating an induction furnace system requires skilled technicians and robust process controls. While it offers precision, achieving that precision demands a higher level of operational expertise than a basic furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use induction melting hinges on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and efficiency: This technology is ideal for foundries, automotive suppliers, and recyclers who need to melt large quantities of standard metals quickly and cost-effectively.
- If your primary focus is material purity and performance: This is the non-negotiable choice for aerospace, medical, and electronics manufacturing where material contamination could lead to catastrophic failure.
- If your primary focus is control over valuable or exotic materials: This method provides the precision required for handling precious metals, creating specialized alloys for research, or producing metal powders for advanced manufacturing.
Ultimately, induction melting empowers industries by providing precise and repeatable control over the fundamental process of transforming solid metal into a liquid state.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Core Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Foundries & Metal Casting | Melting iron, steel, aluminum, copper for parts | High volume efficiency, scrap recycling |
| Automotive & Aerospace | Engine blocks, turbine blades, transmission components | High purity, strength, defect-free production |
| Precious Metals & Alloys | Jewelry, gold, silver, platinum refining | Precise control, minimal waste, high purity |
| Advanced & Green Tech | Solar panels, semiconductors, 3D printing powders | Material purity, specialized alloy production |
| Medical Device Manufacturing | Surgical instruments, implants (e.g., titanium alloys) | Biocompatibility, high strength, contamination-free |
Ready to enhance your metal melting processes with precision and efficiency? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in automotive, aerospace, medical, or other sectors, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency



















