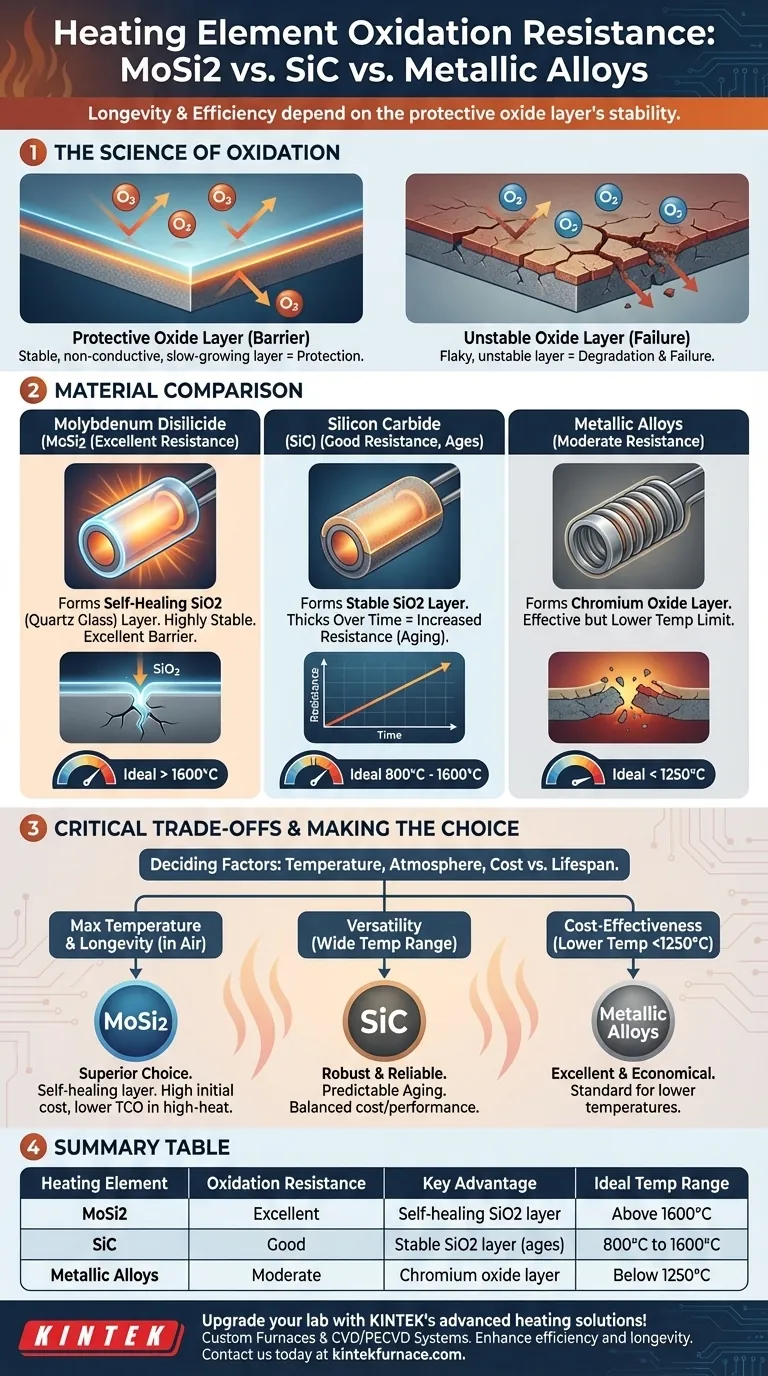
In short, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements offer significantly better oxidation resistance than Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements. When heated, MoSi2 forms a protective, glass-like layer of silicon dioxide (SiO2) that shields the material from further degradation. While SiC also oxidizes, this process can negatively impact its long-term efficiency, whereas the layer on MoSi2 is effectively self-healing.
The longevity and efficiency of a high-temperature heating element are not determined by the material itself, but by the stability of the protective oxide layer it forms when heated. Understanding this principle is the key to selecting the right element for your application.

The Science of Oxidation in Heating Elements
To compare materials, we must first understand why oxidation is the central factor in a heating element's life and performance. It is the primary mechanism of both protection and failure.
What is Oxidation?
Oxidation is the chemical reaction that occurs when a material is exposed to oxygen, especially at high temperatures. This reaction forms a new compound, called an oxide, on the surface of the material.
This process is commonly seen as rust on iron, but in high-performance heating elements, it can be a highly desirable effect.
Why It Determines Element Lifespan
A stable, non-conductive, and slow-growing oxide layer acts as a protective barrier. It prevents oxygen from reaching the underlying core material, dramatically slowing down further degradation.
Conversely, an unstable or flaky oxide layer offers poor protection, leading to rapid material loss and premature element failure. The growth of the oxide layer can also change the element's electrical resistance, a phenomenon known as "aging."
A Comparison of Key Materials
The difference in oxidation resistance comes down to the quality and behavior of the protective layer each material forms.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2): The High-Temperature Champion
MoSi2 elements are renowned for their exceptional performance at very high temperatures, primarily due to their unique oxidation behavior.
Upon heating in an oxidizing atmosphere, MoSi2 forms a thin, non-porous layer of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2), which is essentially quartz glass. This layer is highly stable and provides an excellent barrier against further oxidation. If a crack forms, oxygen penetrates and instantly "heals" the breach by forming new SiO2.
Silicon Carbide (SiC): The Versatile Workhorse
SiC elements are widely used and valued for their high strength and thermal shock resistance across a broad range of temperatures.
Like MoSi2, SiC also forms a protective silicon dioxide (SiO2) layer. However, this layer tends to grow thicker over time. This gradual increase in thickness causes the element's electrical resistance to rise, a predictable aging process that must be managed by the power control system.
Metallic Alloys (e.g., Nichrome): The Common Standard
Metallic heating elements, such as those made from Nichrome (a nickel-chromium alloy), are standard in lower-temperature applications like ovens and toasters.
These alloys work by forming a protective layer of chromium oxide. This layer is very effective but has a lower maximum operating temperature compared to the SiO2 layers formed by MoSi2 and SiC.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing an element is rarely about a single property. You must balance performance against operating conditions and cost.
Temperature is the Deciding Factor
The single most important factor is your target operating temperature. MoSi2 excels above 1600°C, where its protective layer is most effective. SiC is a robust choice for the 800°C to 1600°C range. Metallic alloys are generally best for applications below 1250°C.
Atmospheric Sensitivity
The stability of the protective oxide layer is dependent on the furnace atmosphere. For instance, MoSi2 can be subject to a low-temperature degradation known as "pest" in certain conditions. It's critical to match the element to the chemical environment it will operate in.
Cost vs. Lifespan
MoSi2 elements often carry a higher initial cost. However, in the right high-temperature, oxidizing application, their extreme longevity and stable resistance can result in a lower total cost of ownership over the equipment's lifespan. SiC often represents a balanced middle ground in both cost and performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection should be guided by the specific demands of your heating process.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature and longevity in air: MoSi2 is the superior choice due to its self-healing and highly stable protective layer.
- If your primary focus is versatility across a wide range of high temperatures: SiC offers a robust and reliable solution, provided you account for its predictable aging characteristics.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness in lower-temperature applications (below 1250°C): Metallic elements like Nichrome provide excellent, economical performance.
By understanding how each material behaves under heat, you can select an element that ensures both reliability and long-term efficiency for your specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element | Oxidation Resistance | Key Advantage | Ideal Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Excellent | Self-healing SiO2 layer | Above 1600°C |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Good | Stable SiO2 layer, but ages | 800°C to 1600°C |
| Metallic Alloys (e.g., Nichrome) | Moderate | Chromium oxide layer | Below 1250°C |
Upgrade your lab's high-temperature capabilities with KINTEK's advanced heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems tailored to your unique needs. Our deep customization ensures precise performance for diverse laboratories. Contact us today to discuss how our heating elements can enhance your efficiency and longevity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















