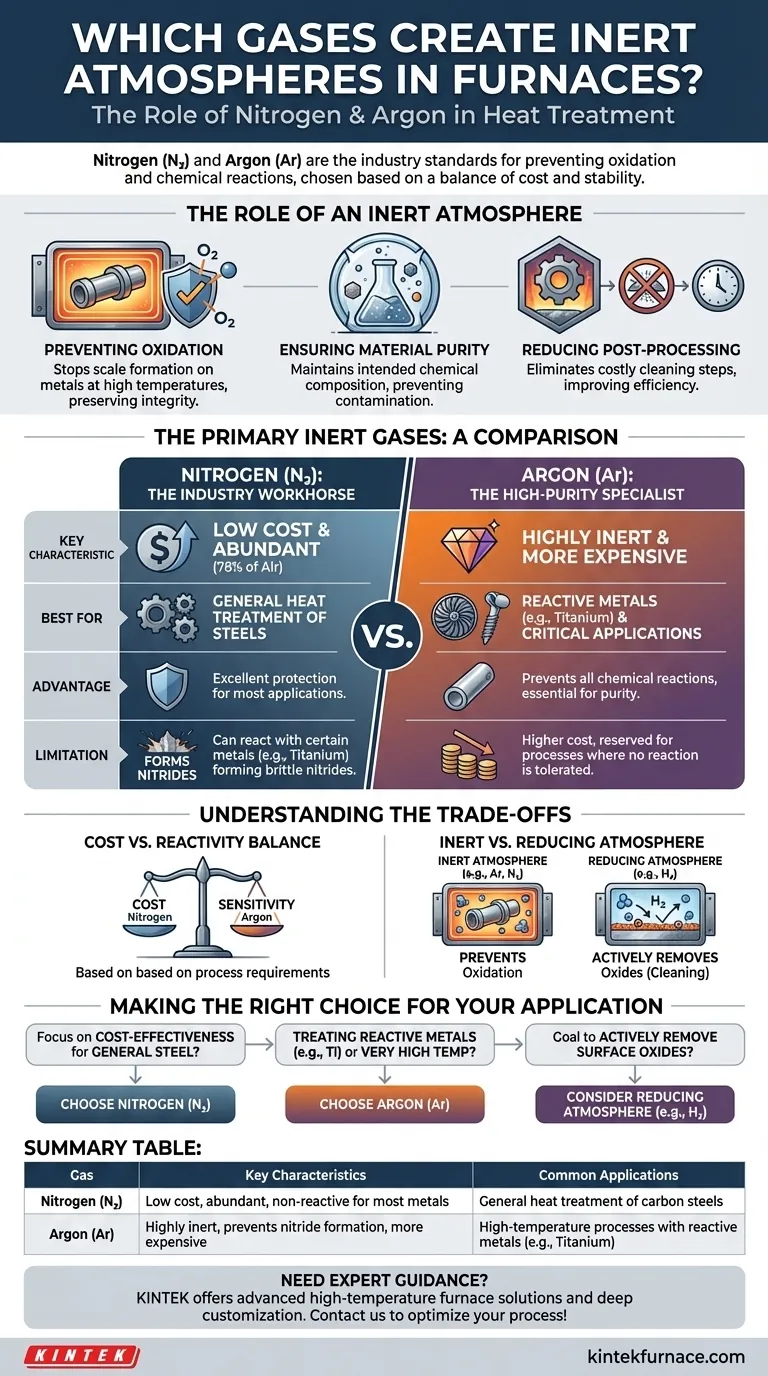
In short, the most common gases used to create inert atmospheres in furnaces are Nitrogen (N₂) and Argon (Ar). Their natural abundance and non-reactive properties make them the industry standards for protecting materials from oxidation and other chemical reactions during heat treatment processes.
The choice between an inert gas is not arbitrary; it's a critical decision based on a trade-off between cost and chemical stability. Nitrogen is the cost-effective workhorse for most applications, while Argon is the high-purity specialist reserved for processes where even the slightest reaction cannot be tolerated.

The Role of an Inert Atmosphere
An inert atmosphere is a controlled environment within a furnace that has been purged of oxygen and other reactive gases. This is fundamental to many modern manufacturing and heat-treating processes.
Preventing Oxidation
The primary goal of an inert atmosphere is to prevent oxidation. When metals are heated to high temperatures in the presence of oxygen, they rapidly form oxides on their surface, commonly known as scale. This scale can compromise the material's dimensions, finish, and structural integrity.
Ensuring Material Purity
Beyond preventing oxidation, an inert environment stops other unwanted chemical reactions. It ensures that the material being treated maintains its intended chemical composition and physical characteristics without being contaminated by atmospheric elements.
Reducing Post-Processing
By preventing scale formation, inert atmospheres significantly reduce or eliminate the need for costly and time-consuming post-processing steps like abrasive blasting or chemical cleaning to remove oxides. This leads to higher efficiency and a smaller environmental footprint.
The Primary Inert Gases: A Comparison
While several gases are inert, the choice for industrial furnaces almost always comes down to Nitrogen and Argon.
Nitrogen (N₂): The Industry Workhorse
Nitrogen is the most widely used inert gas for furnace atmospheres. Its primary advantage is its low cost, driven by its abundance—it makes up approximately 78% of the air we breathe.
For the vast majority of heat-treating applications, such as for carbon steels, Nitrogen provides excellent protection and is the default economic choice.
Argon (Ar): The High-Purity Specialist
Argon is significantly more inert than Nitrogen. While more expensive to produce, it is the required choice for high-temperature applications involving reactive metals like titanium, certain stainless steels, or refractory metals.
In these specific conditions, Nitrogen can actually react with the metal to form undesirable nitrides, which can make the material brittle. Argon does not have this limitation, making it essential for critical applications in aerospace, medical, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right gas requires balancing process requirements against budget. The wrong choice can either incur unnecessary costs or, worse, ruin the workpiece.
Cost vs. Reactivity
The decision is fundamentally a cost-benefit analysis. Is the added cost of Argon justified by the process's sensitivity? For general-purpose steel treatment, the answer is almost always no. For treating a high-value titanium component, the answer is almost always yes.
Considering Other Atmospheres
It is crucial to distinguish between an inert atmosphere and a reducing atmosphere. While both prevent oxidation, a reducing atmosphere goes a step further.
Gases like Hydrogen (H₂) are not inert; they are highly reactive. In a furnace, hydrogen actively strips oxygen atoms from existing oxides on the metal's surface, effectively cleaning it. These "reducing atmospheres" are used for specific applications like brazing or sintering where a chemically clean surface is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal determines the correct atmospheric gas. Use these guidelines to make an informed decision.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general heat treatment of steels: Your best choice is Nitrogen due to its low cost and sufficient inertness.
- If you are treating reactive metals (e.g., titanium) or working at very high temperatures: You must use Argon to prevent the formation of unwanted nitrides.
- If your goal is to actively remove surface oxides, not just prevent them: You should investigate a reducing atmosphere containing Hydrogen, which serves a different function than a purely inert gas.
Ultimately, selecting the right atmosphere is key to ensuring your material emerges from the furnace with the exact properties you intended.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Low cost, abundant, non-reactive for most metals | General heat treatment of carbon steels |
| Argon (Ar) | Highly inert, prevents nitride formation, more expensive | High-temperature processes with reactive metals like titanium |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right inert atmosphere for your furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to optimize your process and protect your materials effectively!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality



















