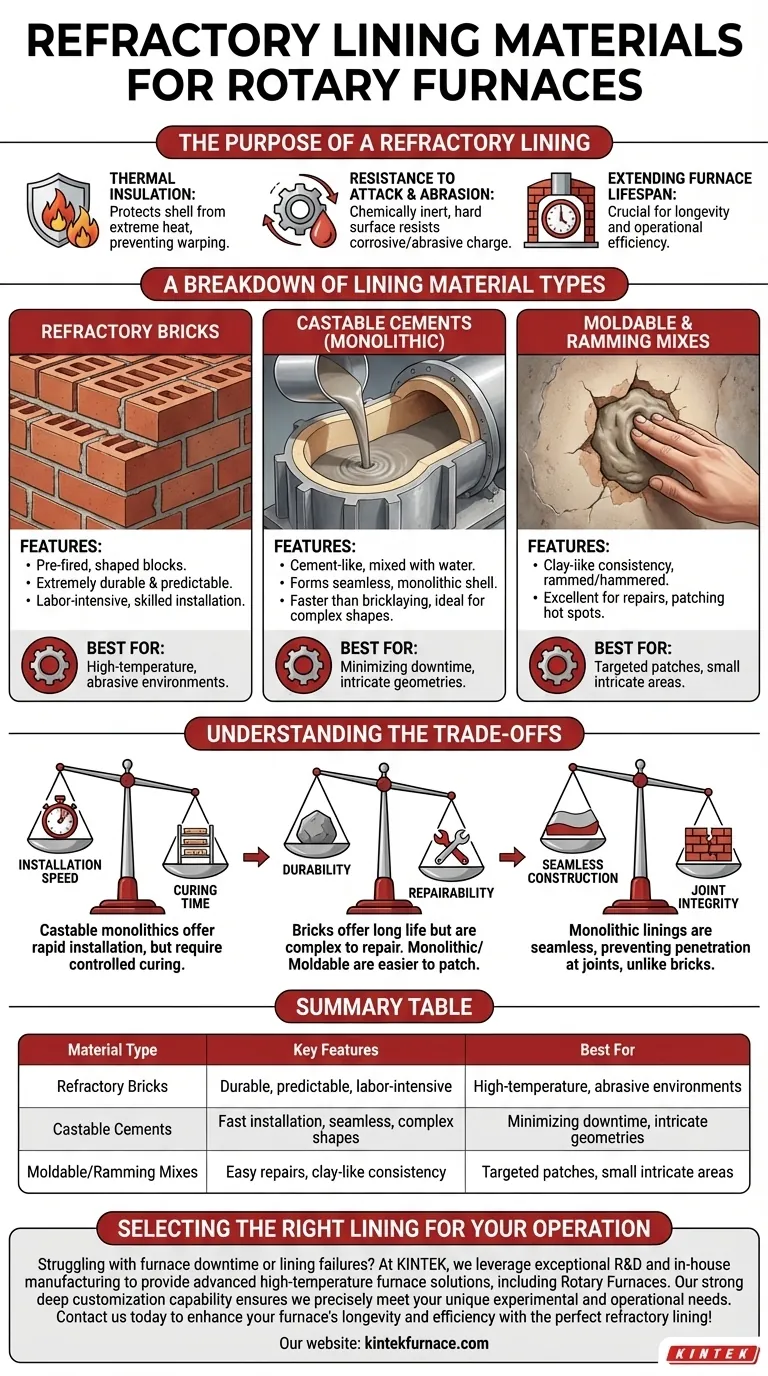
For a rotary furnace, the primary types of refractory linings are specially shaped bricks, castable (monolithic) cements, and moldable or ramming mixes. Each material serves the core purpose of protecting the furnace shell but offers a distinct profile in terms of installation complexity, durability, and application suitability.
The optimal refractory material is not a single "best" choice, but rather a strategic decision that balances the furnace's specific operating conditions—such as temperature, chemical exposure, and abrasion—against the cost and time of installation.

The Purpose of a Refractory Lining
A refractory lining is the critical barrier that protects the furnace's steel structure from the extreme conditions within. Without it, the furnace would fail rapidly.
Protection from Extreme Heat
The most fundamental role of the lining is thermal insulation. It keeps the intense heat generated during processing contained, preventing the structural shell of the furnace from overheating, warping, or melting.
Resistance to Chemical Attack and Abrasion
Materials processed in a rotary furnace, like iron ore pellets or cement clinker, can be highly abrasive and corrosive. The lining must be chemically inert and hard enough to resist being worn away by the tumbling action of the charge.
Extending Furnace Lifespan
By providing robust protection against thermal, chemical, and mechanical stress, a properly selected and installed refractory lining is the single most important factor in determining the longevity and operational efficiency of a rotary furnace.
A Breakdown of Lining Material Types
Choosing a material involves understanding the three main categories and their inherent strengths and weaknesses.
Refractory Bricks
Refractory bricks are pre-fired, shaped blocks that are installed individually with mortar to form a solid, interlocking lining. They are the traditional standard for many high-demand applications.
This method is known for creating an extremely durable and predictable lining. However, it is labor-intensive, requires highly skilled masons for proper installation, and can be time-consuming.
Castable Cements (Monolithic Linings)
Castable refractories are cement-like materials that are mixed with water and then pumped or cast into place inside the furnace, often using forms. Once cured and fired, they form a single, seamless, or monolithic shell.
This approach is much faster than bricklaying and is ideal for creating linings in furnaces with complex shapes. The absence of joints eliminates a common failure point seen in bricked linings.
Moldable and Ramming Mixes
These materials have a clay-like or putty-like consistency. They are rammed or hammered into place to form a dense patch or lining.
They are exceptionally useful for performing repairs on existing linings, especially for hot spots that have worn through. They are also used to line areas with intricate geometries like burner ports or tap holes where casting or bricking is impractical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision to use one material over another is always a matter of balancing competing priorities. No single option is perfect for every scenario.
Installation Speed vs. Curing Time
Castable monolithics offer a significant advantage in rapid installation, drastically reducing furnace downtime compared to bricking. However, they require a carefully controlled drying and curing schedule to drive out moisture and prevent cracking.
Durability vs. Repairability
Brick linings, when installed correctly, often provide the longest service life in high-wear environments. However, repairing a small section of a brick lining can be a complex task. Monolithic linings and moldable mixes are generally easier and faster to patch.
Seamless Construction vs. Joint Integrity
A key advantage of a castable monolithic lining is its seamless nature. This prevents molten material or gases from penetrating joints, which is a common point of failure in brick linings. The integrity of a brick lining depends heavily on the quality of the mortar and the skill of the installer.
Selecting the Right Lining for Your Operation
Your final choice should be guided by your primary operational goal, budget, and the specific material being processed in your furnace.
- If your primary focus is maximum service life and predictable wear in a high-temperature, abrasive environment: Refractory bricks are the most reliable choice, provided you can accommodate the higher installation time and cost.
- If your primary focus is minimizing downtime and accommodating complex furnace geometry: Castable cements provide a fast, flexible, and seamless monolithic lining.
- If your primary focus is targeted repairs or lining small, intricate areas: Moldable plastics and ramming mixes offer the best solution for patching and specialized applications.
Understanding these material profiles empowers you to make an informed engineering decision that optimizes both furnace performance and your operational budget.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Refractory Bricks | Durable, predictable, labor-intensive | High-temperature, abrasive environments |
| Castable Cements | Fast installation, seamless, complex shapes | Minimizing downtime, intricate geometries |
| Moldable/Ramming Mixes | Easy repairs, clay-like consistency | Targeted patches, small intricate areas |
Struggling with furnace downtime or lining failures? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental and operational needs. Contact us today to enhance your furnace's longevity and efficiency with the perfect refractory lining!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating



















