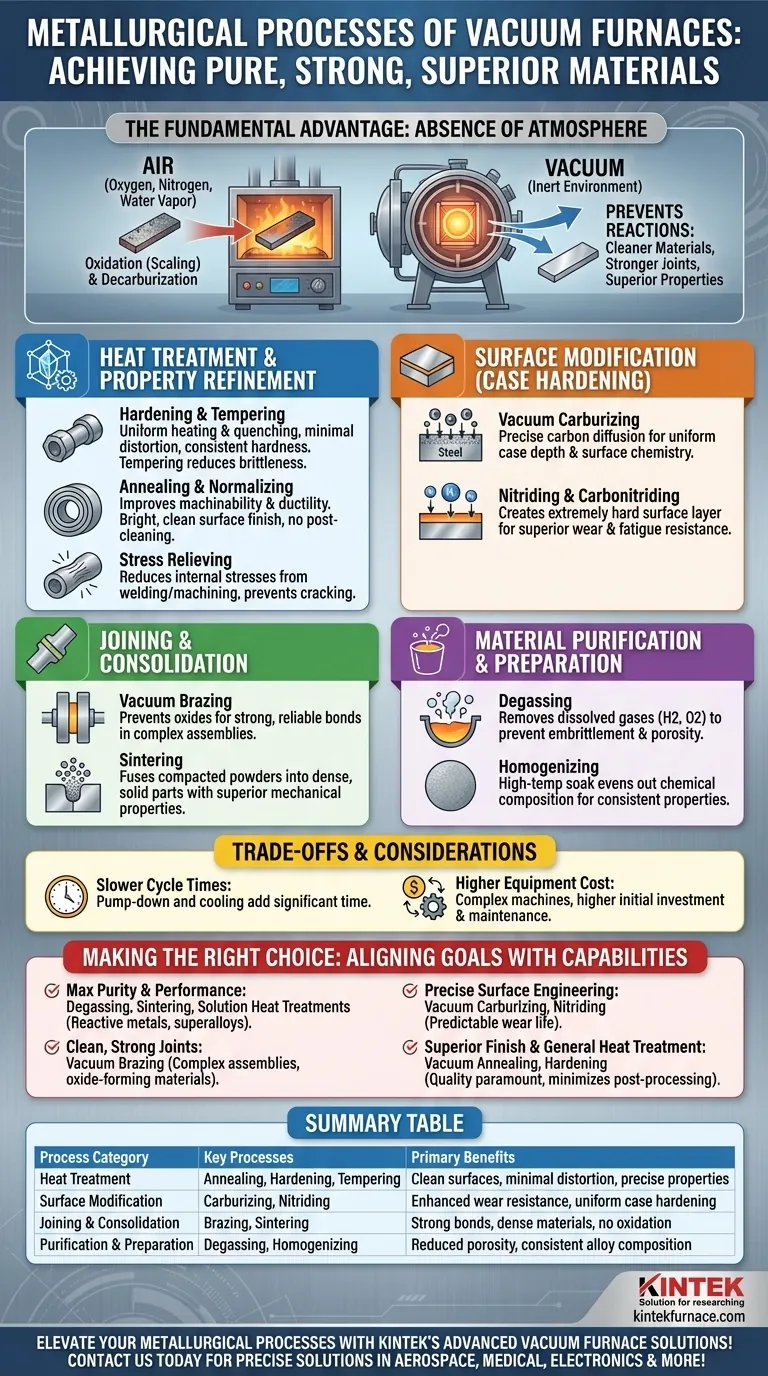
In short, vacuum furnaces excel at a wide range of metallurgical processes where atmospheric contamination must be eliminated. They are used for heat treatments like annealing and hardening, joining processes like brazing, powder metallurgy through sintering, and surface modification techniques such as carburizing and nitriding, all performed in a controlled, oxygen-free environment.
The true value of a vacuum furnace is not the heat, but the absence of atmosphere. By removing reactive gases, it allows for metallurgical processes that result in cleaner materials, stronger joints, and superior mechanical properties that are impossible to achieve in open air.

The Fundamental Advantage of a Vacuum Environment
A standard furnace heats metal in the presence of air, which is rich in oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor. At high temperatures, these gases react with the metal's surface, causing undesirable effects like oxidation (scaling) and decarburization, which can degrade the material's properties.
A vacuum furnace solves this by first pumping out nearly all of the atmosphere. This creates an inert environment that prevents these unwanted reactions. This control is the reason vacuum furnaces are critical in industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics, where material integrity is non-negotiable.
A Breakdown of Key Vacuum Furnace Processes
The list of processes a vacuum furnace can perform is extensive. They can be grouped into a few key functional categories.
Heat Treatment and Property Refinement
These processes alter a material's internal crystalline structure to achieve specific mechanical properties like hardness, ductility, or toughness.
- Hardening & Tempering: A vacuum ensures parts are heated and quenched uniformly without any surface scaling, resulting in consistent hardness and minimal distortion. Tempering reduces the brittleness of the hardened part.
- Annealing & Normalizing: These softening processes improve a material's machinability and ductility. The vacuum environment guarantees a bright, clean surface finish, eliminating the need for post-process cleaning.
- Stress Relieving: This low-temperature process reduces internal stresses caused by manufacturing processes like welding or machining, preventing future cracking or distortion.
Surface Modification (Case Hardening)
These processes modify the chemistry of only the part's surface to create a hard, wear-resistant outer layer while maintaining a softer, tougher core.
- Vacuum Carburizing: After creating a perfect vacuum, a precise amount of a hydrocarbon gas is introduced. This allows carbon to diffuse into the steel's surface with exceptional uniformity and control.
- Nitriding & Carbonitriding: Similar to carburizing, these processes use nitrogen (or a mix of nitrogen and carbon) to create an extremely hard surface case, greatly improving wear and fatigue resistance. The vacuum ensures the base metal is perfectly clean for the reaction to occur.
Joining and Consolidation
A vacuum environment is ideal for creating flawless bonds between materials.
- Vacuum Brazing: Brazing uses a filler metal to join two components. A vacuum prevents the formation of oxides on the joint surfaces, which would otherwise inhibit the filler metal from wetting and flowing, resulting in a significantly stronger and more reliable bond.
- Sintering: Used in powder metallurgy, sintering heats compacted metal powders to just below their melting point. The vacuum prevents oxidation and pulls out trapped gases, allowing the particles to fuse into a dense, solid object with superior mechanical properties.
Material Purification and Preparation
The vacuum itself can be used as a processing tool to refine materials.
- Degassing: A vacuum can literally pull dissolved gases, like hydrogen and oxygen, out of a molten or solid metal. This is critical for preventing embrittlement and porosity in sensitive alloys like titanium.
- Homogenizing: This high-temperature soak evens out the chemical composition of an alloy, ensuring its properties are consistent throughout the entire part.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Cycle Time and Throughput
Vacuum processes are inherently slower than their atmospheric counterparts. The time required to pump the chamber down to the required vacuum level and to backfill it with inert gas for cooling adds significant time to each cycle.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are complex machines involving pumps, seals, and sophisticated control systems. This results in a higher initial investment and more demanding maintenance requirements compared to conventional furnaces.
Process Suitability
For many low-carbon steels or applications where a scaled surface is acceptable or will be machined off anyway, the expense of a vacuum furnace is unnecessary. The choice depends entirely on the material and the final performance requirements of the component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct process requires aligning the capabilities of a vacuum furnace with your specific metallurgical objective.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material purity and performance: Vacuum degassing, sintering, and solution heat treatments are essential for reactive metals and superalloys used in critical applications.
- If your primary focus is creating clean, strong joints: Vacuum brazing is the superior choice over atmospheric methods, especially for complex assemblies or oxide-forming materials.
- If your primary focus is precise surface engineering: Vacuum carburizing and nitriding offer unparalleled control over case depth and surface chemistry, leading to highly predictable and reliable component wear life.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment with a superior finish: Vacuum annealing or hardening eliminates post-processing cleaning and minimizes distortion, justifying the cost when component quality is paramount.
Ultimately, employing a vacuum furnace is a decision to prioritize material integrity and performance above all else.
Summary Table:
| Process Category | Key Processes | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering | Clean surfaces, minimal distortion, precise properties |
| Surface Modification | Carburizing, Nitriding | Enhanced wear resistance, uniform case hardening |
| Joining & Consolidation | Brazing, Sintering | Strong bonds, dense materials, no oxidation |
| Purification & Preparation | Degassing, Homogenizing | Reduced porosity, consistent alloy composition |
Elevate your metallurgical processes with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, delivering cleaner materials, stronger joints, and superior mechanical properties. Don't compromise on quality—contact us today to discuss how our expertise can benefit your specific applications in aerospace, medical, electronics, and more!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















