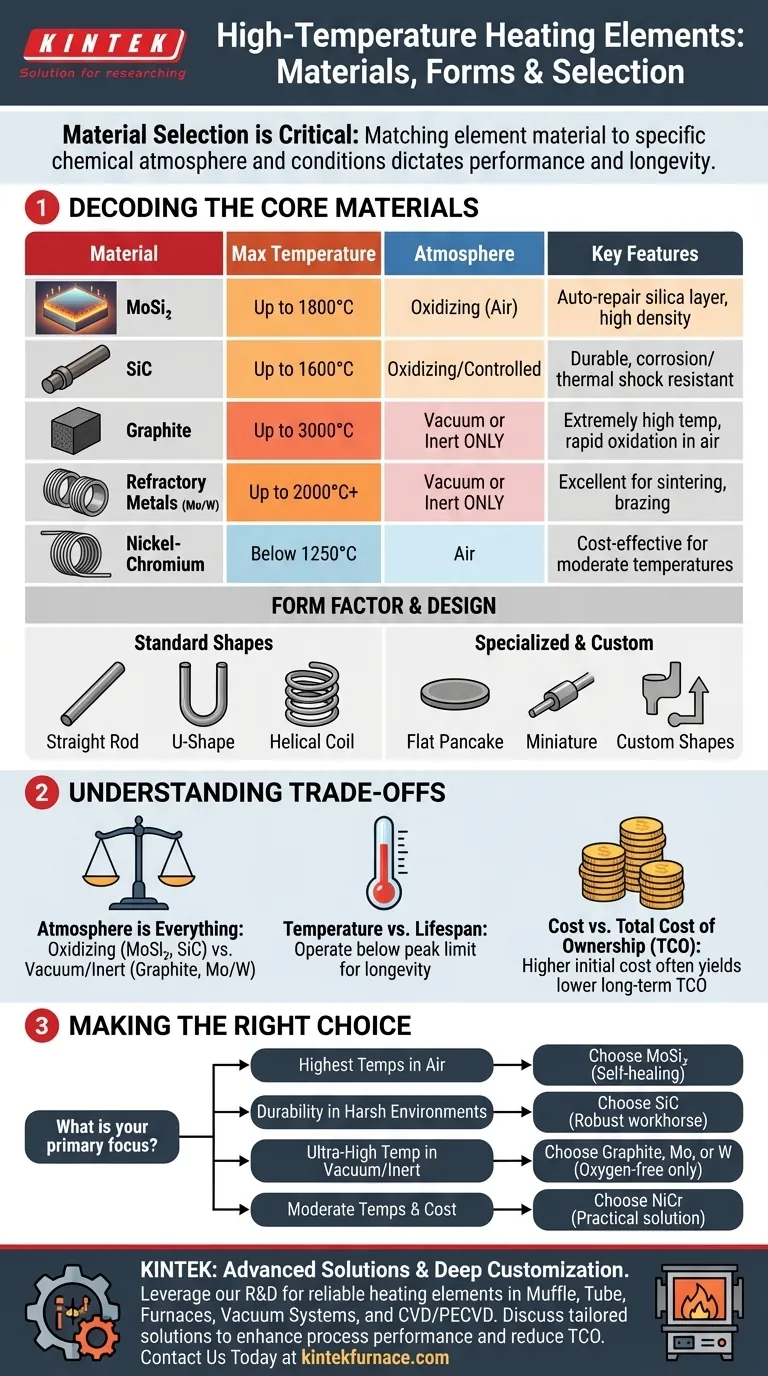
For high-temperature applications, you are primarily choosing between advanced ceramic materials like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) and Silicon Carbide (SiC), or refractory materials like graphite, molybdenum, and tungsten. While available in various forms—such as straight rods, bent elements, coils, and custom shapes—the material itself is the most critical factor dictating performance, temperature limits, and atmospheric compatibility.
The selection of a high-temperature heating element is not just about its shape or maximum temperature rating. The most crucial decision involves matching the element's material to the specific chemical atmosphere and conditions of your process to ensure reliability, longevity, and efficiency.

Decoding the Core Materials
The material of a heating element defines its capabilities. Each option is engineered for a different set of operating conditions, particularly the presence or absence of oxygen at high temperatures.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂)
MoSi₂ elements are a top-tier choice for extremely high temperatures in oxidizing (air-filled) atmospheres. They are known for their high density and excellent electrical conductivity.
Their standout feature is an "auto-repair" function. At high temperatures, MoSi₂ forms a protective layer of silica glass on its surface, which seals cracks and prevents further oxidation, significantly extending its service life.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
SiC is a highly versatile and robust material, often considered an industrial workhorse. It offers exceptional durability, high thermal efficiency, and strong resistance to corrosion and thermal shock.
These elements are ideal for a wide range of industrial applications in harsh environments where consistency and reliability are paramount. They perform well in air and various controlled atmospheres.
Graphite
Graphite elements are capable of reaching exceptionally high temperatures, but they have one critical limitation: they must be used in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere.
In the presence of oxygen at high temperatures, graphite will rapidly oxidize and fail. It is a leading choice for vacuum furnaces used in processes like sintering, hardening, and brazing.
Refractory Metals (Molybdenum & Tungsten)
Like graphite, pure molybdenum and tungsten elements are reserved for vacuum or controlled atmosphere furnaces. They offer excellent performance for high-temperature processes such as metal injection molding (MIM), sintering, and specific types of brazing.
Their use is dictated by the need to avoid reaction with air at their operating temperatures.
Metallic Alloys (Nickel-Chromium)
While common, alloys like nickel-chromium (NiCr) are generally considered for lower-temperature applications, typically below 1250°C. They are often used for processes like aluminum brazing or tempering where extreme temperatures are not required.
Form Factor and System Design
Beyond the material, the physical shape of the element is designed to optimize heat transfer for a specific furnace or process.
Standard Element Shapes
Common shapes include straight rods, U-shaped or W-shaped bent elements, and helical coils. These standard designs offer broad compatibility with many existing furnace types and are often easier to replace.
Specialized and Custom Forms
For unique equipment or processes, elements can be made in specialized forms like flat "pancake" heaters or miniature "microheaters."
Furthermore, manufacturers can create entirely custom-shaped heaters. This allows for precise engineering to maximize thermal uniformity and efficiency, enhancing the overall productivity of the system.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong element for your environment is the most common and costly mistake. The decision hinges on balancing performance needs with operational realities.
Atmosphere is Everything
This is the most critical factor. MoSi₂ and SiC are designed to thrive in oxidizing atmospheres because they form a protective oxide layer. In contrast, Graphite, Molybdenum, and Tungsten will be destroyed by oxygen at high temperatures and must operate in a vacuum or inert environment.
Temperature vs. Lifespan
Every heating element has a maximum recommended operating temperature. Consistently running an element at its absolute peak limit will shorten its service life. Operating slightly below this limit can often dramatically increase its longevity and reliability.
Cost vs. Total Cost of Ownership
Advanced ceramics like MoSi₂ and SiC may have a higher initial purchase price. However, their long service life, energy efficiency, and low maintenance in the correct applications often result in a lower total cost of ownership compared to cheaper elements that require frequent replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal and operating environment should be your definitive guide.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible temperatures in an air atmosphere: MoSi₂ is the superior choice due to its self-healing protective layer and outstanding performance.
- If your primary focus is durability and reliable performance in a harsh or corrosive environment: SiC is an excellent all-around workhorse known for its robustness and consistency.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperature processing in a vacuum or inert gas: Graphite, Molybdenum, or Tungsten are the correct materials, as they are engineered specifically for oxygen-free environments.
- If your primary focus is moderate temperatures (below 1250°C) and cost efficiency: Nickel-Chromium alloys provide a practical and reliable solution for less demanding applications.
Ultimately, aligning the heating element's material properties with your specific process environment is the key to achieving efficient, reliable, and consistent thermal performance.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Atmosphere Compatibility | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| MoSi₂ | Up to 1800°C | Oxidizing (air) | Auto-repair silica layer, high density |
| SiC | Up to 1600°C | Oxidizing and controlled | Durable, corrosion-resistant, thermal shock resistant |
| Graphite | Up to 3000°C | Vacuum or inert | High temperature, rapid oxidation in air |
| Molybdenum/Tungsten | Up to 2000°C+ | Vacuum or inert | Excellent for sintering, brazing |
| Nickel-Chromium | Below 1250°C | Air | Cost-effective for moderate temperatures |
Struggling to select the right heating element for your high-temperature needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, ensuring reliability and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored heating elements can enhance your process performance and reduce total cost of ownership!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion



















