At its core, a vacuum furnace is capable of executing a wide range of heat treatment processes, including annealing, tempering, hardening, quenching, brazing, and sintering. Specialized processes like vacuum carburizing and nitriding are also common. The primary advantage of using a vacuum is not the heat itself, but the creation of a highly controlled, active-gas-free environment that prevents surface reactions like oxidation.
A vacuum furnace should be viewed less as an oven and more as a sophisticated environmental chamber. Its true value lies in protecting the material's surface integrity and enabling metallurgical processes that are difficult or impossible to achieve in the presence of air.
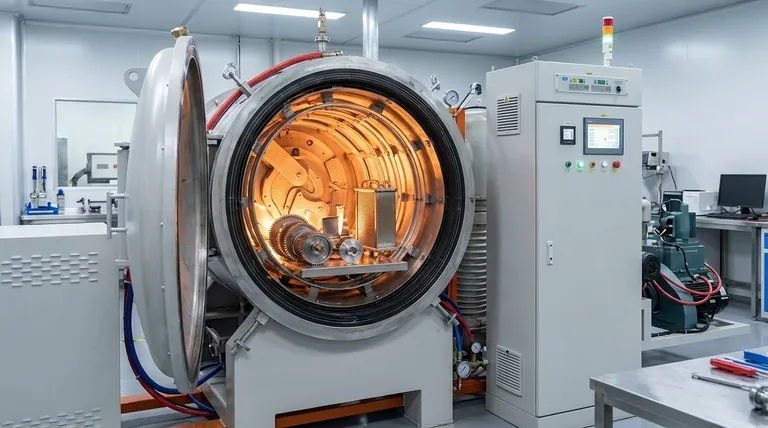

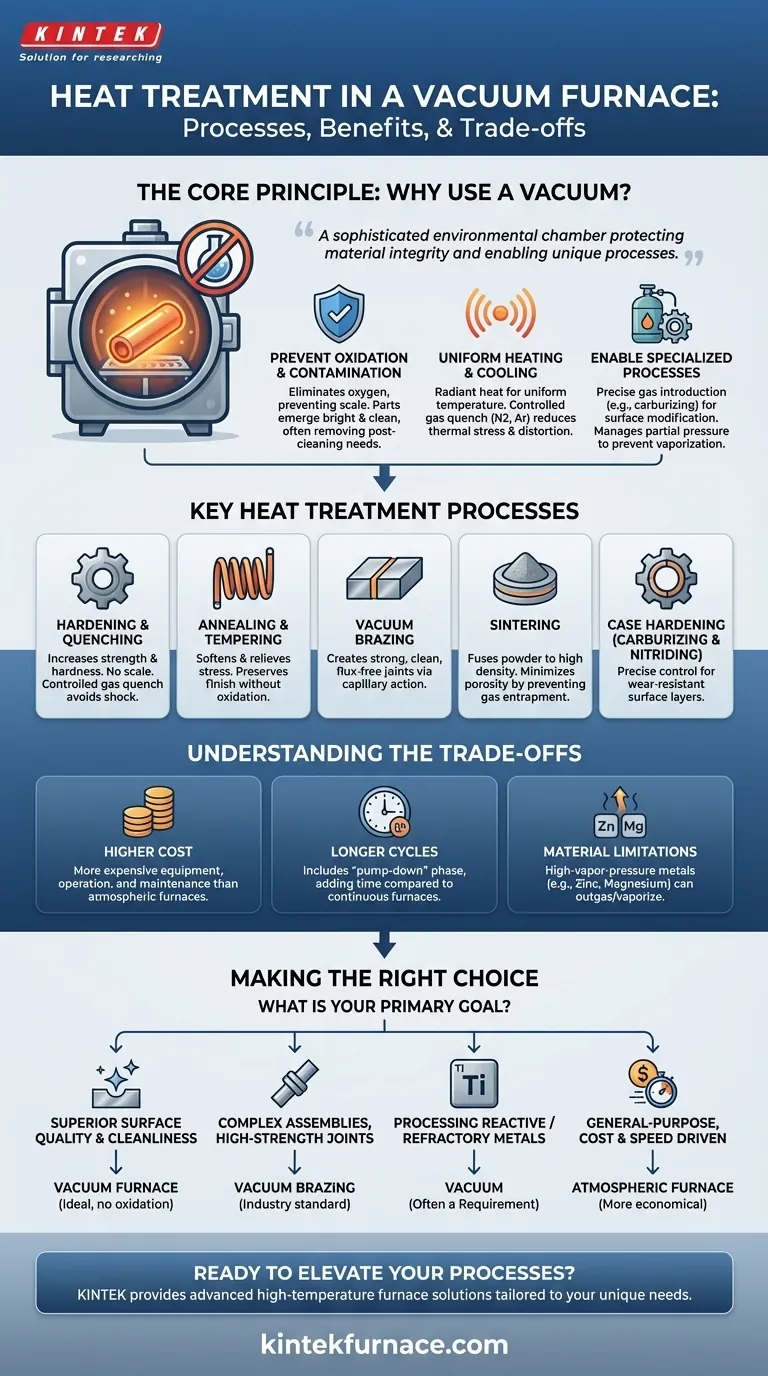
The Core Principle: Why Use a Vacuum?
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven by the need for absolute control over the component's environment during heating and cooling. Removing air and its reactive gases is the key to unlocking superior material properties.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
The most fundamental benefit of a vacuum is the removal of oxygen. At high temperatures, most metals will readily react with oxygen to form a surface layer of oxide, or scale.
A vacuum environment eliminates this reaction, resulting in parts that emerge from the furnace bright, clean, and with their original surface finish intact. This often eliminates the need for post-treatment cleaning or machining.
Achieving Uniform Heating and Cooling
In a vacuum, heat is transferred primarily through radiation. This allows for extremely uniform heating, even for parts with complex geometries, reducing the risk of thermal stress and distortion.
Similarly, gas quenching—rapidly backfilling the chamber with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon—provides controlled and uniform cooling, which is critical for hardening processes.
Enabling Specialized Processes
A vacuum creates a clean slate. This allows for the precise introduction of specific gases for surface modification. Processes like vacuum carburizing use this to introduce carbon in a highly controlled manner, creating a hard, wear-resistant surface layer.
It also allows for managing the partial pressure to prevent elements within the alloy, like chromium in steel, from vaporizing off the surface at high temperatures.
Key Heat Treatment Processes in a Vacuum
While many processes are possible, a vacuum furnace excels in applications where surface quality, joint integrity, and material purity are paramount.
Hardening and Quenching
This process increases a metal's hardness and strength. Vacuum hardening ensures the part is heated uniformly without forming surface scale, and the subsequent controlled gas quench achieves the desired metallurgical structure without the shock and distortion associated with oil or water quenching.
Annealing and Tempering
Annealing softens metals and relieves internal stresses, while tempering reduces the brittleness that can result from hardening. In a vacuum, these often lengthy processes can be performed without any risk of surface oxidation, preserving the component's dimensional accuracy and finish.
Vacuum Brazing
This is a premier application for vacuum furnaces. Brazing joins two components using a filler metal. In a vacuum, the absence of oxides allows the molten braze alloy to wet the parent materials perfectly.
The vacuum also helps pull the alloy deep into the joint via capillary action, creating an exceptionally strong, clean, and void-free bond without the need for corrosive fluxes.
Sintering
Sintering is the process of fusing powdered materials (often metals or ceramics) into a solid, high-density component by applying heat below the melting point. A vacuum is ideal for sintering because it prevents gas entrapment within the part, minimizing porosity and maximizing final density and strength.
Case Hardening (Carburizing & Nitriding)
These processes introduce carbon or nitrogen into a steel's surface to create a hard "case." Vacuum carburizing and nitriding offer unparalleled control over the depth and concentration of this hardened layer, resulting in superior wear resistance and fatigue life.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A vacuum furnace is a powerful tool, but it is not always the right choice. Understanding its limitations is critical for making sound engineering decisions.
Higher Equipment and Operational Cost
Vacuum furnaces are complex systems involving vacuum pumps, sophisticated controls, and robust chamber construction. This makes them significantly more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than standard atmospheric furnaces.
Longer Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum requires a "pump-down" phase, which adds time to the overall process cycle. For high-volume, low-margin parts, this can be a significant drawback compared to the speed of a continuous belt furnace in an open atmosphere.
Material Limitations
High-vapor-pressure metals like zinc, magnesium, lead, and cadmium can "outgas" or vaporize in a high vacuum. This can not only deplete the element from the part but also contaminate the furnace interior, affecting future cycles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heat treatment method depends entirely on the technical requirements and economic constraints of your project.
- If your primary focus is superior surface quality and cleanliness: A vacuum furnace is the ideal choice, as it prevents oxidation and eliminates the need for post-process cleaning.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies with high-strength joints: Vacuum brazing is the industry standard for creating clean, strong, and flux-free joints, especially in aerospace and medical applications.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals like titanium or refractory metals: A vacuum is not just beneficial, it is often a requirement to prevent catastrophic contamination.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment with cost as the main driver: A traditional atmospheric furnace may be a more economical and faster solution, provided some surface oxidation is acceptable.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is an investment in control, cleanliness, and the final quality of your component.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening & Quenching | Uniform heating, no surface scale, controlled gas quench | Tool steels, automotive parts |
| Annealing & Tempering | Stress relief, no oxidation, preserved finish | Aerospace components, precision instruments |
| Vacuum Brazing | Strong, flux-free joints, capillary action | Medical devices, aerospace assemblies |
| Sintering | High density, minimal porosity, no gas entrapment | Powdered metals, ceramics |
| Case Hardening (Carburizing/Nitriding) | Controlled depth, superior wear resistance | Gears, bearings, industrial machinery |
Ready to elevate your heat treatment processes with precision and reliability? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, or industrial sectors, our vacuum furnaces ensure superior surface quality, contamination-free environments, and enhanced material properties. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your laboratory's efficiency and achieve your specific experimental goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance



















