Vacuum furnaces are used for nearly every major category of heat treatment, including annealing, hardening, tempering, brazing, and sintering. The defining feature is not the specific thermal cycle, but the controlled, contamination-free environment that a vacuum provides. This allows for superior metallurgical properties, a clean surface finish, and minimal distortion, which are unattainable in traditional atmospheric furnaces.
The crucial insight is not which processes can be done in a vacuum, but why they are performed there. Using a vacuum furnace is a deliberate choice to eliminate atmospheric variables, granting precise control over the material's final properties and achieving a level of quality that justifies the investment.
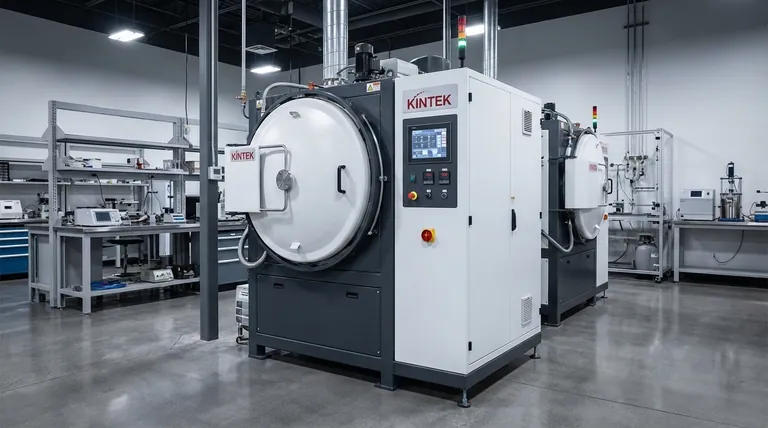

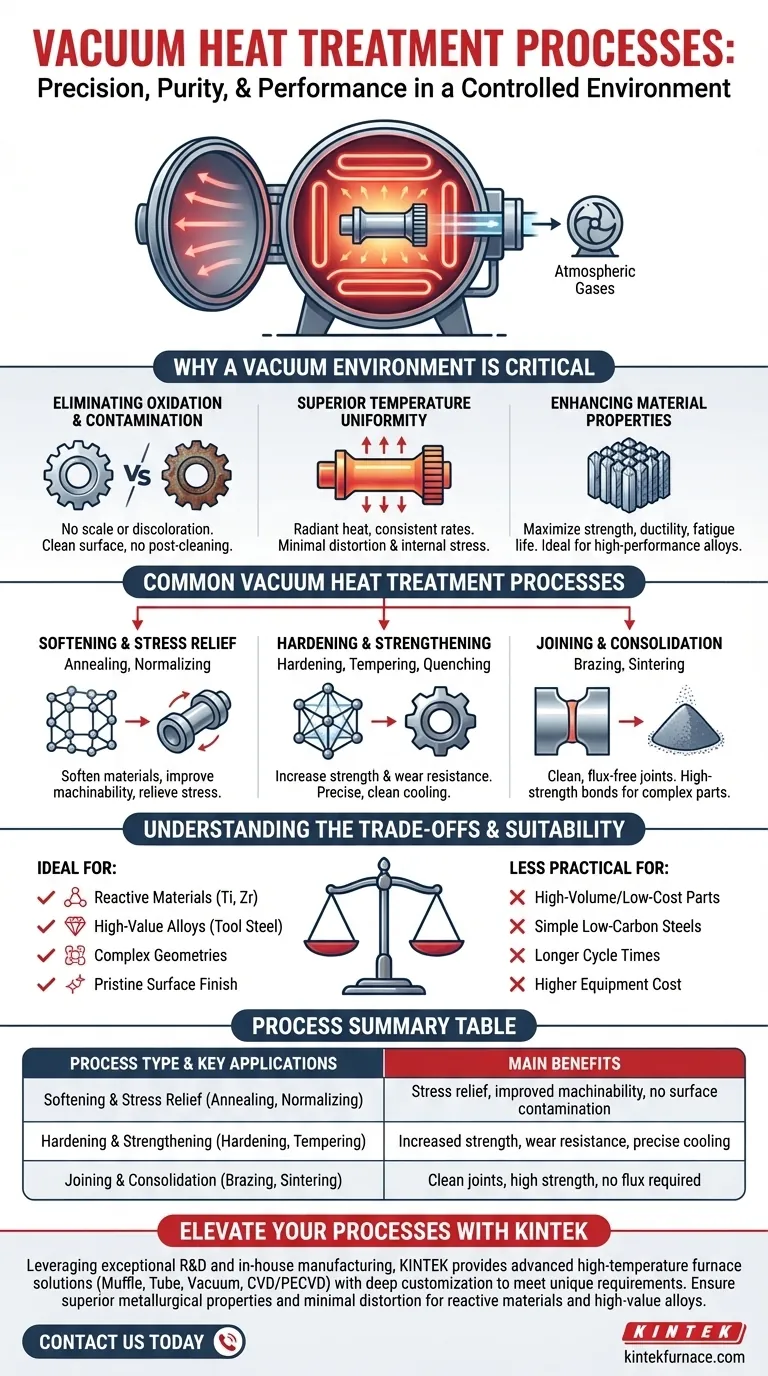
Why a Vacuum Environment is Critical
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven by the need for absolute control. By removing atmospheric gases, you fundamentally change how heat interacts with the material, leading to superior and more repeatable results.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
In a traditional furnace, ambient air—primarily nitrogen and oxygen—reacts with the hot metal surface. This causes oxidation (scale), discoloration, and potentially decarburization, which degrades the surface properties of the component.
A vacuum removes these reactive gases. This ensures parts emerge from the furnace with a clean, bright, and unaltered surface, eliminating the need for post-process cleaning or machining.
Achieving Superior Temperature Uniformity
Vacuum furnaces heat parts primarily through radiation, not convection. This radiant heat transfer is inherently more uniform, ensuring that the entire part, regardless of its complexity, heats and cools at a consistent rate.
This uniformity minimizes thermal gradients within the material, which are the primary cause of distortion and internal stress. The result is a more dimensionally stable and reliable component.
Enhancing Material Properties
By preventing surface reactions and ensuring uniform heating, vacuum treatment allows materials to achieve their full theoretical potential. This translates to measurable improvements in strength, ductility, fatigue life, and overall performance, especially in high-performance alloys like tool steels, superalloys, and titanium.
Common Vacuum Heat Treatment Processes
While the environment is the key, vacuum furnaces are designed to execute specific thermal profiles to achieve different metallurgical goals.
Softening and Stress Relief
Processes like vacuum annealing, normalizing, and stress relieving are designed to soften materials, improve machinability, and relieve internal stresses built up during manufacturing. The vacuum prevents any surface contamination during these often lengthy high-temperature soaks.
Hardening and Strengthening
This category includes vacuum hardening (quenching), tempering, precipitation hardening, and solutionizing and aging. These processes are used to increase the strength and wear resistance of materials. Vacuum quenching, often using high-pressure inert gas, provides precise and repeatable cooling rates without the risk of oxidation associated with oil or water quenches.
Joining and Consolidation
Vacuum brazing uses a filler metal to join two components without melting the base materials. The vacuum environment is essential because it allows the braze alloy to flow freely without the use of corrosive fluxes, creating exceptionally strong, clean, and hermetic joints.
Vacuum sintering is a process used to consolidate metal powders into a solid mass. Heating the compacted powder in a vacuum removes binders and creates strong metallurgical bonds between particles, forming a dense, high-strength component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its advantages, vacuum heat treatment is not the universal solution. It involves specific considerations that make it ideal for some applications but less practical for others.
Process Time and Throughput
Vacuum furnace cycles are inherently longer than atmospheric ones due to the time required to pump down the chamber to the required vacuum level and to perform controlled backfill cooling. This often makes vacuum processing less suitable for high-volume, low-cost parts where throughput is the primary driver.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment. They are complex systems that require specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance, including vacuum pumps, control systems, and chamber integrity checks.
Material Suitability
The benefits of vacuum treatment are most pronounced for reactive materials (like titanium and zirconium), high-value alloys (like tool steels and nickel-based superalloys), and components where a pristine surface and minimal distortion are non-negotiable. For simple, low-carbon steels, a traditional atmospheric furnace is often more cost-effective.
Matching the Process to Your Application
Choosing the right technology requires a clear understanding of your end goal. The material, component complexity, and required performance dictate the optimal approach.
- If your primary focus is a flawless surface finish and material purity: Vacuum annealing or brazing is ideal, as it completely prevents surface oxidation.
- If your primary focus is maximizing strength and minimizing distortion: Vacuum hardening and tempering provide the precise thermal control needed for high-performance alloys and complex geometries.
- If your primary focus is joining critical assemblies without flux: Vacuum brazing creates clean, high-integrity joints that are otherwise impossible to achieve.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production of simple parts: Traditional atmospheric heat treatment may be a more suitable and economical choice.
Ultimately, selecting the right heat treatment is about aligning the process capabilities with the non-negotiable properties your final component requires.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Key Applications | Main Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Softening & Stress Relief | Annealing, Normalizing | Stress relief, improved machinability, no surface contamination |
| Hardening & Strengthening | Hardening, Tempering | Increased strength, wear resistance, precise cooling |
| Joining & Consolidation | Brazing, Sintering | Clean joints, high strength, no flux required |
Ready to elevate your heat treatment processes with precision and reliability? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with reactive materials, high-value alloys, or need contamination-free results, KINTEK's expertise ensures superior metallurgical properties and minimal distortion. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your applications and deliver unmatched quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















