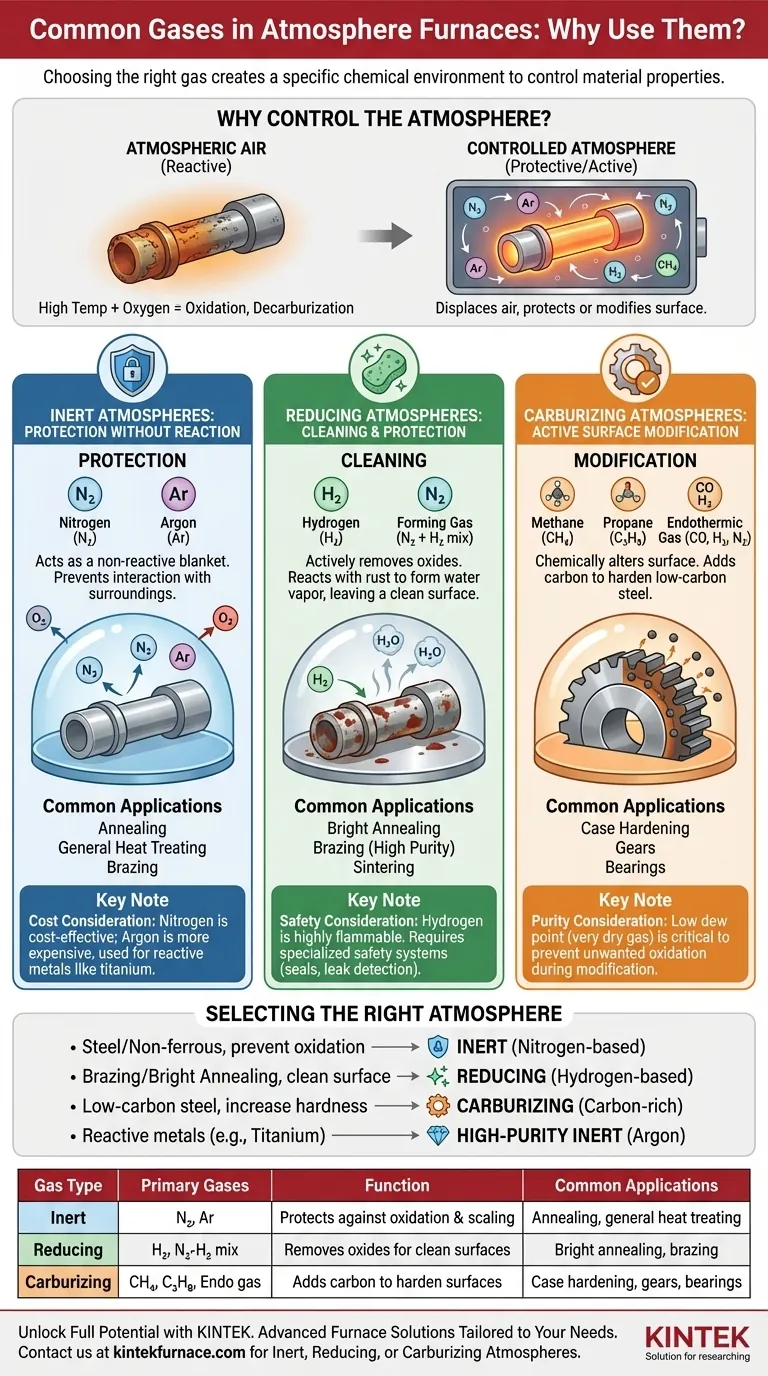
The primary gases used in atmosphere furnaces are nitrogen, argon, hydrogen, and carbon-based gases like methane or propane. These gases are not interchangeable; they are chosen to create a specific chemical environment at high temperatures. The selection of a gas determines whether the furnace atmosphere is inert (protective), reducing (cleaning), or carburizing (surface-modifying), directly controlling the final properties of the material being treated.
Choosing an atmosphere gas is not merely a protective measure; it is a fundamental process variable that directly controls whether a material's surface remains unchanged, is cleaned of oxides, or is chemically altered to enhance its properties.
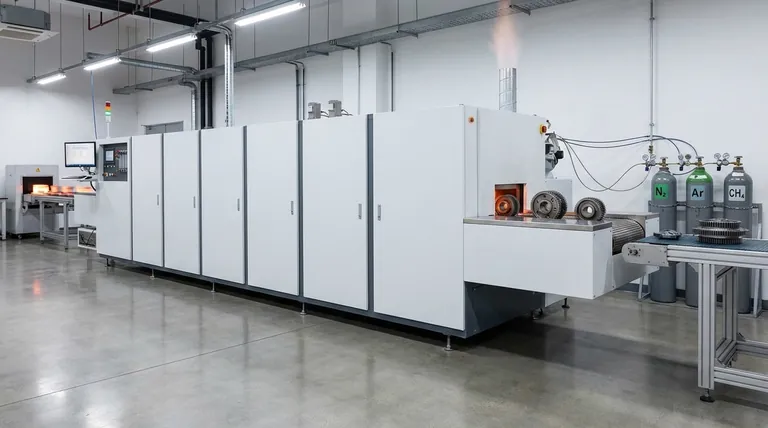

The Purpose of a Controlled Atmosphere
Why Not Just Use Air?
At room temperature, the oxygen in the air is relatively benign. At the high temperatures required for heat treatment, however, oxygen becomes highly reactive.
Exposing hot metal to ambient air leads to rapid oxidation (scaling), decarburization (loss of carbon and hardness in steel), and other unwanted chemical reactions that degrade the material's surface and structural integrity.
The Goal: Process Integrity
A controlled furnace atmosphere displaces the ambient air with a specific gas or gas mixture. This ensures the material is only exposed to a known, non-detrimental environment.
The goal is to protect the part during processes like annealing, brazing, sintering, and hardening, ensuring it emerges with the precise surface finish and mechanical properties intended by the design.
Classifying Furnace Atmospheres by Function
The most effective way to understand furnace gases is by the function they perform. The atmosphere can be categorized into three main types.
Inert Atmospheres: Protection Without Reaction
An inert atmosphere is designed to be non-reactive, acting as a protective blanket that prevents the material from interacting with its surroundings.
The primary gases used are Nitrogen (N₂) and Argon (Ar). They work by physically displacing oxygen.
This is the most common type of atmosphere, used for general-purpose heat treating, annealing, and brazing where the main goal is simply to prevent scaling and oxidation.
Reducing Atmospheres: Cleaning and Protection
A reducing atmosphere goes a step further than an inert one. It not only prevents new oxidation but also actively removes existing oxides from the material's surface.
The key gas for this is Hydrogen (H₂). At high temperatures, hydrogen reacts with metal oxides (like iron oxide or rust) to form water vapor, which is then purged from the furnace, leaving a clean, bright metal surface.
These atmospheres, often a mix of nitrogen and hydrogen called "forming gas," are essential for applications like bright annealing of stainless steel and high-purity copper brazing, where a pristine surface is critical.
Carburizing Atmospheres: Active Surface Modification
This type of atmosphere is intentionally reactive. Its purpose is to chemically alter the surface of the material, specifically by adding carbon to it.
The gases used are rich in carbon, such as Methane (CH₄), Propane (C₃H₈), or a generated mixture known as endothermic gas (CO, H₂, N₂).
This process, known as carburizing or case hardening, is used on low-carbon steels to create a very hard, wear-resistant surface layer while maintaining a softer, tougher core. It is fundamental for manufacturing parts like gears and bearings.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Choosing the right gas involves balancing performance, cost, and safety.
Cost: Nitrogen vs. Argon
Nitrogen is the workhorse of inert atmospheres because it is abundant and relatively inexpensive to produce.
Argon is significantly more expensive. Its use is reserved for materials that can react with nitrogen at high temperatures, such as titanium, certain stainless steels, or refractory metals.
Safety: The Hydrogen Factor
Hydrogen is extremely effective as a reducing agent but is also highly flammable and can be explosive in certain concentrations with air.
Furnaces running hydrogen atmospheres require specialized safety systems, including robust seals, leak detection sensors, and controlled purging procedures, which adds to the operational complexity and cost.
Purity and Dew Point
Even in a supposedly pure atmosphere, trace contaminants like oxygen or water vapor can cause unwanted oxidation.
The dew point of a gas is a measure of its water vapor content. For sensitive materials, a very low dew point (very dry gas) is critical to achieving a perfect, oxide-free finish.
Selecting the Right Atmosphere for Your Process
Your choice of atmosphere gas is a direct function of your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation on most steels and non-ferrous metals: Use a cost-effective nitrogen-based inert atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is creating an exceptionally clean, oxide-free surface for brazing or bright annealing: Use a hydrogen-based reducing atmosphere, accounting for the necessary safety requirements.
- If your primary focus is increasing the surface hardness of low-carbon steel: Use a carbon-rich carburizing atmosphere with a gas like methane or endothermic gas.
- If your primary focus is treating highly reactive metals like titanium: Use a high-purity argon atmosphere to avoid unwanted chemical reactions like nitride formation.
By understanding these principles, you can select the precise atmosphere to transform it from a simple protective blanket into an active tool for material engineering.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Primary Gases | Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar) | Protects against oxidation and scaling | Annealing, general heat treating |
| Reducing | Hydrogen (H₂), Nitrogen-Hydrogen mixes | Removes oxides for clean surfaces | Bright annealing, brazing |
| Carburizing | Methane (CH₄), Propane (C₃H₈), Endothermic gas | Adds carbon to harden surfaces | Case hardening of steels, gears, bearings |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Heat Treatment with KINTEK
Struggling to select the right atmosphere gas for your specific material and process? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with inert, reducing, or carburizing atmospheres, we ensure optimal performance, safety, and efficiency. Don't let gas selection hold you back—contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your laboratory's outcomes and drive innovation in your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality



















