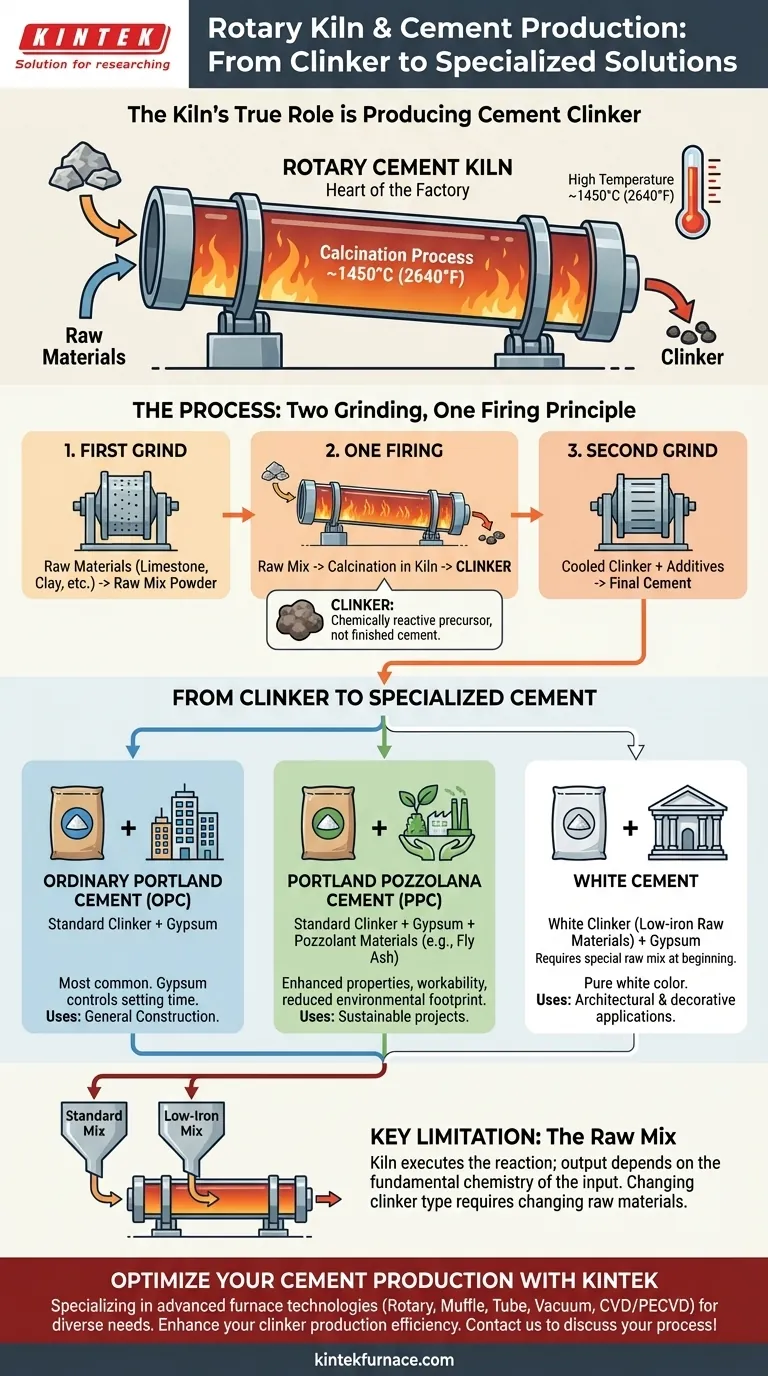
At its core, a rotary kiln is a highly versatile furnace capable of producing the foundational component for nearly any modern cement. While the end products include Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC), Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC), and White Cement, the kiln's direct output is not cement itself, but an intermediate product called clinker. The specific type of cement is determined by how this clinker is processed after it leaves the kiln.
The essential function of a rotary cement kiln is to transform raw materials into clinker through a high-temperature chemical reaction. The versatility of the kiln allows for the production of different types of clinker, which are then ground with various additives to create a wide range of final cement products.
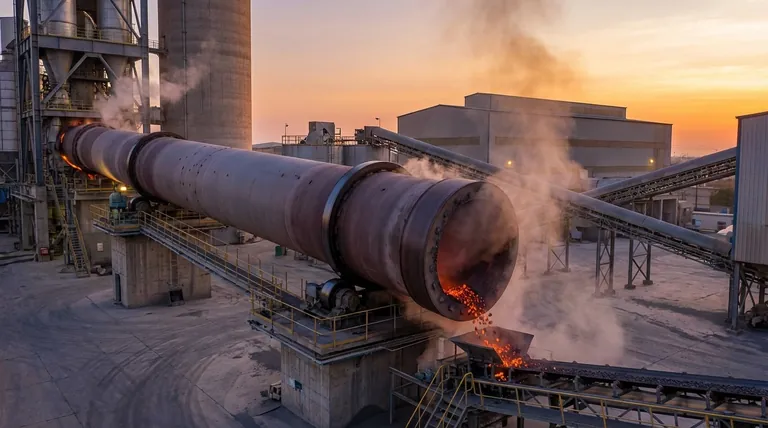

The Kiln's True Role: Producing Cement Clinker
To understand the kiln's capabilities, you must first distinguish between clinker and cement. The kiln’s job is to produce clinker; the final blending creates the cement.
What is Clinker?
Clinker is a hard, nodular material produced by heating a precise mixture of limestone, clay, and other materials to around 1450°C (2640°F) inside the rotary kiln.
These nodules are the universal, chemically reactive precursor to cement. On its own, clinker is not a finished construction material.
The "Heart of the Cement Factory"
The rotary kiln is often called the "heart" of a cement plant because this high-temperature conversion process, known as calcination, is the most critical step.
It functions as a chemical reactor, heat exchanger, and conveyor all at once. The slow rotation and immense heat ensure the raw materials are processed uniformly into high-quality clinker.
The "Two Grinding, One Firing" Principle
The cement manufacturing process is often summarized as "two grinding, one firing."
- First Grind: Raw materials (limestone, clay, etc.) are ground into a fine powder called the "raw mix."
- One Firing: The raw mix is fed into the rotary kiln and fired to produce clinker. This is the kiln's only role.
- Second Grind: The cooled clinker is ground into a fine powder with a small amount of gypsum and other additives to produce the final cement.
From Clinker to Specialized Cement
The type of cement produced is determined during the final grinding stage, based on what is added to the standard clinker.
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC)
This is the most common type of cement. It is created by grinding standard Portland cement clinker with a small percentage of gypsum, which controls the setting time.
Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC)
To create PPC, standard clinker is ground with gypsum and a pozzolanic material, such as fly ash. This enhances the cement's properties, improves workability, and often reduces its environmental footprint.
White Cement
Producing white cement requires a change at the very beginning of the process. It is made using raw materials with extremely low iron and manganese content.
This special raw mix is fired in the kiln to produce a white clinker, which is then ground to create the final white cement used for architectural and decorative purposes.
Understanding the Key Limitation
While incredibly versatile, the rotary kiln's output is constrained by a single, critical factor: the input.
The Kiln is Adaptable, the Raw Mix is Specific
The kiln itself can handle different raw mixes, but it cannot change the fundamental chemistry of the materials fed into it.
To produce a different type of clinker (like the white clinker needed for white cement), the entire raw material sourcing and mixing process must be changed. The kiln simply executes the chemical reaction on whatever it is given.
Energy and Operational Demands
The primary trade-off of a rotary kiln is its immense energy consumption. Maintaining temperatures over 1400°C requires a significant and continuous fuel supply, making it the most cost-intensive part of the cement manufacturing process. Its role as a multi-purpose reactor and conveyor also demands sophisticated operational control.
How to Apply This to Your Production Goal
Your choice of cement dictates your process long before the material ever reaches the final grinding stage.
- If your primary focus is standard construction: Your goal is the efficient production of high-quality, standard Portland cement clinker.
- If your primary focus is sustainable or enhanced performance cement: The key step is blending your standard clinker with specific pozzolanic materials during the final grinding phase.
- If your primary focus is specialized aesthetic applications: Your entire process must be dedicated to sourcing and processing low-iron raw materials to create a pure white clinker.
Understanding the kiln's role as a clinker producer is the key to mastering the production of any type of cement.
Summary Table:
| Cement Type | Key Clinker Input | Final Grinding Additives | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) | Standard clinker | Gypsum | General construction |
| Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) | Standard clinker | Gypsum, pozzolanic materials (e.g., fly ash) | Sustainable, enhanced workability projects |
| White Cement | White clinker (low-iron raw materials) | Gypsum | Architectural, decorative applications |
Ready to optimize your cement production with precision high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced furnace technologies tailored for diverse laboratory needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive product line—including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—supported by deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Whether you're producing standard OPC, sustainable PPC, or specialized White Cement, our solutions ensure efficient clinker production and superior performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your cement manufacturing process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions



















