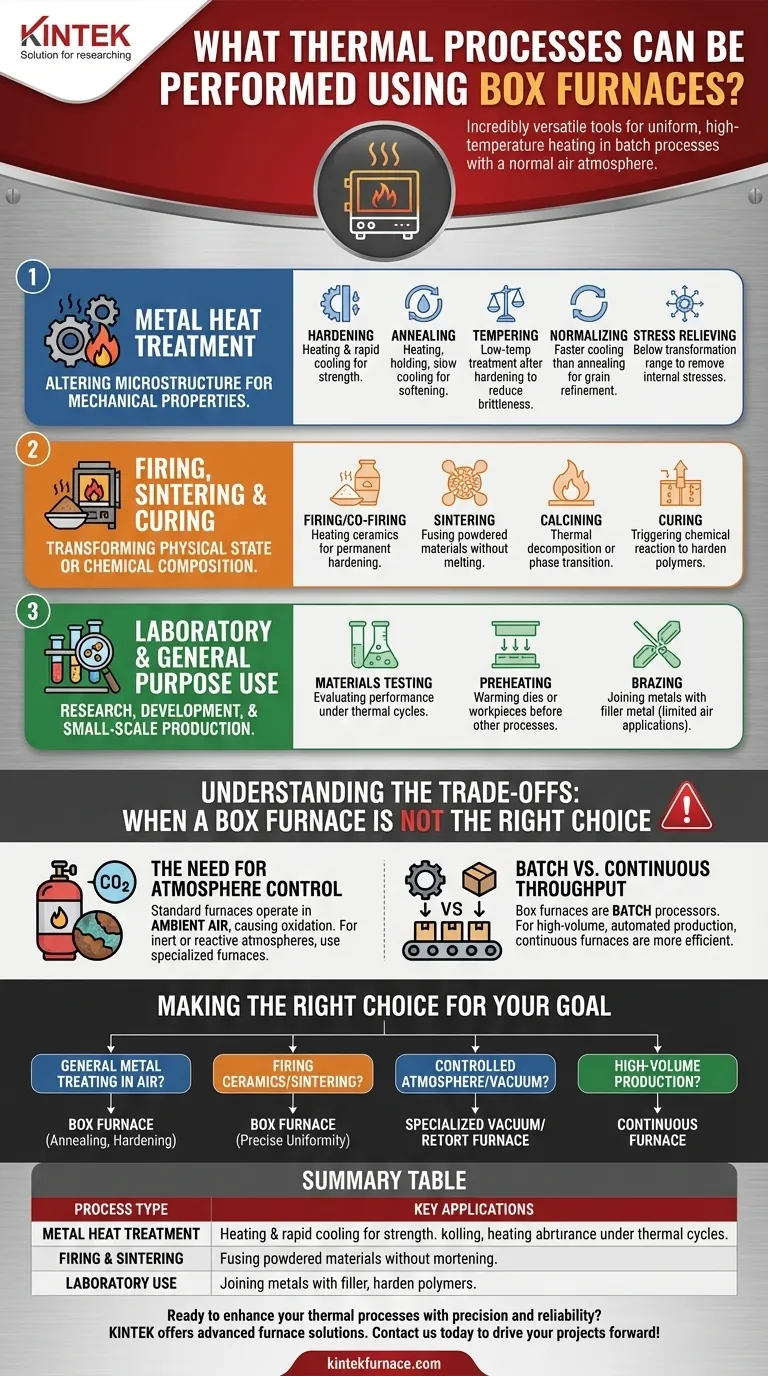
At their core, box furnaces are incredibly versatile tools capable of executing a wide range of thermal processes. They are most commonly used for metal heat treatments like hardening, annealing, tempering, normalizing, and stress relieving, but njihov capabilities extend to firing ceramics, sintering powdered materials, preheating, and general laboratory testing.
The defining characteristic of a standard box furnace is its ability to provide uniform, high-temperature heating for batch processes in a normal air atmosphere. Understanding this core function is the key to determining if it is the right tool for your specific application.

The Principle: Uniform Heating for Batch Processing
A box furnace, also known as a muffle furnace, is fundamentally a chamber with a front-loading door and internal heating elements. Its simple, robust design is optimized for heating parts or materials placed inside to a precise and uniform temperature.
Metal Heat Treatment
This is the most common application category. The goal is to alter the microstructure of metals to achieve desired mechanical properties like hardness, toughness, or ductility.
- Hardening: Heating steel above a critical temperature and then rapidly cooling (quenching) to increase its hardness and strength.
- Annealing: Heating a material and holding it at a specific temperature before cooling it slowly. This process softens the material, relieves internal stresses, and improves its machinability.
- Tempering: A low-temperature heat treatment performed after hardening to reduce brittleness and increase toughness.
- Normalizing: Similar to annealing but with a slightly faster, air-cooling rate. It refines the grain structure and improves mechanical properties.
- Stress Relieving: Heating a part to a temperature below its transformation range to relieve stresses induced by welding, machining, or cold working.
Firing, Sintering, and Curing
These processes are common in ceramics, powder metallurgy, and materials science. They use heat to transform the material's physical state or chemical composition.
- Firing / Co-firing: Heating ceramic materials (green parts) to high temperatures to achieve permanent hardening and densification.
- Sintering: A process that uses heat to fuse particles of powdered material together, creating a solid or porous mass without melting it. This is critical for powder metallurgy and some ceramics.
- Calcining: Heating a material to a high temperature in the presence of air to cause thermal decomposition, phase transition, or the removal of a volatile fraction.
- Curing: Using heat to trigger a chemical reaction to harden a material, such as a polymer or composite.
Laboratory and General Purpose Use
The versatility of box furnaces makes them a staple in research and development or small-scale production environments.
- Materials Testing: Exposing material samples to controlled thermal cycles to evaluate their performance and durability.
- Preheating: Warming dies, molds, or large workpieces to a specific temperature before another process like forging or welding.
- Brazing: Joining two metal pieces using a filler metal that is melted and flows into the joint. While some brazing can be done in a box furnace, high-purity applications often require a controlled atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When a Box Furnace Is Not the Right Choice
The primary limitation of a standard box furnace is its atmosphere. Trustworthy analysis requires understanding what a tool cannot do.
The Need for Atmosphere Control
Standard box furnaces operate in ambient air. The oxygen present will cause oxidation and scaling on the surface of many metals at high temperatures.
If your process requires an inert environment (like argon or nitrogen) or a chemically active atmosphere (like in carburizing or nitriding), you must use a specialized furnace, such as a retort, tube, or vacuum furnace.
Batch vs. Continuous Throughput
By design, a box furnace is a batch processor. Parts are loaded, the door is closed, the cycle runs, and the parts are unloaded. This is perfect for lab work, one-off jobs, or low-volume production.
For high-volume manufacturing, a continuous furnace (such as a belt or conveyor furnace) that moves parts through different heating and cooling zones is a far more efficient solution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace टाइप hinges on the requirements of your specific process, particularly the atmosphere and production volume.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose metal heat treating in air: A box furnace is an excellent and cost-effective choice for annealing, hardening, and tempering.
- If your primary focus is firing ceramics, sintering powders, or lab testing: The precise temperature uniformity of a box furnace makes it the ideal tool for these applications.
- If your primary focus requires a controlled atmosphere or vacuum: You must look beyond a standard box furnace to a specialized vacuum or retort furnace to prevent oxidation or introduce reactive gases.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, automated production: A continuous-style furnace will be necessary to meet throughput demands.
Ultimately, matching the furnace's core capability—uniform heating in a batch, air-atmosphere process—to your objective is the key to a successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Metal Heat Treatment | Hardening, Annealing, Tempering, Normalizing, Stress Relieving |
| Firing & Sintering | Ceramics Firing, Powder Sintering, Calcining, Curing |
| Laboratory Use | Materials Testing, Preheating, Brazing |
Ready to enhance your thermal processes with precision and reliability? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in materials science, ceramics, or metalworking, our furnaces deliver uniform heating and durability for optimal results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications and drive your projects forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















