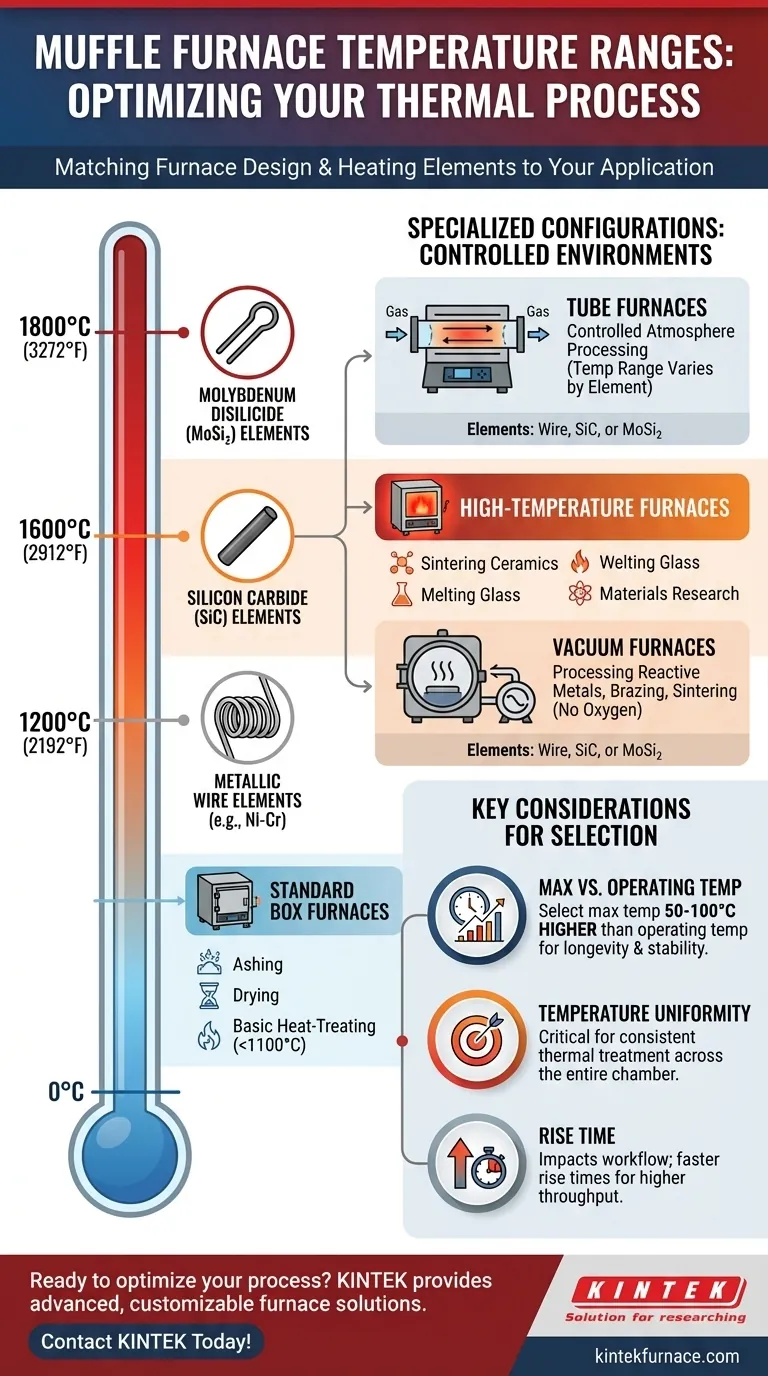
In short, muffle furnace operating temperatures are dictated by their construction and heating elements. Standard box-type furnaces typically operate up to 1200°C (2192°F), while high-temperature models designed for advanced materials can reach 1600°C to 1800°C (2912°F to 3272°F). Specialized designs like tube or vacuum furnaces operate within these ranges but in controlled environments.
Choosing a muffle furnace is less about finding the highest possible temperature and more about matching the furnace's heating technology to your specific thermal process. The type of heating element is the single most important factor determining its sustainable operating range and cost.

How Furnace Design Dictates Temperature Range
A muffle furnace is essentially an insulated box with a high-temperature heating source. The maximum temperature it can safely and consistently achieve is a direct result of the materials used in its construction, particularly the heating elements.
Standard Muffle Furnaces (Up to 1200°C)
These are the most common furnaces found in general laboratory and light industrial settings. They are ideal for applications like ashing, drying, and basic heat-treating of metals.
Their temperature limitation comes from their metallic wire heating elements, typically made from a nickel-chromium or iron-chromium-aluminum alloy. These elements provide excellent performance and longevity up to about 1200°C but will degrade rapidly if pushed beyond this limit.
High-Temperature Muffle Furnaces (1200°C to 1800°C)
When processes require temperatures above 1200°C, such as for sintering advanced ceramics, melting glasses, or high-temperature materials research, the furnace must use more robust, non-metallic heating elements.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements: These are used for furnaces operating in the 1200°C to 1600°C range. They are more durable than wire elements at these higher temperatures.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Elements: For the highest temperature ranges, from 1600°C up to 1800°C, furnaces rely on MoSi₂ heating elements. These are the standard for demanding industrial and research applications.
Specialized Furnace Configurations
While heating elements determine the temperature, the furnace's physical design enables specific processes.
- Tube Furnaces: These use a cylindrical heating chamber. Their primary advantage is the ability to process samples in a controlled atmosphere by flowing specific gases through the tube. Their temperature range is still dictated by their heating elements (wire, SiC, or MoSi₂).
- Vacuum Furnaces: These are designed to heat materials in a high vacuum, which prevents oxidation and other atmospheric reactions. They are critical for processing reactive metals and for certain brazing and sintering applications.
Key Considerations and Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace solely on its maximum temperature can be a costly mistake. You must consider the relationship between performance, longevity, and your specific application.
Maximum vs. Operating Temperature
A furnace's maximum temperature is a short-term rating, not a sustainable working temperature. Continuously running a furnace at its absolute maximum will drastically shorten the life of its heating elements.
As a rule of thumb, select a furnace with a maximum temperature at least 50°C to 100°C higher than your typical operating temperature. This provides a buffer that ensures stable control and significantly extends the equipment's lifespan.
The Impact of Heating Elements
The move from metallic wire elements to SiC and MoSi₂ elements represents a significant jump in both performance and cost. Higher-temperature furnaces are a larger investment due to these specialized components.
Rise Time and Temperature Uniformity
Rise time is the time it takes for the furnace to reach its setpoint. While not always the primary concern, it can impact workflow and throughput. More powerful or better-insulated furnaces may have faster rise times.
Temperature uniformity describes how consistent the temperature is throughout the entire heating chamber. This is critical for ensuring that all parts of your sample receive the exact same thermal treatment, which is vital for repeatable scientific experiments and quality control in manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct furnace, focus on the thermal requirements of your material and process.
- If your primary focus is general lab work like ashing, drying, or basic heat treating below 1100°C: A standard box muffle furnace with wire elements is the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is sintering technical ceramics, melting certain glasses, or materials testing between 1200°C and 1700°C: You must invest in a high-temperature furnace with SiC or MoSi₂ elements.
- If your primary focus is processing materials that cannot be exposed to oxygen or air: Your choice must be a vacuum or tube furnace, with a temperature range specified to match your material's needs.
Ultimately, understanding your process requirements is the key to selecting a furnace that will perform reliably for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Temperature Range | Heating Element | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Box Furnace | Up to 1200°C | Metallic Wire (e.g., Ni-Cr) | Ashing, drying, basic heat-treating |
| High-Temperature Furnace | 1200°C to 1800°C | Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Sintering ceramics, melting glass, materials research |
| Tube Furnace | Varies (based on elements) | Wire, SiC, or MoSi₂ | Controlled atmosphere processing |
| Vacuum Furnace | Varies (based on elements) | Wire, SiC, or MoSi₂ | Processing reactive metals, brazing, sintering |
Ready to optimize your thermal processes? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—offers deep customization to precisely match your experimental requirements. Whether you're in research, industrial production, or specialized labs, we ensure reliable performance and extended equipment lifespan. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a muffle furnace required for SnO2/ZnO composites? Achieve High-Purity Calcination
- How does Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) compare to traditional muffle furnace sintering? Achieve Fine-Grained Ceramics
- What is the difference between electric furnace and muffle furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heating Solution
- Why is a laboratory furnace with an open quartz vessel utilized for CD2-type carbon dots? Precise Thermal Synthesis
- What is the critical role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in converting biomass into Fe-N-BC?
- How are muffle furnaces used in ceramic material processing? Unlock Precision Sintering for High-Performance Ceramics
- What conditions does a muffle furnace provide for SLG/Cu oxidation testing? Achieve Precise Graphene Evaluation
- Why is a precision muffle furnace required for TiO2 sintering? Optimize Your Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Performance



















