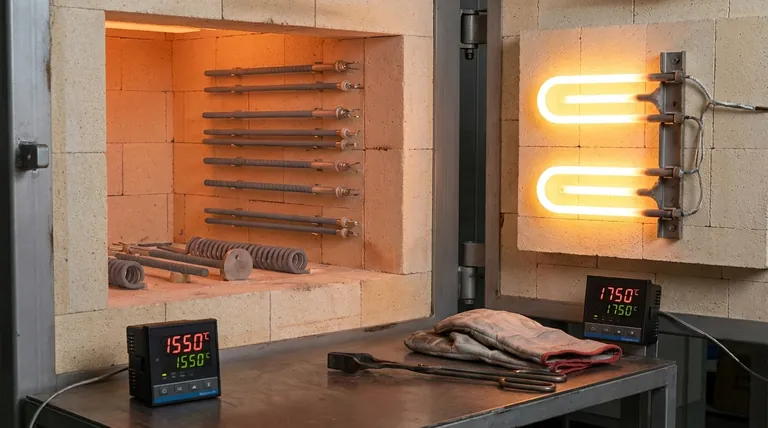
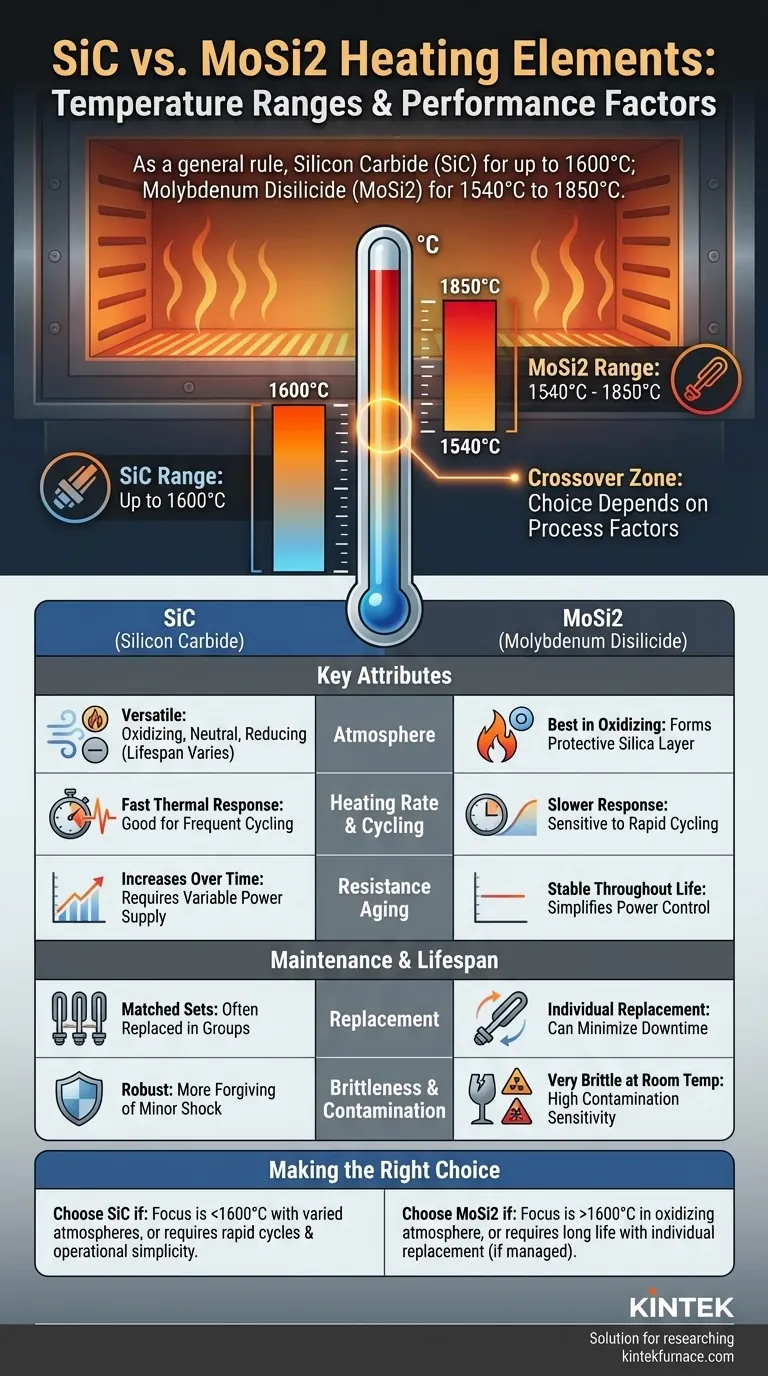
As a general rule, Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are recommended for applications with maximum temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F). Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements are designed for higher temperature ranges, operating effectively from approximately 1540°C (2804°F) up to 1850°C (3362°F). The small overlap between 1540°C and 1600°C means the choice in that specific window depends on other critical factors.
While temperature is the primary filter, the correct choice between SiC and MoSi2 is not just about the maximum heat. The decision ultimately hinges on a balance between your furnace atmosphere, required heating behavior, and your team's maintenance philosophy.

The Critical Factor: Operating Temperature
The most straightforward way to begin your selection process is by defining the temperature range required for your process. The two materials are designed for distinctly different thermal duties.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements
SiC elements are the established workhorses for a vast range of mid-to-high-temperature industrial and laboratory furnaces.
Their optimal operating range is typically up to 1600°C. Below this, they provide reliable, efficient heat.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Elements
MoSi2 elements are the specialists for extreme-temperature applications where SiC elements cannot perform.
They excel in environments from 1540°C up to 1850°C, making them one of the highest-rated electric heating element types available.
The Crossover Zone: ~1540°C to 1600°C
If your process operates within this narrow window, temperature alone is not a sufficient guide. Here, secondary characteristics like furnace atmosphere and operational demands become the deciding factors.
Beyond Temperature: Comparing Key Attributes
Choosing the right element requires looking beyond the maximum temperature and considering how the element behaves within your specific process environment.
Furnace Atmosphere
The atmosphere inside your furnace is a critical consideration. MoSi2 elements perform best and achieve their longest life in oxidizing atmospheres, which allows them to form a protective silica glass layer.
SiC elements are significantly more versatile and can be used in a wider variety of oxidizing, neutral, or reducing atmospheres, though their lifespan may be affected.
Heating Rate and Cycling
For processes requiring very fast heat-up times or frequent thermal cycling, SiC is often favored due to its rapid thermal response.
MoSi2 elements, while robust at stable high temperatures, can be more sensitive to the mechanical stresses of rapid heating and cooling cycles.
Aging and Energy Efficiency
SiC elements age in a way that their electrical resistance gradually increases over their service life. This requires a power supply with variable voltage to maintain consistent power output.
MoSi2 elements, by contrast, maintain a relatively stable resistance throughout their life, simplifying power control requirements.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Maintenance and Lifespan
The long-term operational cost and uptime of your furnace are directly tied to the maintenance requirements and failure modes of its heating elements.
Element Lifespan and Brittleness
SiC elements are generally considered more robust and "forgiving" of minor process deviations or occasional mechanical shock. However, they have a finite lifespan defined by their gradual increase in resistance.
MoSi2 elements can have a very long service life if operated correctly, but they are extremely brittle at room temperature. They are also highly sensitive to chemical contamination, which can cause rapid failure.
Replacement and Maintenance
This is a crucial operational difference. MoSi2 elements can typically be replaced individually when one fails, minimizing downtime and replacement cost.
In contrast, SiC elements often need to be replaced in matched sets or series-connected groups to ensure balanced electrical loading, which can be more costly and time-consuming.
Contamination Sensitivity
MoSi2's biggest vulnerability is its susceptibility to certain chemical contaminants that attack its protective silica layer. This requires more careful process control and furnace maintenance to prevent premature failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be based on a clear-eyed assessment of your primary goals.
- If your primary focus is process temperatures up to 1600°C with varied atmospheres: Choose SiC for its versatility and robustness.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures (above 1600°C) in an oxidizing atmosphere: MoSi2 is the only suitable choice.
- If your primary focus is operational simplicity and rapid heating cycles: SiC is generally more forgiving and responsive.
- If your primary focus is long-term maintenance flexibility for a high-temperature application: MoSi2's ability to be replaced individually is a significant advantage, provided you can manage its specific operational requirements.
By understanding these fundamental trade-offs, you can select the heating element that best aligns with your technical goals and operational reality.
Summary Table:
| Attribute | SiC Heating Elements | MoSi2 Heating Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 1600°C | Up to 1850°C |
| Optimal Range | Up to 1600°C | 1540°C to 1850°C |
| Atmosphere | Versatile (oxidizing, neutral, reducing) | Best in oxidizing |
| Heating Rate | Fast, good for cycling | Slower, sensitive to cycling |
| Resistance Aging | Increases over time | Stable throughout life |
| Lifespan | Finite, robust | Long if operated correctly |
| Replacement | Often in matched sets | Can be replaced individually |
| Brittleness | Less brittle | Very brittle at room temperature |
| Contamination Sensitivity | Moderate | High, requires careful control |
Struggling to choose the right heating element for your furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you need versatile SiC elements or high-temperature MoSi2 options, we ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory processes and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















