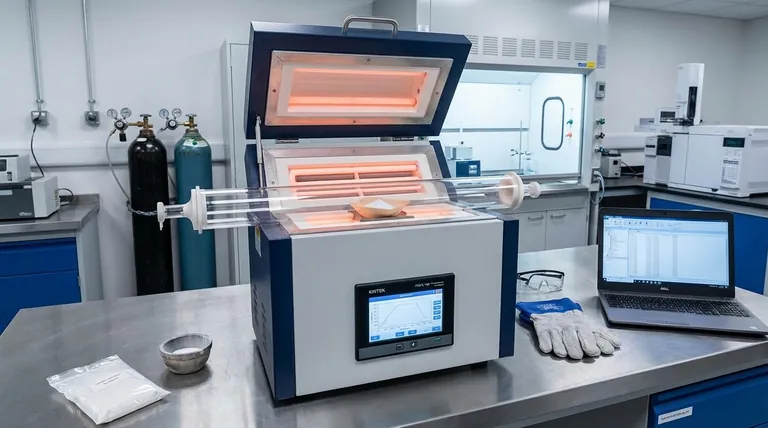
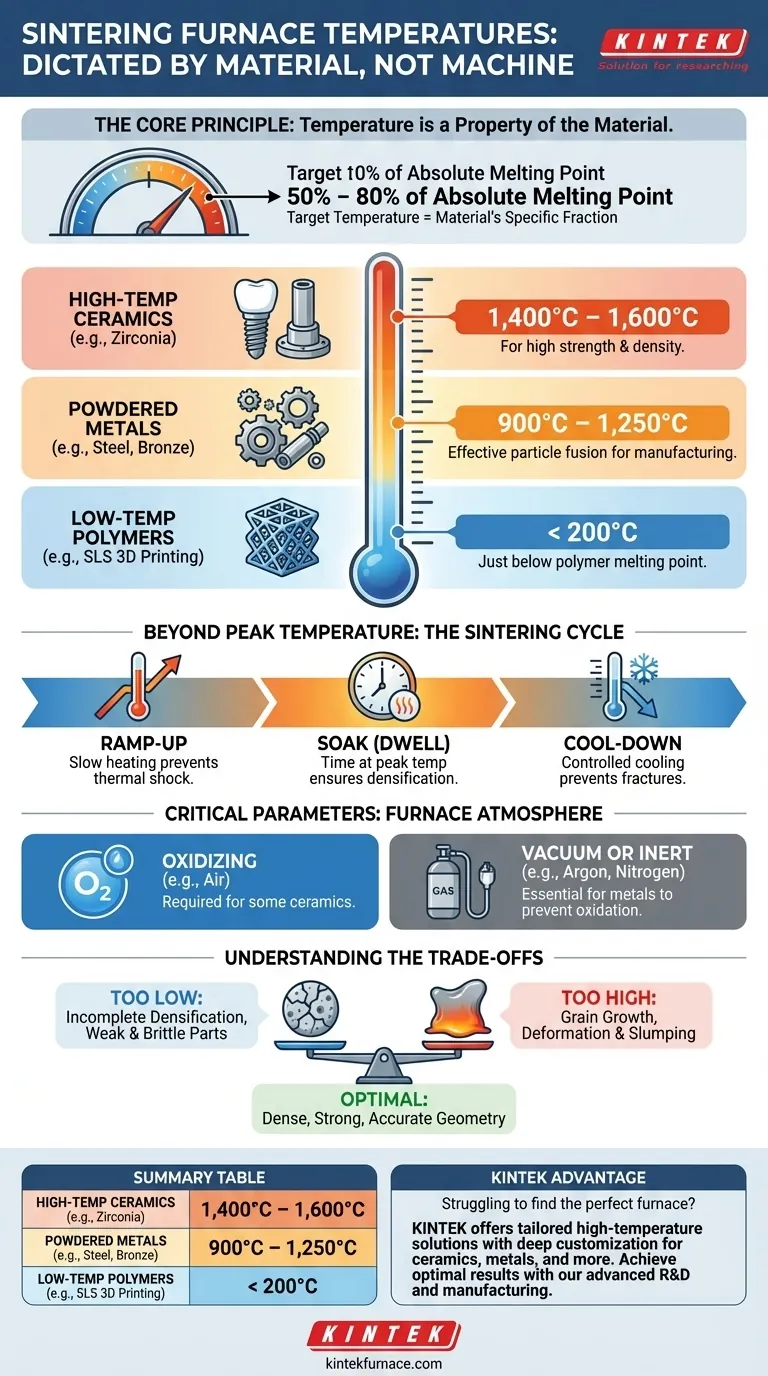
In practice, there is no single temperature range for a sintering furnace. The required temperature is dictated entirely by the material being processed. For high-performance ceramics like zirconia, this is typically between 1,400°C and 1,600°C, while general-purpose laboratory furnaces processing powdered metals often operate between 900°C and 1,200°C.
The core principle to understand is that sintering temperature is not a feature of the furnace, but a property of the material. It is always a specific fraction of the material's absolute melting point, making the material itself the sole determinant of the required operating temperature.

The Core Principle: Temperature is Dictated by the Material
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction. The target temperature is a critical parameter derived directly from the material's fundamental properties.
Sintering and Melting Point
The ideal sintering temperature is typically between 50% and 80% of the material's absolute melting point. This provides enough thermal energy for atoms to diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing them together and reducing porosity.
Going below this range results in incomplete bonding and a weak final part. Exceeding it risks uncontrolled grain growth or even melting, which causes deformation and part failure.
Examples by Material Type
The vast difference in melting points is why furnace temperature ranges vary so widely.
- High-Temperature Ceramics (e.g., Zirconia): Used in dental implants and industrial applications, zirconia requires a high-temperature cycle, often peaking between 1,400°C and 1,600°C, to achieve its renowned strength and density.
- Powdered Metals (e.g., Steel, Bronze): Common in manufacturing, these materials are sintered at lower temperatures. A typical range is 900°C to 1,250°C, which is hot enough to fuse the metal particles effectively.
- Low-Temperature Polymers (e.g., SLS 3D Printing): Though also a form of sintering, processes like Selective Laser Sintering for plastics operate at significantly lower temperatures, often below 200°C, just below the polymer's specific melting point.
Beyond Temperature: Other Critical Sintering Parameters
Achieving a successful outcome depends on more than just the peak temperature. The entire heating and cooling cycle is a carefully controlled process.
Time and Temperature Profile
The process is not about simply reaching a temperature. It involves a "temperature profile" with three key phases:
- Ramp-up: The rate at which the furnace heats. A slow ramp is crucial to prevent thermal shock and cracks.
- Soak (or Dwell): The period spent at the peak sintering temperature. This duration ensures the entire part reaches thermal equilibrium and full densification.
- Cool-down: The controlled cooling rate, which is equally important for preventing stress and fractures in the final part.
Furnace Atmosphere
The gas inside the furnace is a critical variable. An oxidizing atmosphere (like air) is required for some ceramics, but for most metals, it would cause destructive scaling.
For metals, a vacuum or an inert atmosphere (using gases like argon or nitrogen) is necessary to prevent oxidation, ensuring the purity and integrity of the final sintered component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sintering temperature is a balancing act with clear consequences for getting it wrong. Following the material manufacturer's datasheet is non-negotiable.
Too Low: Incomplete Densification
If the temperature is too low or the soak time is too short, atomic diffusion will be insufficient. This leaves behind excessive porosity, resulting in a part that is mechanically weak and brittle.
Too High: Grain Growth and Deformation
If the temperature is too high or the soak time is too long, the material's microscopic grains can grow too large. This coarsening effect can paradoxically reduce the material's final strength and toughness.
Getting too close to the melting point will cause the part to slump or deform under its own weight, destroying its geometry.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Always start with the official technical data sheet for your specific material. From there, your goal will determine your focus.
- If your primary focus is high-performance ceramics like zirconia: You must use a high-temperature furnace capable of reaching 1400°C to 1600°C and holding it with high stability.
- If your primary focus is powdered metals or general research: A furnace with a common operating range of 900°C to 1200°C will cover the majority of applications.
- If your primary focus is preventing defects: You must precisely follow the material supplier's recommended profile, paying closest attention to the ramp-up and cool-down rates.
Ultimately, successful sintering is a precise balancing act where temperature is the most critical, but not the only, lever you control.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Typical Sintering Temperature Range | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature Ceramics (e.g., Zirconia) | 1,400°C to 1,600°C | High strength, dense parts for implants and industrial uses |
| Powdered Metals (e.g., Steel, Bronze) | 900°C to 1,250°C | Effective particle fusion for manufacturing applications |
| Low-Temperature Polymers (e.g., SLS 3D Printing) | Below 200°C | Used in additive manufacturing processes |
Struggling to find the perfect sintering furnace for your material? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with high-performance ceramics, powdered metals, or other materials, we can help you achieve optimal sintering results. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your lab's efficiency and success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















