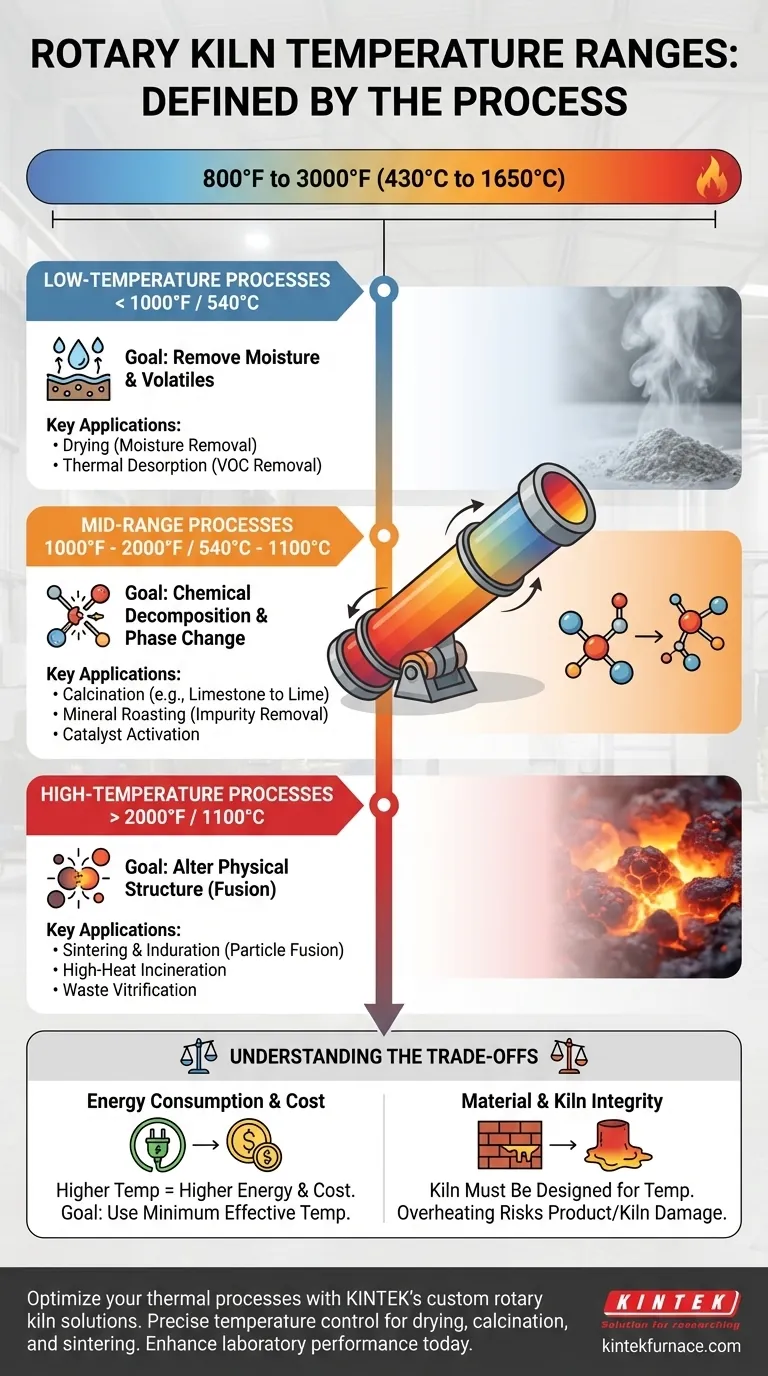
Rotary kilns operate across a vast temperature spectrum, with the specific heat level determined entirely by the material being processed. Generally, this range falls between 800°F and 3000°F (430°C to 1650°C). This wide variance exists because a kiln is a tool for inducing a specific physical or chemical change, and each transformation—from simple drying to complex chemical decomposition—has a unique temperature requirement.
The operating temperature of a rotary kiln is not a feature of the equipment itself, but a direct function of the process it is performing. To determine the correct temperature, you must first define the desired outcome for your material, whether that is drying, calcining, or sintering.

Why Temperature Varies: The Process Defines the Heat
A rotary kiln is essentially a rotating, inclined cylinder that tumbles material through a heated zone. This design ensures uniform heat exposure. The temperature inside is not set arbitrarily; it is precisely controlled to trigger a specific reaction in the material passing through it.
Low-Temperature Processes (< 1000°F / 540°C)
At the lower end of the spectrum, the goal is typically to drive off moisture or volatile compounds without altering the material's fundamental chemistry.
Drying is the most common low-heat application, focused solely on removing water content.
Thermal desorption is another key process, used to heat materials like contaminated soil just enough to vaporize volatile organic compounds (VOCs) for removal.
Mid-Range Processes (1000°F - 2000°F / 540°C - 1100°C)
This range is where most chemical decomposition and phase-change reactions occur.
Calcination is the defining process in this temperature bracket. It involves thermally decomposing a material, most famously converting limestone (CaCO₃) into lime (CaO) by driving off carbon dioxide.
Other applications include mineral roasting to remove impurities like sulfur, or catalyst activation, which prepares catalysts for industrial use.
High-Temperature Processes (> 2000°F / 1100°C)
The highest temperatures are reserved for processes that fundamentally alter the physical structure of a material, often bringing it close to its melting point.
Sintering and induration are prime examples. These processes heat fine particles, like iron ore pellets, until their surfaces fuse, creating a single, hardened mass without fully melting.
High-heat incineration and waste vitrification also operate in this range to achieve maximum volume reduction and create a stable, glass-like slag.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a temperature is a critical decision with direct consequences for cost, efficiency, and product quality. Misunderstanding these trade-offs is a common and costly pitfall.
Energy Consumption vs. Throughput
Higher temperatures require significantly more energy, which is often the largest operational cost associated with a kiln.
The objective is always to use the minimum effective temperature that achieves the desired reaction. Using excessive heat wastes fuel and offers no benefit.
Material Integrity and Kiln Design
The kiln itself, particularly its internal refractory brick lining, must be designed to withstand the target operating temperature. A low-temperature drying kiln cannot be repurposed for high-temperature sintering.
Likewise, overheating can ruin the end product (e.g., melting instead of sintering), while underheating results in an incomplete reaction and a useless or out-of-spec product.
Matching Temperature to Your Thermal Goal
Your process goal is the single most important factor in determining the correct operating temperature for your rotary kiln.
- If your primary focus is moisture removal or drying: You will operate at the lower end of the spectrum, typically below 1000°F (540°C), to avoid chemical changes.
- If your primary focus is chemical decomposition (calcination): You will require a mid-range temperature, often between 1500°F and 2000°F (815°C - 1100°C), to drive the reaction.
- If your primary focus is creating a hardened, solid mass (sintering): You must plan for high-temperature operation, often exceeding 2200°F (1200°C), to achieve particle fusion.
Ultimately, the right temperature is the one that precisely and efficiently achieves the desired transformation in your material.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Temperature Range (°F) | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Temperature | < 1000°F | < 540°C | Drying, Thermal Desorption |
| Mid-Range | 1000°F - 2000°F | 540°C - 1100°C | Calcination, Mineral Roasting |
| High-Temperature | > 2000°F | > 1100°C | Sintering, Incineration |
Ready to optimize your thermal processes with a custom rotary kiln solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, tailored to your unique experimental needs. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise temperature control for applications like drying, calcination, and sintering, maximizing efficiency and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency



















