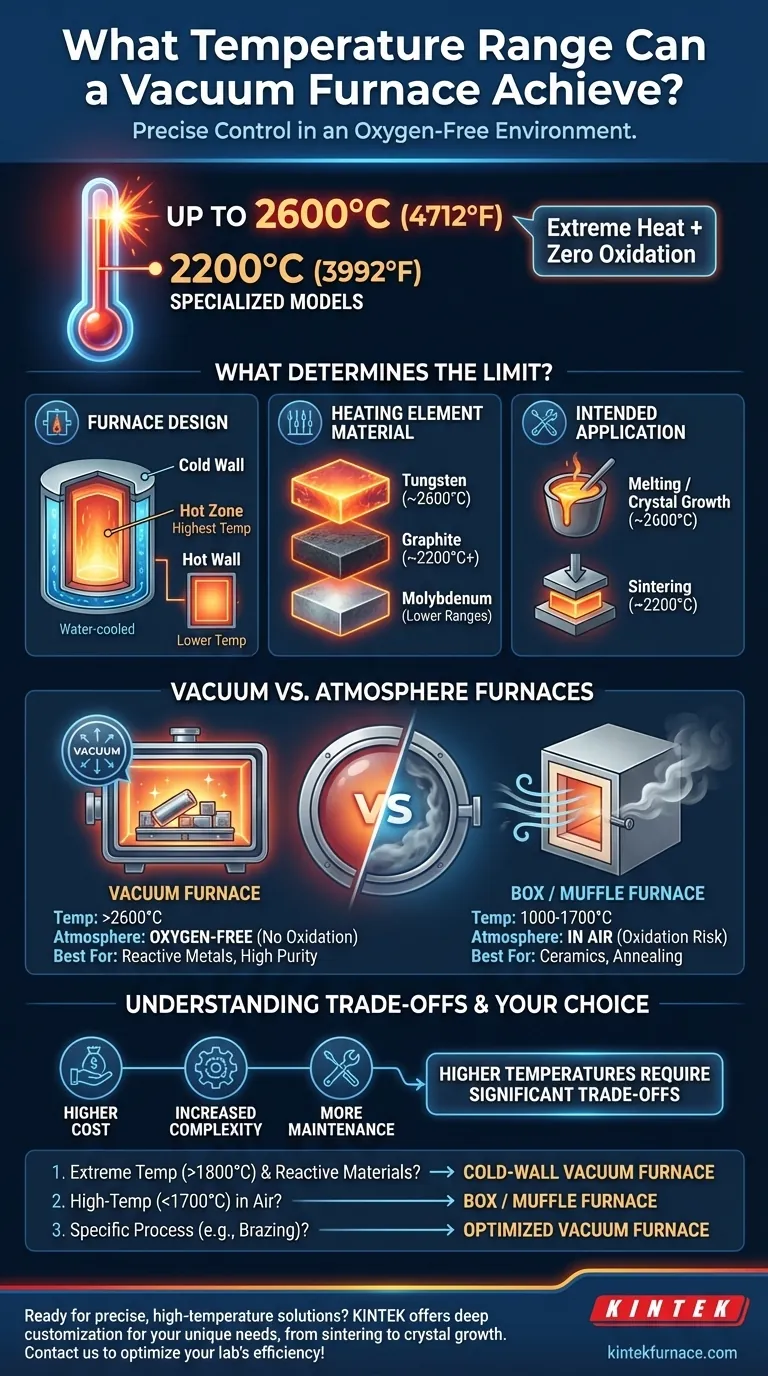
To be direct, a high-performance vacuum furnace can reach temperatures as high as 2600°C (4712°F). However, the operational temperature range depends heavily on the furnace's specific design, materials, and intended application, with many specialized models operating in the 2200°C (3992°F) range.
While the absolute maximum temperature is an impressive figure, the true value of a vacuum furnace lies in its ability to achieve extreme heat with precise control in an oxygen-free environment. The specific temperature you can achieve is a direct result of the furnace's fundamental design.
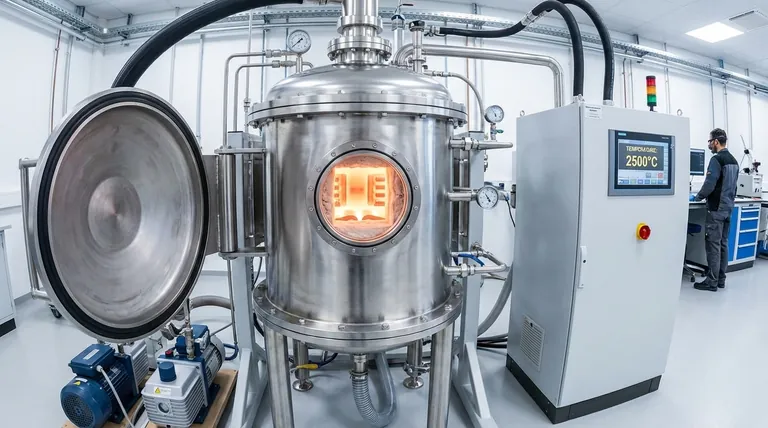

What Determines a Vacuum Furnace's Temperature Range?
A furnace's maximum temperature is not an arbitrary number; it is a limit imposed by its core components and engineering principles. Understanding these factors is key to selecting the right equipment.
The Critical Role of Cold Wall vs. Hot Wall Design
The most significant factor is the furnace's construction. Cold wall furnaces enable the highest operating temperatures. They contain the heating elements and insulation within an internal "hot zone," while the outer vessel wall remains cool, often water-cooled.
This design contains the extreme heat, allowing for faster heating/cooling cycles and better temperature uniformity at much higher ranges. In contrast, hot wall furnaces, where the entire chamber is heated, have a lower maximum temperature.
Heating Element Material
The material used for the heating elements directly dictates the upper temperature limit. You cannot heat a chamber to a temperature that would destroy the elements themselves.
Common materials include graphite, which is often used for temperatures up to and beyond 2200°C, and refractory metals like molybdenum (for lower ranges) and tungsten (for the highest ranges, approaching 2600°C).
Intended Application
Furnaces are often optimized for a specific process, which influences their design and temperature range. For example, a vacuum furnace built for sintering might be designed to operate consistently at 2200°C.
One designed for melting specialized alloys or growing synthetic crystals may be engineered with tungsten elements to reach the 2600°C peak. The required precision and cycle frequency for the application will guide its construction.
How Vacuum Furnaces Compare to Other Options
The defining feature of a vacuum furnace is not just its heat, but its atmosphere. The vacuum environment prevents oxidation and contamination, which is critical for processing reactive metals and high-purity materials.
Box and Muffle Furnaces
These are common high-temperature furnaces, but they typically operate in air. Their temperature ranges generally fall between 1000°C and 1700°C (1800°F to 3100°F).
They are excellent for many applications like annealing, ashing, and certain ceramic processes, but they cannot provide the inert environment of a vacuum furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace with the highest possible temperature rating is not always the best strategy. The pursuit of extreme heat involves significant trade-offs.
Cost and Complexity
As the maximum temperature requirement increases, so does the cost and complexity. Furnaces capable of reaching over 2000°C require exotic heating elements, advanced insulation, and robust cooling systems, all of which dramatically increase the initial investment and operating costs.
Process Cycle Time
While a cold wall furnace can heat and cool its internal hot zone quickly, the overall process cycle includes the time needed to pump down the chamber to the required vacuum level. This can add significant time compared to an atmospheric furnace that simply needs to be heated up.
Maintenance Requirements
The components that enable extreme temperatures—graphite or tungsten elements, multi-layer insulation, and high-capacity vacuum pumps—are consumables that require regular inspection and specialized maintenance to ensure reliability and performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be driven by the specific requirements of your material and process, not just a temperature figure.
- If your primary focus is extreme high-temperature processing (>1800°C) with reactive metals or alloys: A cold-wall vacuum furnace is your necessary choice to prevent oxidation and achieve the required heat.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature heat treatment or ceramics processing in air (up to 1700°C): A traditional box or muffle furnace offers a much more cost-effective and simpler solution.
- If your primary focus is a specific process like brazing or sintering: Select a vacuum furnace designed and optimized for that task's temperature range, as it will be more efficient than an over-specified model.
Ultimately, understanding these design principles allows you to select a furnace based on its suitability for your specific goal, ensuring both process success and economic efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| Design Type | Cold wall: Up to 2600°C; Hot wall: Lower max temperature |
| Heating Element | Graphite: Up to 2200°C+; Tungsten: Up to 2600°C |
| Application | Sintering: ~2200°C; Melting/Crystal growth: Up to 2600°C |
| Comparison to Other Furnaces | Box/Muffle: 1000-1700°C in air; Vacuum: Higher ranges with no oxidation |
Ready to elevate your high-temperature processes with precision and reliability? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced vacuum furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're sintering, melting alloys, or growing crystals, our furnaces deliver extreme heat up to 2600°C with unmatched control. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your lab's efficiency and achieve your specific goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness



















