The key technological alternative to traditional rotary kilns is the adoption of electromagnetic heating systems. This innovation represents a fundamental shift from external combustion-based heating to direct, internal energy transfer, offering significant improvements in energy efficiency and environmental performance.
The core challenge with traditional kilns is inefficient and indirect heating, leading to high energy costs and emissions. Electromagnetic heating solves this by directly energizing the material, fundamentally changing the energy-transfer equation for thermal processing.

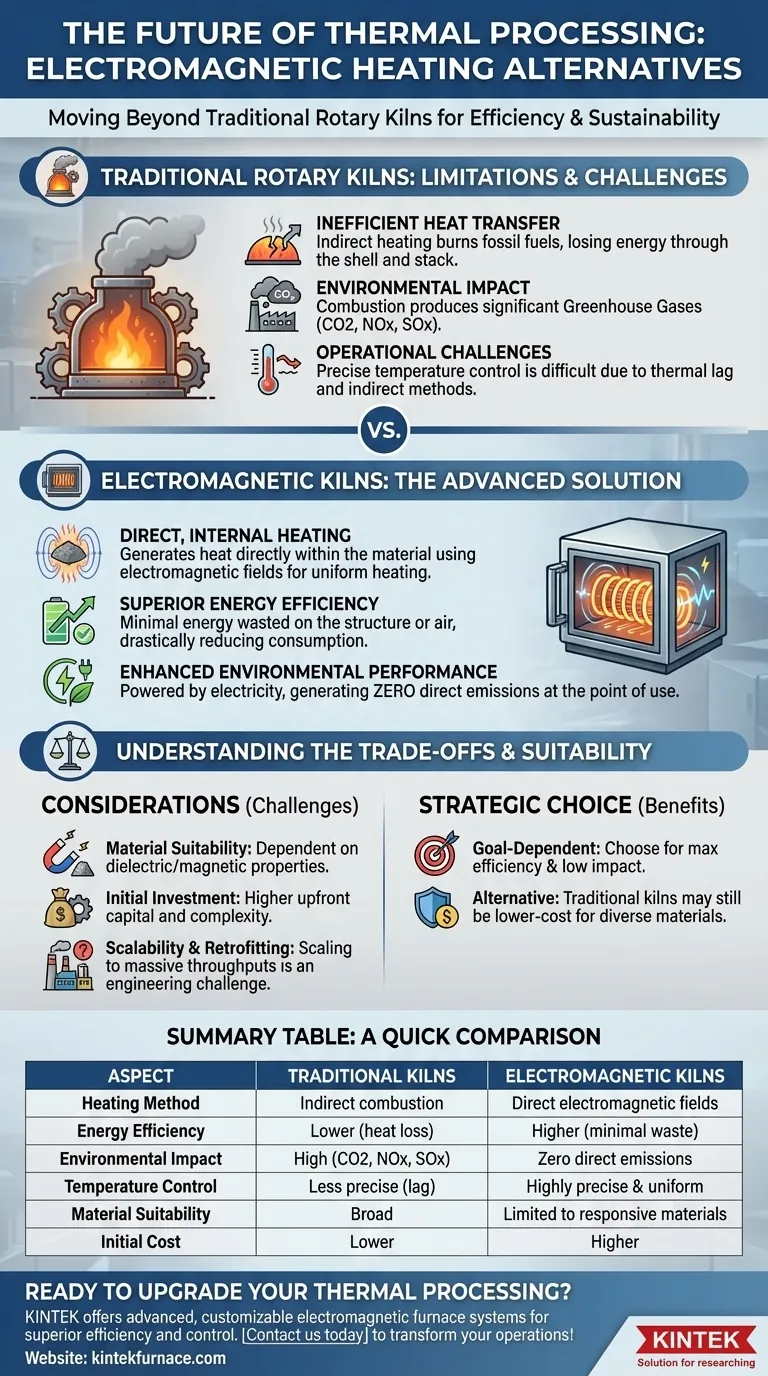
The Limitations of Conventional Kiln Technology
Traditional rotary kilns, while a cornerstone of industrial processing for over a century, have inherent inefficiencies. Most advancements have focused on optimizing an already limited system rather than redesigning its core.
Inefficient Heat Transfer
Conventional kilns are typically heated by burning fossil fuels like natural gas or coal. This heat is transferred indirectly to the material through the kiln's shell and the surrounding air. A significant portion of this thermal energy is lost to the environment through the exhaust stack and the kiln shell itself.
Environmental Impact
The combustion of fossil fuels is the primary heat source for traditional kilns, which inherently produces greenhouse gases (like CO2) and other pollutants (like NOx and SOx). This creates a direct and unavoidable environmental footprint for the heating process.
Operational Challenges
Despite modern enhancements like high-precision pumps and speed controls, traditional kilns still struggle with precise temperature regulation. The large thermal mass and indirect heating method create a lag, making it difficult to make rapid adjustments and maintain a perfectly uniform temperature profile across the material bed.
How Electromagnetic Kilns Provide a Solution
Electromagnetic heated rotary kilns do not just improve upon the old design; they replace the fundamental heating mechanism. This allows for a level of precision and efficiency that combustion cannot match.
The Principle of Direct Heating
Instead of heating the kiln from the outside, this technology uses electromagnetic fields to generate heat directly within the material itself. By selecting appropriate frequencies, the system can selectively energize the target materials, causing them to heat up rapidly and uniformly from the inside out.
Superior Energy Efficiency
Because the energy is transferred directly to the material being processed, minimal energy is wasted heating the kiln's structure or the surrounding air. This dramatically reduces overall energy consumption compared to the indirect, high-loss method of fuel combustion.
Enhanced Environmental Performance
The heating process itself is powered by electricity and generates no direct emissions. This decouples the heating process from combustion, eliminating the CO2, NOx, and SOx pollutants associated with burning fossil fuels at the point of use.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While electromagnetic heating offers clear advantages, it is not a universal replacement for every application. The decision to adopt this technology involves practical considerations and trade-offs.
Material Suitability
The effectiveness of electromagnetic heating is highly dependent on the dielectric and magnetic properties of the material being processed. Materials that do not respond well to the applied electromagnetic field cannot be heated efficiently, making this technology unsuitable for certain applications.
Initial Investment and Complexity
Implementing an electromagnetic heating system often requires a higher upfront capital investment compared to a traditional kiln. The technology is also more sophisticated, potentially requiring specialized knowledge for operation, maintenance, and process design.
Scalability and Existing Infrastructure
While the technology is advancing rapidly, scaling it to the massive throughputs of some industries (like cement production) remains a significant engineering challenge. Retrofitting existing kiln infrastructure is often not feasible, requiring a full system replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice between a state-of-the-art traditional kiln and an electromagnetic one depends entirely on your primary operational objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency and minimizing environmental impact: Electromagnetic heating is the definitive path forward for suitable materials.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse materials with a proven, lower-cost setup: An advanced traditional kiln with modern controls for stability and yield may still be the more practical choice.
Ultimately, choosing the right kiln technology is a strategic decision between the proven versatility of combustion and the precise, clean efficiency of electromagnetics.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Traditional Rotary Kilns | Electromagnetic Kilns |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect combustion (fossil fuels) | Direct electromagnetic fields |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower due to heat loss | Higher with minimal waste |
| Environmental Impact | High emissions (CO2, NOx, SOx) | Zero direct emissions |
| Temperature Control | Less precise with lag | Highly precise and uniform |
| Material Suitability | Broad, but less efficient | Limited to responsive materials |
| Initial Cost | Lower upfront investment | Higher capital investment |
Ready to upgrade your thermal processing with cutting-edge solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're aiming for superior energy efficiency, reduced environmental impact, or precise temperature control, we have the expertise to help. Contact us today to discuss how our electromagnetic heating technologies can transform your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes



















