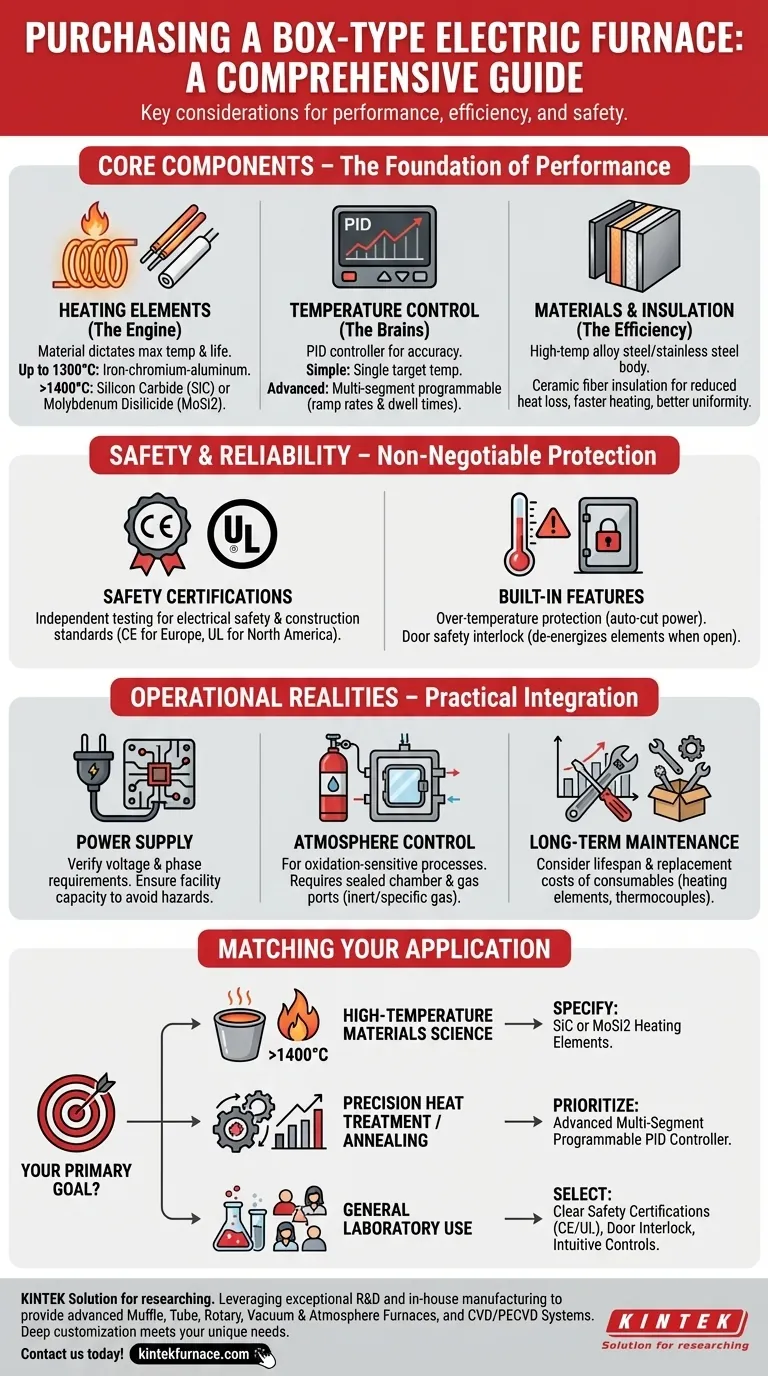
When purchasing a box-type electric furnace, your decision must be guided by four critical factors: the heating elements, the temperature control system, the furnace construction materials, and its safety certifications. These components work together to determine the furnace's performance, efficiency, and operational safety, directly impacting the success of your thermal processing work.
The goal is not simply to buy a furnace that reaches a certain temperature. The real objective is to acquire a tool that provides precise, repeatable, and safe thermal processing that perfectly matches the requirements of your specific application.

Deconstructing the Core Components
A furnace is a system of interconnected parts. Understanding how each part contributes to the overall performance is key to making an informed choice.
The Heating Element: The Engine of the Furnace
The heating elements are responsible for generating the heat. The material used for the element dictates the furnace's maximum operating temperature and its service life.
Common materials like iron-chromium-aluminum alloys are suitable for temperatures up to around 1200-1300°C. For higher temperatures, you will need more robust elements made from silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2).
The Temperature Control System: The Brains of the Operation
This system is how you command and regulate the heat. A modern furnace should use a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller for high temperature accuracy.
Simple controllers allow you to set a single target temperature. More advanced, multi-segment programmable controllers allow you to define complex heating profiles with specific ramp rates and dwell times, which is essential for many sensitive processes.
Furnace Materials and Insulation: The Foundation of Efficiency
The furnace chamber and body are typically built from high-temperature alloy steel or stainless steel. The critical factor here is the quality and thickness of the insulation layer.
Proper insulation, often made of ceramic fiber, reduces heat loss, which leads to faster heating speeds, better temperature uniformity within the chamber, and lower energy consumption. A well-built furnace is an efficient one.
Ensuring Safe and Reliable Operation
A furnace operates at high temperatures and high power. Its safety and reliability are non-negotiable features that protect both the operator and the workpiece.
The Critical Role of Safety Certifications
Look for recognized safety certifications like CE (for Europe) or UL (for North America). These certifications indicate that the furnace has been independently tested and meets stringent standards for electrical safety and construction.
Built-in Safety Features
Standard safety mechanisms are essential. These include over-temperature protection, which automatically cuts power if the temperature exceeds a safe limit, and a door safety interlock, which de-energizes the heating elements when the door is opened.
Understanding the Operational Realities
Beyond the core specifications, you must consider the practical aspects of integrating the furnace into your workflow.
Power Supply Requirements
Box-type electric furnaces are high-power devices. Before purchasing, verify the furnace's voltage and phase requirements and confirm that your facility's electrical supply can safely support the load. Improper power connection is a significant safety hazard.
Atmosphere Control Needs
While a standard furnace operates in air, many material processes are sensitive to oxidation. If your work requires an inert or specific gas environment, you must select a furnace specifically designed with a sealed chamber and gas inlet/outlet ports for atmosphere control.
Long-Term Maintenance
Heating elements and thermocouples (temperature sensors) are consumables with a finite lifespan. Inquire about the expected life of these components under your typical operating conditions and the cost and availability of replacements.
Matching the Furnace to Your Application
Your final choice should be a direct reflection of your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature materials science (>1400°C): You must specify a furnace with silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements.
- If your primary focus is precision heat treatment or annealing: Prioritize a furnace with an advanced, multi-segment programmable PID controller to ensure precise ramp and soak profiles.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory use with multiple operators: Select a furnace with clear safety certifications (CE/UL), a door interlock, and simple, intuitive controls.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is an investment in the integrity and repeatability of your work.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Material (e.g., iron-chromium-aluminum, SiC, MoSi2) dictates max temperature and lifespan |
| Temperature Control | PID controllers for accuracy; programmable for complex profiles |
| Construction Materials | High-temperature alloy steel with ceramic fiber insulation for efficiency |
| Safety Certifications | Look for CE or UL to ensure compliance and reliability |
| Power Supply | Verify voltage and phase requirements for safe operation |
| Atmosphere Control | Needed for inert gas environments; requires sealed chamber |
| Maintenance | Consider lifespan and replacement costs of elements and thermocouples |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing with a reliable box-type electric furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures your unique experimental needs are met precisely. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your work with tailored, high-performance furnaces!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of a quartz tube furnace? Discover High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a quartz tube furnace? Ensure Reliable High-Temperature Processing
- How does the work process of a quartz tube furnace typically proceed? Master Precision Heating for Advanced Materials
- What technical requirements affect the external thermal strength of furnace tubes? Optimize for High-Temp Performance
- What is the necessity of using vacuum-sealed quartz tubes? Ensuring Integrity in Ti-Cu Alloy Heat Treatment



















