Choosing a muffle furnace manufacturer begins not with evaluating company websites, but with a precise definition of your technical requirements. The best manufacturer is simply the one that provides a furnace perfectly suited to your specific application, so the selection process is an exercise in technical specification first and vendor evaluation second.
The core task is not to find a good manufacturer, but to clearly define the job the furnace needs to do. By first establishing your required temperature range, chamber size, material compatibility, and atmospheric needs, you can effectively filter the market and identify the few manufacturers who can meet your specific goals.
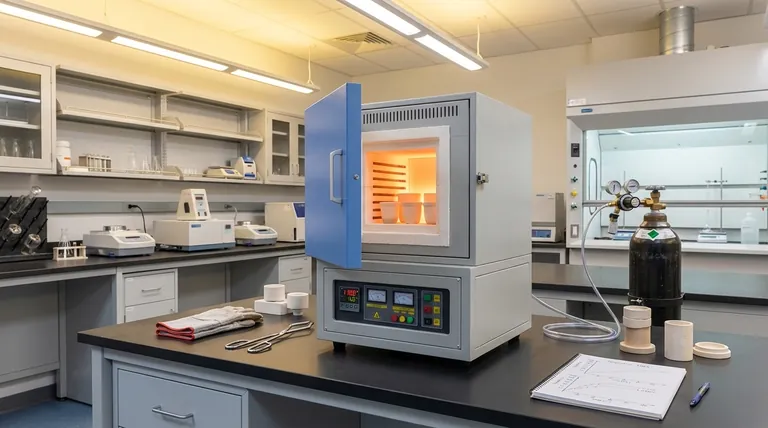

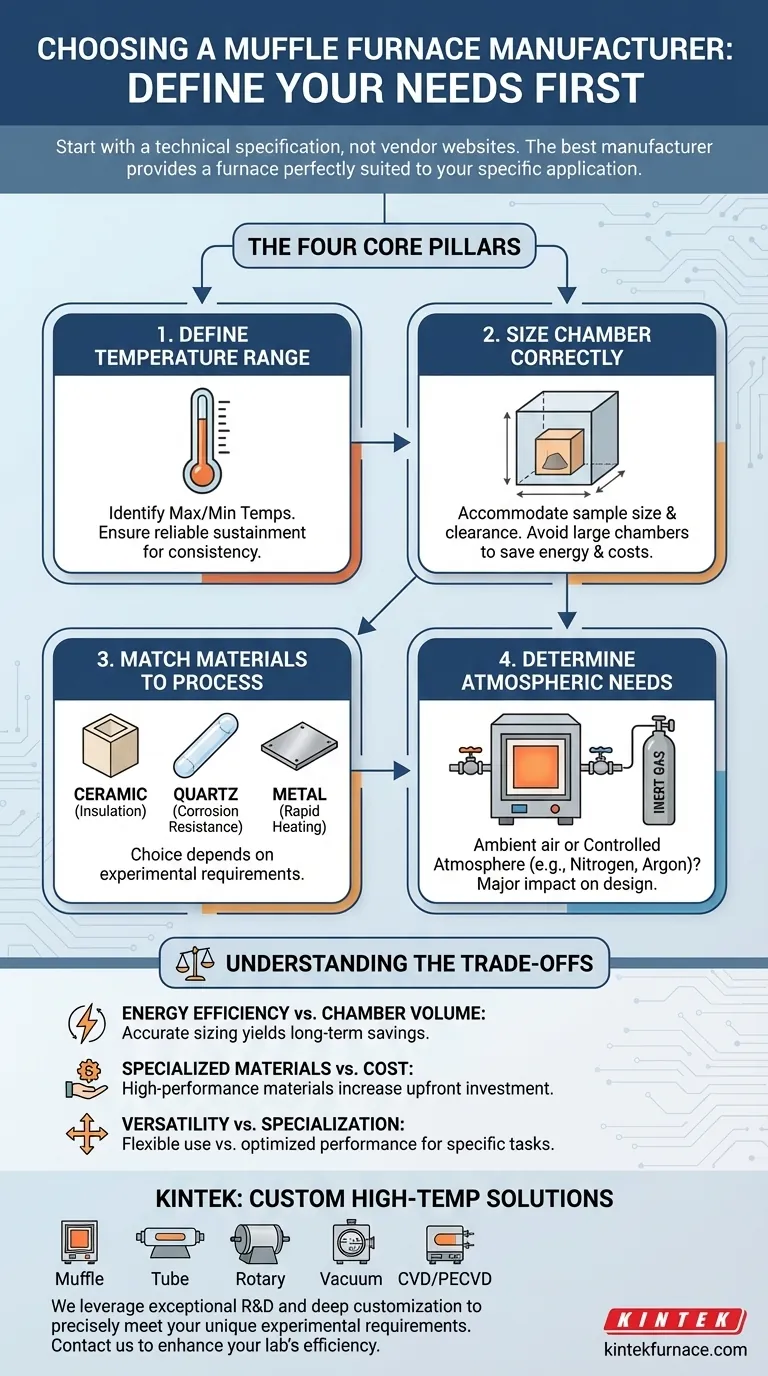
Deconstructing Your Application: The Four Core Pillars
Before you can assess any manufacturer, you must translate your lab or production process into a technical specification. This is built on four key pillars.
Pillar 1: Defining Your Temperature Range
The temperature range is the most critical initial filter. You must identify the maximum and minimum temperatures your process requires.
A furnace must be able to not only reach but also sustain these temperatures reliably to ensure consistent and successful outcomes for your application.
Pillar 2: Sizing the Chamber Correctly
The internal chamber must be large enough to accommodate your sample size and weight. Crucially, it must also provide adequate clearance for the process to occur effectively.
However, a chamber that is too large is a significant drawback. It wastes energy by heating unnecessary empty space, leading to higher operational costs and potentially slower heating cycles.
Pillar 3: Matching Materials to Your Process
The furnace's internal chamber material dictates its capabilities. The choice depends entirely on your experimental requirements.
- Ceramic bodies offer excellent insulation and low thermal expansion, making them ideal for many chemical reactions, heat treatment, and processing electronic components.
- Quartz bodies provide high-temperature resistance and superior corrosion resistance, suiting them for aggressive chemical environments.
- Metal bodies have excellent thermal conductivity, enabling rapid heating. This makes them a strong choice for certain high-temperature heating applications and mass production scenarios.
Pillar 4: Do You Need a Controlled Atmosphere?
You must determine if your process simply requires high-temperature heating in ambient air or if it needs a controlled atmosphere.
Many advanced applications, such as brazing, reducing, or working with oxygen-sensitive materials, require the chamber to be purged and filled with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon. This represents a major difference in furnace design, complexity, and cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace involves balancing competing priorities. Being aware of these trade-offs is key to making an objective decision.
Energy Efficiency vs. Chamber Volume
There is a direct relationship between chamber size and energy consumption. Resist the temptation to buy a larger furnace "just in case." Accurately sizing the furnace to your most common sample load will yield significant long-term savings in operational costs.
Specialized Materials vs. Cost
High-performance chamber materials like high-purity alumina fiber or quartz offer superior performance in extreme temperatures or corrosive environments, but they also increase the equipment's upfront cost. A standard ceramic-lined furnace is often the most cost-effective solution for general-purpose applications.
Versatility vs. Specialization
A furnace designed for a wide array of applications (e.g., material research, alloying, glass formation, ashing) offers flexibility. However, a furnace built for a single purpose, like ashing samples, may include features like enhanced ventilation that make it far more effective and safe for that specific task.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Once you have a clear technical specification based on the pillars above, you are equipped to evaluate manufacturers. Use your specification as a checklist to guide your conversations and comparisons.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature material research: Prioritize furnaces with heat-resistant ceramic or alumina fiber insulation and precise, programmable temperature controllers.
- If your primary focus is ashing or burning off organics: Select a furnace specifically designed with robust ventilation to handle corrosive fumes and ensure complete combustion.
- If your primary focus is processing sensitive materials: Confirm the furnace provides the controlled atmosphere capabilities you need, including reliable seals and gas inlets/outlets.
- If your primary focus is budget-conscious general lab use: A standard ceramic-body furnace from a reputable manufacturer offers the best balance of performance, versatility, and cost.
By defining your need before you evaluate the provider, you ensure the equipment serves the work, not the other way around.
Summary Table:
| Consideration | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Define max/min temperatures and ensure reliable sustainment for consistent results. |
| Chamber Size | Match to sample size to avoid energy waste; balance efficiency and capacity. |
| Materials | Choose ceramic for insulation, quartz for corrosion resistance, or metal for rapid heating. |
| Atmosphere Control | Decide if inert gas (e.g., nitrogen) is needed for sensitive processes like brazing. |
| Trade-offs | Balance energy efficiency vs. volume, specialized materials vs. cost, and versatility vs. specialization. |
Ready to find the perfect muffle furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















