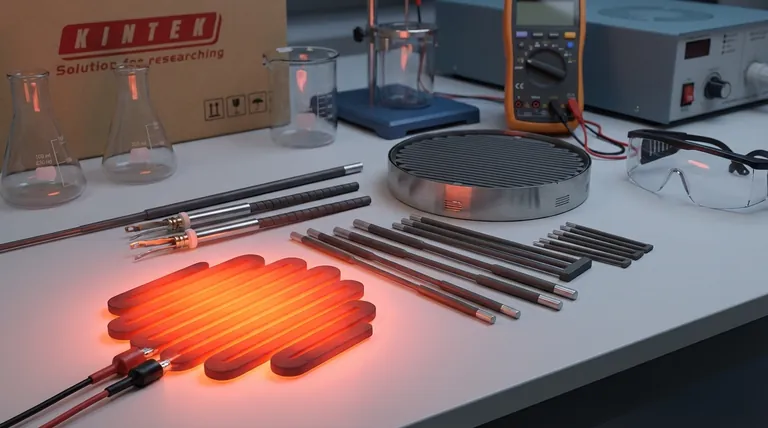
From a technical standpoint, the safety advantages of ceramic heating elements are rooted in their fundamental material properties. They are exceptional electrical insulators, which dramatically reduces the risk of shocks and short circuits. Furthermore, their non-flammable nature and ability to withstand extreme temperatures without melting or deforming minimize the potential for fires and thermal runaway.
The safety of a ceramic heater is not an added feature, but an inherent consequence of its material science. Unlike metal elements that can corrode and fail, ceramics provide intrinsic electrical and thermal stability, ensuring a safer operational lifespan.
The Foundation of Ceramic Safety: Material Properties
To truly understand why ceramic heaters are safer, we must look beyond features and examine the core characteristics of the material itself. These properties create a system that is inherently resistant to common failure modes.
Superior Electrical Insulation
Ceramics are excellent electrical insulators. This means they do not conduct electricity.
This property provides a robust, built-in safety layer. Even if the internal heating wire were to become damaged, the ceramic body prevents electricity from escaping, mitigating the risk of electrical shock or short circuits.
High-Temperature Stability and Fire Resistance
Ceramic elements have extremely high melting points and do not burn. They can operate at very high temperatures without warping, degrading, or changing state.
This stability is critical for preventing two major hazards: fires and thermal runaway. Because the material is non-flammable, it will not ignite. Its ability to handle high heat prevents the uncontrolled temperature increases that can damage equipment or spark a fire.
Long-Term Structural Integrity
Ceramic materials are highly resistant to corrosion, oxidation, and abrasion.
This durability is a crucial, though often overlooked, safety advantage. An element that doesn't rust or degrade over time maintains its structural and electrical integrity, making it far less likely to fail in a hazardous way.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Ceramic vs. Metal
The safety benefits of ceramic become even clearer when contrasted with traditional metallic heating elements. The way these two materials age and fail is fundamentally different.
The Failure Mode of Metal Elements
Metal heating elements are susceptible to oxidation and thermal fatigue, especially when cycled repeatedly to high temperatures.
Over time, this can cause the metal to become brittle, crack, or corrode. Such failures can lead to dangerous short circuits or create hot spots that pose a significant fire risk, necessitating more frequent inspection and replacement.
The Robust Nature of Ceramic
Ceramic elements are largely immune to the oxidation and corrosion that plagues metal. Their rigid structure is not prone to the same thermal fatigue.
This ensures a significantly longer, more reliable service life. A longer functional lifespan means the component maintains its original safety specifications for a greater duration, reducing the chance of an age-related failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal will determine which safety aspect is most critical.
- If your primary focus is preventing electrical hazards: Ceramic's inherent insulation makes it the superior choice, especially in applications like water heaters or equipment where user contact is possible.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature operation: The stability and high melting point of ceramic elements, used in applications like industrial furnaces and soldering irons, prevent material failure and reduce fire risk.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Ceramic's resistance to corrosion and fatigue ensures a longer, safer operational life with lower maintenance, making it ideal for critical systems in HVAC or manufacturing.
Ultimately, choosing a ceramic heating element is a decision to engineer safety into the core of your system, not just treat it as an afterthought.
Summary Table:
| Safety Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Superior Electrical Insulation | Reduces risk of shocks and short circuits |
| High-Temperature Stability | Prevents fires and thermal runaway |
| Long-Term Structural Integrity | Resists corrosion and ensures reliable lifespan |
Upgrade your lab's safety and efficiency with KINTEK's advanced heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing reliability and reducing hazards. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















