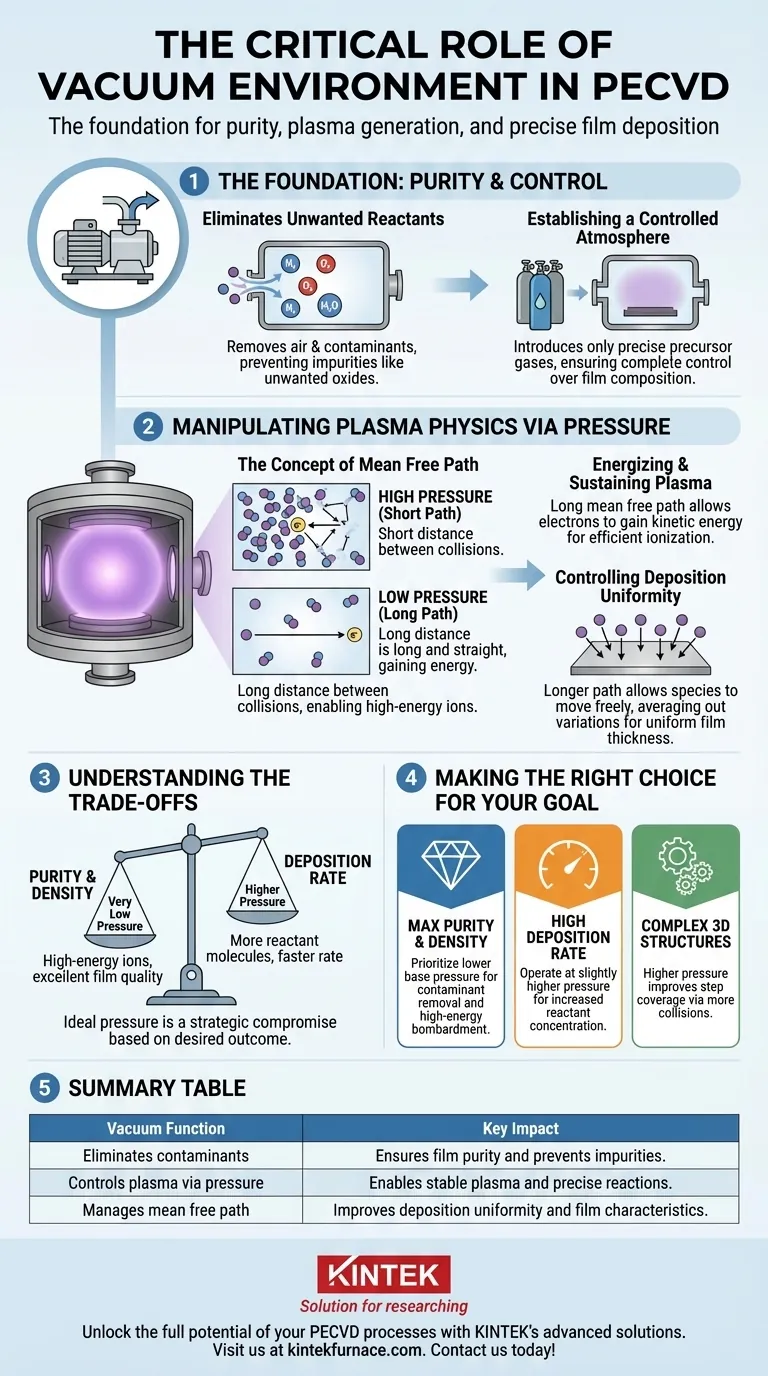
In Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD), the vacuum environment is not just a prerequisite; it is the entire foundation for the process. The vacuum serves two primary, non-negotiable functions: it eliminates unwanted atmospheric contaminants that would otherwise compromise the film's purity, and it provides the low-pressure conditions necessary to generate and sustain a stable, effective plasma. This highly controlled environment is what enables the precise chemical reactions needed to form high-quality thin films on a substrate.
A common misconception is that the vacuum's only job is to remove air. In reality, controlling the vacuum level is the primary method for manipulating the plasma's physical properties, which directly dictates the quality, uniformity, and characteristics of the final deposited film.

The Foundation: Purity and Control
The initial pump-down of a PECVD chamber creates a clean slate, which is essential for any high-precision material deposition. This is about controlling what is allowed to participate in the reaction.
Eliminating Unwanted Reactants
The air around us is a mixture of reactive gases, primarily nitrogen, oxygen, and water vapor. If these molecules were present during deposition, they would inevitably incorporate themselves into the growing film, creating contaminants like unwanted oxides or nitrides.
These impurities severely degrade the desired electrical, optical, or mechanical properties of the film, rendering the process ineffective. The vacuum acts as a chemical "cleanroom," ensuring that the only species present are the ones you intentionally introduce.
Establishing a Controlled Atmosphere
Once the chamber is evacuated to a low "base pressure," specific precursor gases can be introduced in precise, measured amounts. The vacuum guarantees that the process environment consists solely of these chosen gases. This gives the operator complete control over the stoichiometry and chemical composition of the resulting thin film.
Manipulating Plasma Physics via Pressure
After establishing a pure environment, the vacuum level is adjusted to a specific "process pressure." This pressure is a critical variable that directly governs the physics of the plasma.
The Concept of Mean Free Path
Mean free path is the average distance a particle, such as an electron or a gas molecule, travels before it collides with another particle. This distance is inversely proportional to pressure.
At high pressure (like atmospheric pressure), the mean free path is extremely short. At low pressure (in a vacuum), particles are much farther apart, so the mean free path is significantly longer.
Energizing and Sustaining the Plasma
A long mean free path is crucial for creating plasma. In PECVD, an electric field accelerates free electrons. A long mean free path allows these electrons to gain a large amount of kinetic energy before colliding with a gas molecule.
When an electron with sufficient energy strikes a gas molecule, it can knock another electron loose, creating a positive ion. This process, known as ionization, is what creates and sustains the plasma. If the pressure were too high and the mean free path too short, electrons would collide too frequently, fail to gain enough energy, and be unable to create a stable plasma.
Controlling Deposition Uniformity
The mean free path also influences how reactive chemical species travel from the plasma to the substrate. A longer path allows these species to move more freely throughout the chamber before landing on the substrate surface. This helps average out any local variations in plasma density, leading to a more uniform and consistent film thickness across the entire wafer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of process pressure is not about finding the lowest possible value; it is a strategic compromise based on the desired outcome.
Purity and Density vs. Deposition Rate
A very low process pressure (high vacuum) results in a long mean free path, which is excellent for creating high-energy ions that can produce very pure and dense films. However, a lower pressure also means there are fewer reactant gas molecules available, which can significantly slow down the deposition rate.
Plasma Stability
While a vacuum is essential, a pressure that is too low can make it difficult to strike and sustain a dense, stable plasma. There needs to be a sufficient number of gas molecules to serve as a target for ionization. The ideal pressure is a balance point: low enough for a useful mean free path, but high enough to maintain a robust plasma.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal vacuum level is not a single value but depends entirely on the desired film properties. When setting up a PECVD process, consider the primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum film purity and density: Prioritize a lower base pressure to remove contaminants and a process pressure that creates a long mean free path for high-energy ion bombardment.
- If your primary focus is a high deposition rate: You may need to operate at a slightly higher process pressure to increase the concentration of reactant species, accepting a potential trade-off in film quality.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D structures: A higher pressure (and shorter mean free path) may be beneficial, as it promotes more collisions and less directional deposition, improving how well the film covers vertical sidewalls.
Ultimately, mastering the vacuum environment is the key to controlling the outcome of the PECVD process itself.
Summary Table:
| Vacuum Function | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Eliminates contaminants | Ensures film purity and prevents impurities |
| Controls plasma via pressure | Enables stable plasma and precise reactions |
| Manages mean free path | Improves deposition uniformity and film characteristics |
Unlock the full potential of your PECVD processes with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like CVD/PECVD Systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for superior thin-film deposition. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties
- What are the advantages of using CVD? Achieve High-Purity, Conformal Thin Films for Your Applications
- How is silicon dioxide deposited from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality SiO2 Films
- What are the classifications of CVD based on vapor characteristics? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- What is plasma-deposited silicon nitride, and what are its properties? Discover Its Role in Solar Cell Efficiency



















