In vacuum induction melting, electromagnetic stirring is an inherent and crucial secondary effect of the induction heating process. It actively circulates the molten metal, transforming a simple melting pot into a dynamic refining vessel. This forced convection is essential for ensuring the molten bath has a uniform temperature and chemical composition, which directly impacts the quality and consistency of the final alloy.
While induction's primary purpose is to generate heat, its secondary effect—electromagnetic stirring—is what enables true metallurgical control. It moves the process beyond simple melting to active refining, guaranteeing the homogeneity and cleanliness required for high-performance materials.

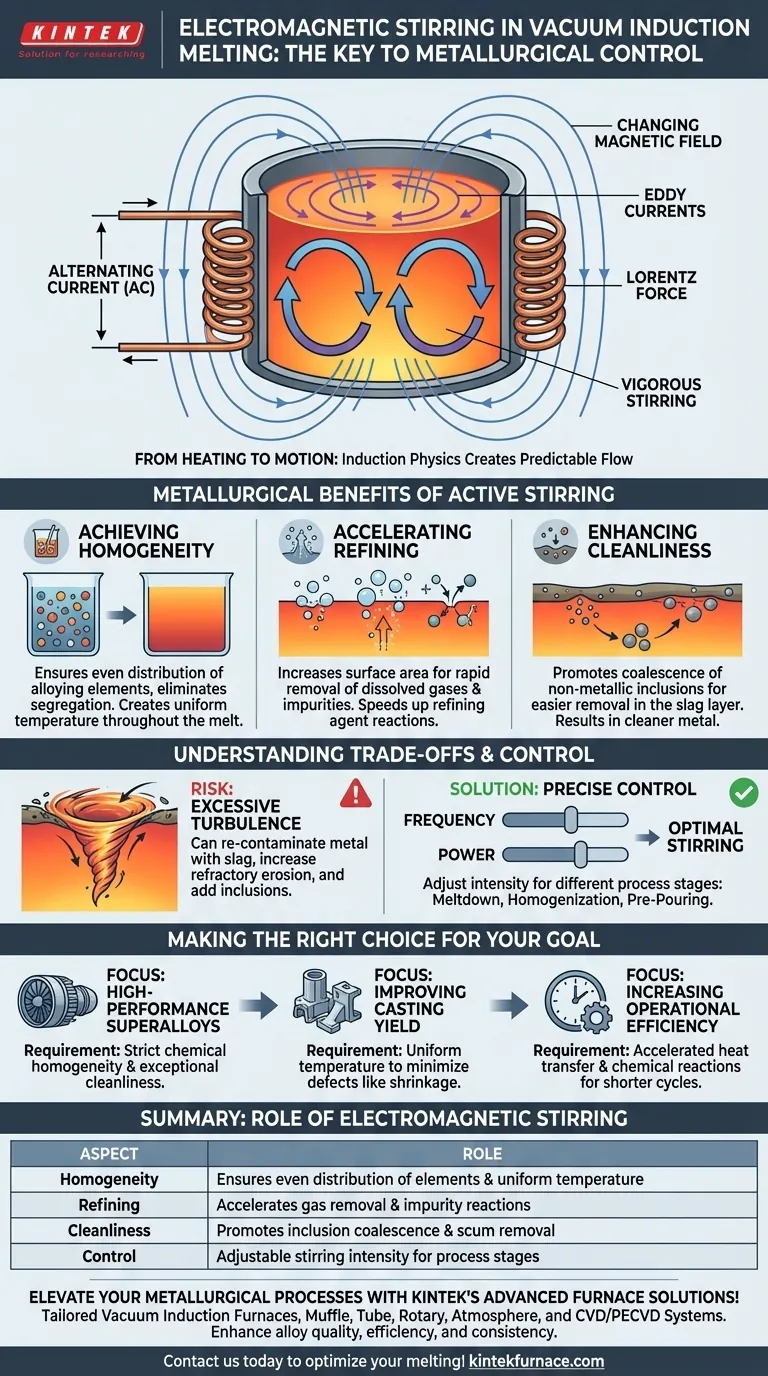
The Core Principle: From Heating to Motion
The same physics that melts the metal also stirs it. Understanding this connection is key to appreciating its role in producing high-quality alloys.
How Induction Creates Stirring
An induction furnace uses a powerful alternating current (AC) passed through a copper coil. This creates a rapidly changing magnetic field that penetrates the metal charge inside. This field, in turn, induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, within the metal. The metal's natural resistance to these eddy currents generates intense heat, causing it to melt.
However, the interaction between the coil's magnetic field and the eddy currents in the molten metal also produces a physical force (a Lorentz force). This force pushes the liquid metal, creating a deliberate and predictable flow pattern. The metal is typically pushed down the center and up along the sides of the crucible, resulting in a continuous, vigorous stirring action.
The Importance of a Controlled Flow
This natural stirring is not a random side effect; it is a controllable process parameter. In modern furnaces, operators can adjust the frequency and power of the electrical current. This allows them to precisely manage the intensity of the stirring, optimizing it for different alloys and for different stages of the melting and refining cycle.
The Metallurgical Benefits of Active Stirring
The constant circulation of the melt provides several critical advantages that are impossible to achieve in a static (un-stirred) molten bath.
Achieving Absolute Homogeneity
Without stirring, heavier alloying elements would sink and lighter ones would float, leading to segregation. Electromagnetic stirring powerfully blends the entire molten bath, ensuring that every element is evenly distributed.
This also applies to temperature. Stirring eliminates hot and cold spots, creating a uniform temperature throughout the melt. This thermal and compositional homogeneity is the foundation for producing an alloy with predictable, consistent properties.
Accelerating Refining and Purification
Stirring dramatically increases the surface area of the melt that is exposed to the vacuum. This accelerates the removal of undesirable dissolved gases (like oxygen and nitrogen) and elements with high vapor pressure.
It also ensures that any refining agents or slag added to the surface are quickly mixed into the melt, speeding up chemical reactions that capture and remove impurities.
Enhancing Melt Cleanliness
The stirring motion helps smaller, non-metallic inclusions (impurities) collide and coalesce into larger particles. These larger, lighter particles are then more easily floated to the surface, where they can be trapped by the slag layer and removed. This process of scum removal results in a cleaner, higher-quality metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential, electromagnetic stirring must be properly managed. It is not a simple case of "more is better."
The Risk of Excessive Turbulence
If the stirring action is too violent, it can create a turbulent and unstable melt surface. This can lead to a vortex that pulls the surface slag layer back down into the clean metal, re-contaminating it.
Excessively strong stirring can also accelerate the erosion of the furnace's ceramic refractory lining, increasing maintenance costs and the risk of refractory particles entering the melt as inclusions.
The Need for Precise Control
The goal is not maximum stirring, but optimal stirring. Different phases of the process require different levels of agitation. For example, a gentle stir may be used during initial meltdown, followed by a more vigorous stir to ensure homogenization, and then a calmer phase just before pouring to allow any remaining inclusions to float to the surface. This level of control is a hallmark of modern vacuum induction furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the role of stirring allows you to tailor the process to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is producing high-performance superalloys: Controlled stirring is non-negotiable for achieving the strict chemical homogeneity and exceptional cleanliness these materials demand.
- If your primary focus is improving casting yield: Leveraging stirring to maintain a uniform temperature will minimize casting defects like shrinkage and porosity, leading to fewer rejected parts.
- If your primary focus is increasing operational efficiency: Using stirring to accelerate heat transfer and chemical reactions will shorten the overall melt cycle, increasing furnace throughput.
Ultimately, mastering electromagnetic stirring elevates the process from simply melting metal to precisely engineering its final properties.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of Electromagnetic Stirring |
|---|---|
| Homogeneity | Ensures even distribution of elements and uniform temperature |
| Refining | Accelerates gas removal and impurity reactions |
| Cleanliness | Promotes inclusion coalescence and scum removal |
| Control | Adjustable stirring intensity for different process stages |
Elevate your metallurgical processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored vacuum induction furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing alloy quality, efficiency, and consistency. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your vacuum induction melting and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















