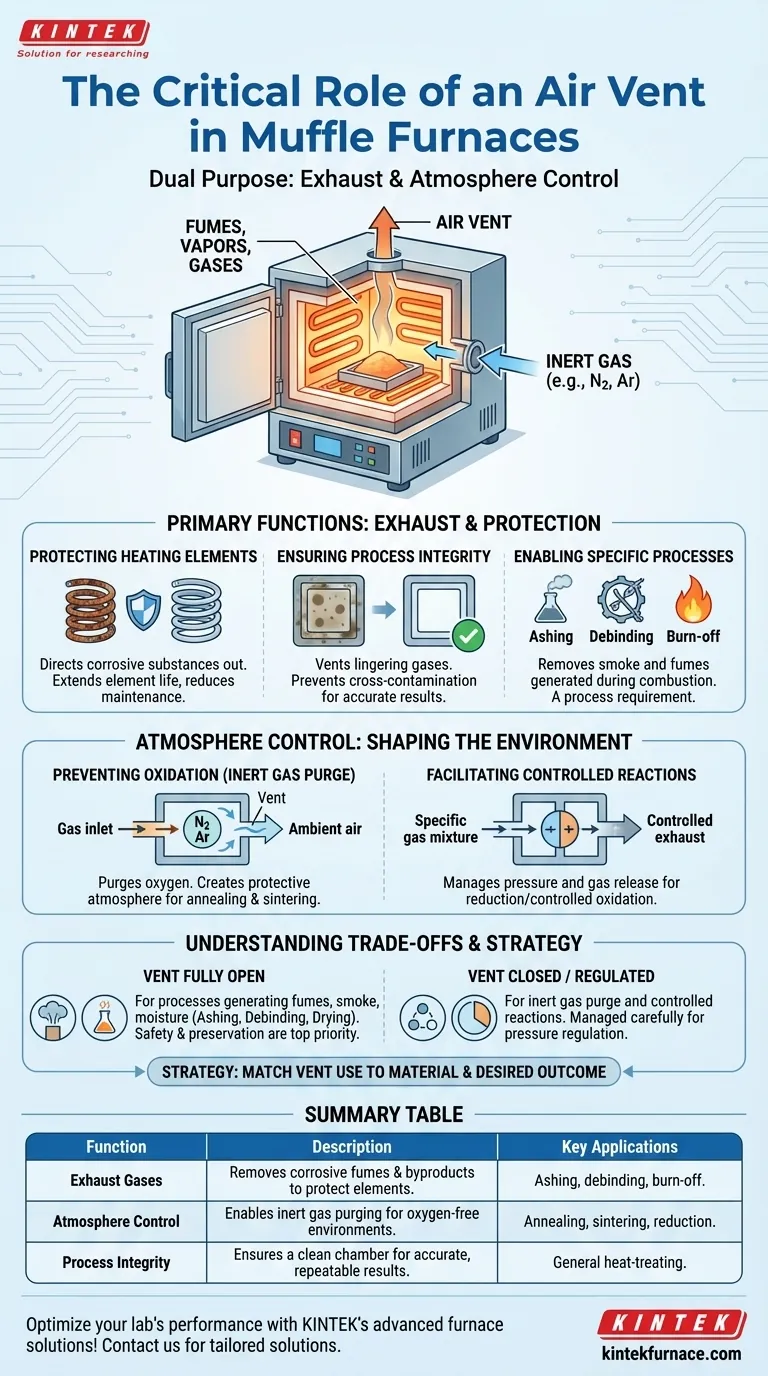
At its core, the air vent in a muffle furnace serves a critical dual purpose: it exhausts potentially corrosive gases generated during heating, and it enables control over the internal atmosphere. This protects the furnace's vital components, like the heating elements, from oxidation and ensures the integrity of the material being processed.
The air vent is more than just an exhaust port; it is a fundamental tool for controlling the chemical environment within the furnace. Mastering its use is essential for achieving precise, repeatable results and maximizing the equipment's lifespan.

The Primary Functions of the Air Vent
A muffle furnace operates at extreme temperatures, causing materials to release vapors, fumes, and gases. The air vent is the primary mechanism for managing these byproducts.
Protecting the Heating Elements
Many samples release volatile or corrosive substances when heated. These gases can attack the furnace's heating elements, leading to rust, oxidation, and premature failure.
The air vent directs these harmful fumes out of the chamber, significantly extending the operational life of the furnace and reducing maintenance costs.
Ensuring Process Integrity
Gases produced during a heating cycle can linger and contaminate the furnace lining. This can interfere with subsequent processes or cross-contaminate future samples.
By thoroughly venting the chamber, you ensure that each heat-treating run starts with a clean, neutral environment, which is critical for scientific accuracy and manufacturing consistency.
Enabling Specific Processes
Certain applications, such as ashing, debinding, or burn-off, are designed specifically to remove organic material or binders through combustion.
These processes generate significant amounts of smoke and fumes that must be removed. An open air vent is not just recommended for these applications; it is a requirement for the process to succeed.
Beyond Exhaust: The Vent as an Atmosphere Control Tool
While its protective function is vital, the air vent's more advanced role is in actively shaping the environment for sophisticated material treatments. This is where the furnace transitions from a simple oven to a precise metallurgical instrument.
Preventing Unwanted Oxidation
Many metals and materials are highly reactive to oxygen at high temperatures, leading to unwanted surface oxidation that can ruin the component's properties.
By using the vent in conjunction with a gas inlet port, you can purge the chamber of oxygen. A continuous flow of an inert gas, like nitrogen or argon, pushes the ambient air out through the vent, creating a protective, oxygen-free atmosphere for processes like annealing or sintering.
Facilitating Controlled Reactions
Some advanced processes require a specific gas mixture to achieve a desired chemical reaction on a material's surface, such as reduction (removing oxygen) or controlled oxidation.
The air vent helps manage this delicate balance. It allows for the controlled release of pressure and exhaust gases while a specific gas mixture is fed into the chamber, ensuring the internal atmosphere remains consistent with process parameters.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision to open, close, or regulate the vent is not arbitrary; it is determined entirely by the goal of your process. Using it incorrectly can damage the furnace or compromise your results.
When to Keep the Vent Fully Open
Always keep the vent open for any process that you know will generate fumes, smoke, or moisture. This includes ashing, debinding, drying, and any heat treatment of materials with coatings, oils, or unknown contaminants. Safety and equipment preservation are the top priorities here.
When to Keep the Vent Closed or Regulated
For processes that require a controlled atmosphere, the vent must be managed carefully. It is often closed initially while the chamber is purged with an inert gas. Afterward, it may be opened slightly to allow for pressure regulation without letting a significant amount of oxygen back into the chamber.
Matching Vent Strategy to Your Application
Your approach to using the air vent should be dictated by your specific material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is ashing, debinding, or burning off substances: You must keep the vent open to safely exhaust byproducts and protect the furnace interior.
- If your primary focus is annealing or treating oxygen-sensitive metals: You must use the vent as part of an inert gas purging system to create an oxygen-free environment.
- If your primary focus is general heat-treating of clean, stable materials: It is often wise to leave the vent slightly ajar as a precaution against unexpected off-gassing.
Properly managing the air vent transforms it from a simple part into a powerful tool for controlling your process outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Function | Description | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Exhaust Gases | Removes corrosive fumes and byproducts to protect heating elements and prevent contamination. | Ashing, debinding, burn-off processes. |
| Atmosphere Control | Enables purging with inert gases to create oxygen-free environments for sensitive material treatments. | Annealing, sintering, reduction processes. |
| Process Integrity | Ensures a clean chamber for accurate, repeatable results by venting contaminants. | General heat-treating of materials. |
Optimize your lab's performance with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can elevate your processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















