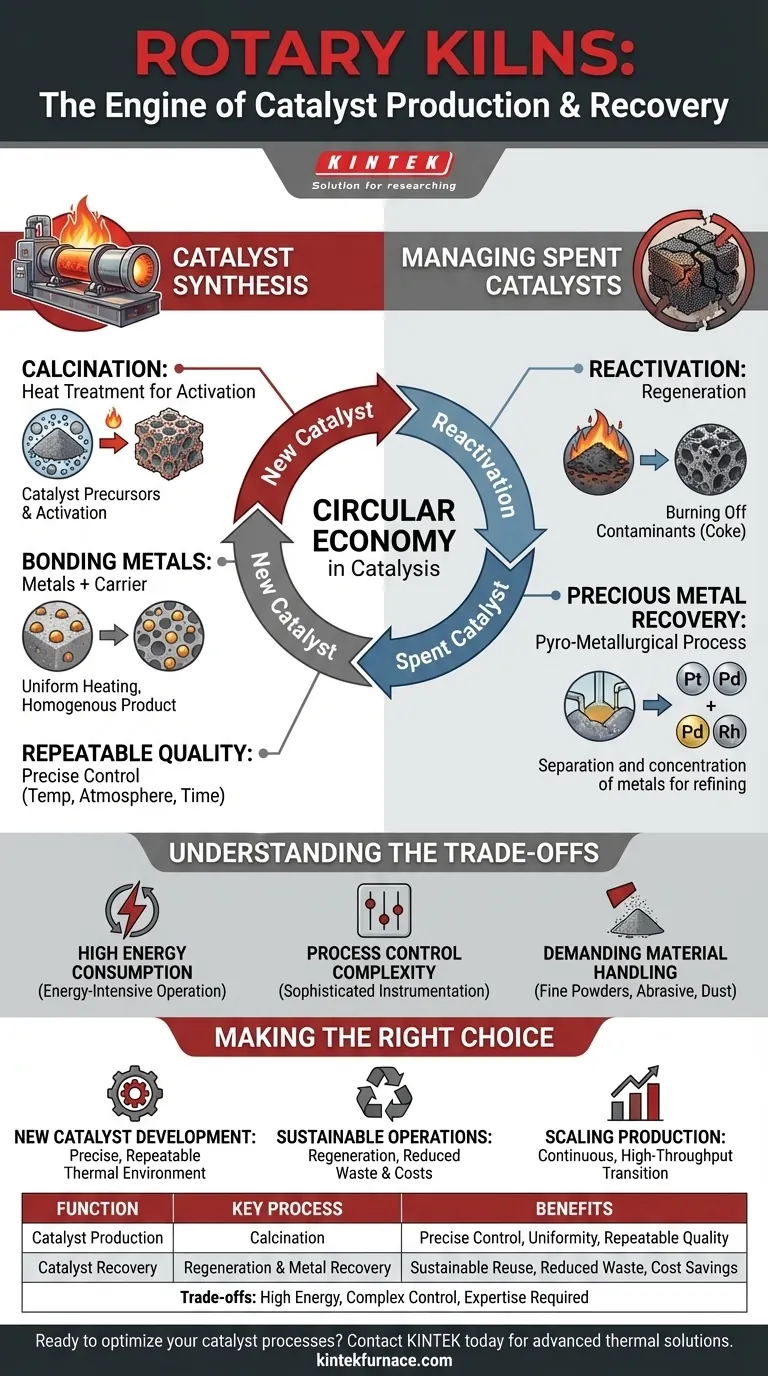
In the world of industrial chemistry, rotary kilns are the essential thermal processing units that drive both the creation and renewal of catalysts. They perform two primary functions: producing new catalysts through a high-temperature process called calcination, and sustainably managing spent catalysts by recovering precious metals or regenerating them for reuse. This dual role makes them indispensable to the entire catalyst lifecycle.
Catalysts are high-value assets with a limited operational life. The core value of a rotary kiln is its ability to provide the precise, controlled thermal environment required to not only synthesize catalysts but also to recover value from them, making it a cornerstone of a sustainable, circular economy in catalysis.

The Kiln's Role in Catalyst Synthesis
The creation of a new, effective catalyst depends on achieving a specific chemical structure and bond. A rotary kiln provides the exact environment needed to accomplish this at an industrial scale.
The Principle of Calcination
Calcination is a heat treatment process used to induce a chemical change or phase transition in a solid material. In catalyst production, it is the critical step for activating the material.
The kiln heats the catalyst precursor to a precise temperature, often driving off water, decomposing salts, and creating the desired porous structure and active metallic sites.
Bonding Metals to a Carrier
Most catalysts consist of active metal components, like platinum or palladium, distributed on a stable, porous support material called a carrier.
During calcination in a rotary kiln, the high temperature firmly bonds these active metals to the carrier. The slow, tumbling action of the kiln ensures every particle is heated uniformly, resulting in a homogenous and highly effective final product.
Ensuring Repeatable Quality
The effectiveness of a catalyst is highly sensitive to its production conditions. Rotary kilns offer precise control over key variables like temperature profile, gas atmosphere, and material residence time.
This level of control ensures that every batch of catalyst meets the exact same specifications, delivering the repeatable, high-quality performance required for demanding industrial applications.
Managing Spent Catalysts for a Circular Economy
Over time, catalysts become "spent" or deactivated by contaminants. Rotary kilns provide a thermal pathway to either restore them or recover their valuable components, minimizing waste and economic loss.
Reactivation and Regeneration
For many catalysts, deactivation is caused by the buildup of carbon (coke) or other organic residues on the active surfaces.
A rotary kiln can perform regeneration by heating the spent catalyst in a controlled atmosphere containing oxygen. This process carefully burns off the contaminants without damaging the underlying catalyst structure, restoring its activity for reuse.
Precious Metal Recovery
When a catalyst cannot be regenerated, it is often processed to recover the valuable metals it contains. This is especially true for catalysts using platinum, palladium, rhodium, or other precious metals.
The rotary kiln facilitates pyro-metallurgical recovery. It uses high temperatures to process the spent material, separating and concentrating the valuable metals so they can be refined and used to produce new catalysts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable, rotary kilns are not without their operational complexities. A clear understanding of the trade-offs is crucial for effective implementation.
High Energy Consumption
Operating at the high temperatures required for calcination and metal recovery is energy-intensive. Energy costs represent a significant portion of the operational budget for any kiln-based process.
Process Control Complexity
Achieving the precise thermal and atmospheric control needed for sensitive catalysts requires sophisticated instrumentation, control systems, and operational expertise. It is not a simple "set and forget" operation.
Demanding Material Handling
Catalyst materials can be fine powders, abrasive, or prone to creating dust. The design of the kiln and its associated material handling systems must account for these properties to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your strategic objective will determine which aspect of the rotary kiln's capability is most critical to your operation.
- If your primary focus is new catalyst development: The kiln's ability to provide a precisely controlled and repeatable thermal environment is paramount for optimizing synthesis.
- If your primary focus is sustainable operations: The key is the kiln's role in regenerating spent catalysts and recovering precious metals, which directly reduces waste and raw material costs.
- If your primary focus is scaling production: The continuous, high-throughput nature of rotary kilns makes them the ideal technology for transitioning from lab-scale synthesis to full industrial production.
Ultimately, mastering the rotary kiln's function is fundamental to managing the complete, circular lifecycle of industrial catalysts.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Process | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Catalyst Production | Calcination | Precise temperature control, uniform heating, repeatable quality |
| Catalyst Recovery | Regeneration & Metal Recovery | Sustainable reuse, reduced waste, cost savings |
| Trade-offs | High energy use, complex control | Requires expertise but offers high throughput |
Ready to optimize your catalyst processes with advanced thermal solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your catalyst production and recovery efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















