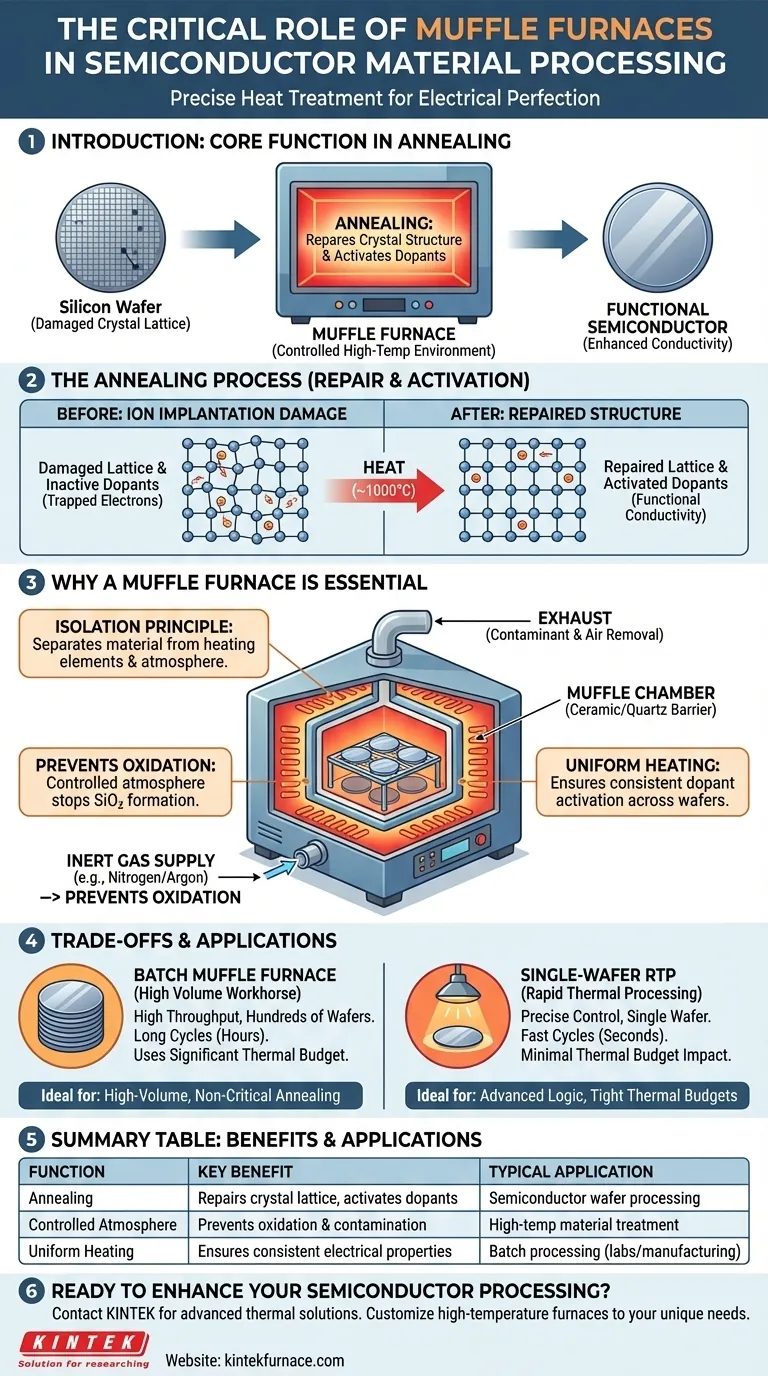
In semiconductor processing, a muffle furnace performs a critical heat treatment step called annealing. This process uses precise, uniform high temperatures in a controlled atmosphere to repair the crystalline structure of silicon wafers and activate implanted dopants, which is essential for achieving the required electrical conductivity and performance of the final microchip.
The role of a muffle furnace is not just to heat the semiconductor material, but to do so in an exceptionally clean and controlled environment. Its key advantage is isolating the material from both atmospheric oxygen and heating-element contaminants, preventing defects that would otherwise render the electronic device useless.

The Core Function: Annealing for Electrical Perfection
In semiconductor fabrication, raw silicon wafers undergo numerous steps that damage their perfect crystal structure. The muffle furnace is a primary tool used to reverse this damage and prepare the material electrically.
Repairing the Crystal Lattice
Processes like ion implantation, where atoms are fired into the silicon to change its conductivity, are violent at a microscopic level. They shatter the orderly silicon crystal lattice, creating defects that trap electrons and hinder current flow.
Annealing in a muffle furnace heats the wafer to a high temperature (around 1000°C for silicon). This gives the displaced silicon atoms enough energy to move back into their proper positions, effectively repairing the crystal structure.
Activating Dopants
The dopant atoms introduced during implantation are useless until they are part of the silicon crystal's structure. Annealing allows these dopants to settle into the lattice, where they can donate or accept electrons. This process, known as dopant activation, is what turns a non-conductive region of silicon into a functional part of a transistor.
Why a Muffle Furnace is Essential
While many furnaces can reach high temperatures, the specific design of a muffle furnace makes it uniquely suited for the stringent demands of semiconductor manufacturing.
The Principle of Isolation
The term "muffle" refers to the inner chamber or tube (often made of ceramic or quartz) that holds the semiconductor wafers. This muffle acts as a physical barrier, separating the wafers from the furnace's heating elements and the outside atmosphere.
This isolation is critical for preventing microscopic particles from the heating elements from contaminating the pristine surface of the silicon wafers.
Preventing Catastrophic Oxidation
At the high temperatures required for annealing, silicon reacts instantly with any available oxygen to form silicon dioxide (SiO₂)—an insulator. Uncontrolled oxidation would ruin the wafer's electrical properties.
The sealed muffle allows operators to pump out the ambient air and fill the chamber with an inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon. This controlled atmosphere prevents oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions, ensuring the material's integrity.
Ensuring Uniform Temperature
A key function of the furnace is to provide extremely uniform heat distribution across every wafer in a batch. It achieves this through a combination of radiative and convective heat transfer. Any temperature variation could cause inconsistent dopant activation or crystal repair, leading to failed devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While foundational, muffle furnaces are part of a larger toolkit, and their use involves specific trade-offs.
Batch Processing vs. Single-Wafer RTP
Traditional muffle furnaces are batch tools, processing hundreds of wafers at once in long, slow cycles (often several hours). This provides high throughput for many applications.
However, for advanced microchips, the long heating time can be a disadvantage. Modern alternatives like Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) heat a single wafer in seconds, offering more precise control but lower overall throughput.
Thermal Budget Constraints
Every high-temperature step "spends" from the wafer's total "thermal budget." Exceeding this budget can cause previously placed dopants to diffuse out of position, blurring the microscopic circuit patterns. The long cycles in a muffle furnace consume a large portion of this budget.
Purity and Contamination Risks
Despite the muffle's isolation, the furnace chamber itself must be maintained with extreme diligence. Any impurities within the chamber or the inert gas supply can still introduce killer defects onto the wafers, making process control a constant challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal process depends entirely on the technical requirements and economic goals of the specific manufacturing step.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, non-critical annealing: The high throughput and reliability of a batch muffle furnace make it a cost-effective and powerful workhorse.
- If your primary focus is advanced logic with tight thermal budgets: Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) is often preferred for its precise control and minimal impact on dopant diffusion.
- If your primary focus is materials research and development: A versatile muffle furnace with precise atmosphere control is an indispensable tool for testing material properties under various controlled conditions.
Ultimately, mastering thermal processing is fundamental to translating raw silicon into the high-performance electronic devices that power our world.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Repairs crystal lattice and activates dopants | Semiconductor wafer processing |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation and contamination | High-temperature material treatment |
| Uniform Heating | Ensures consistent electrical properties | Batch processing in labs and manufacturing |
Ready to enhance your semiconductor processing with reliable thermal solutions? Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum Furnaces, can be customized to meet your unique needs—ensuring precise temperature control, contamination-free environments, and superior performance for your laboratory or production line. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















