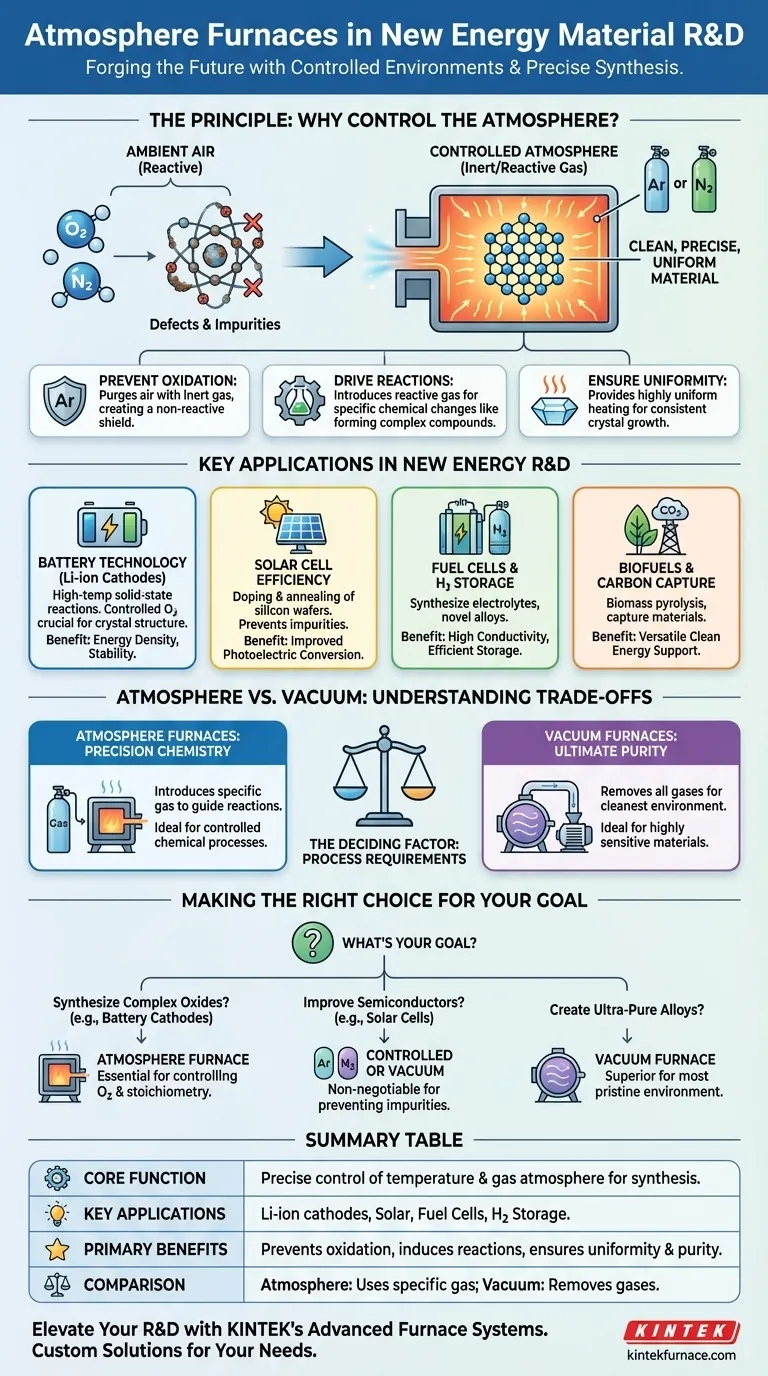
At their core, atmosphere furnaces are the controlled environments where the next generation of energy materials is forged. They are indispensable tools in research and development, enabling the synthesis of high-performance components for lithium-ion batteries, solar cells, fuel cells, and hydrogen storage systems by providing precise control over temperature and atmospheric chemistry.
The central challenge in creating new energy materials is achieving perfect atomic-level structure. Atmosphere furnaces solve this by replacing ambient air with a meticulously controlled gas environment, preventing defects and guiding the chemical reactions necessary to build materials with superior performance.
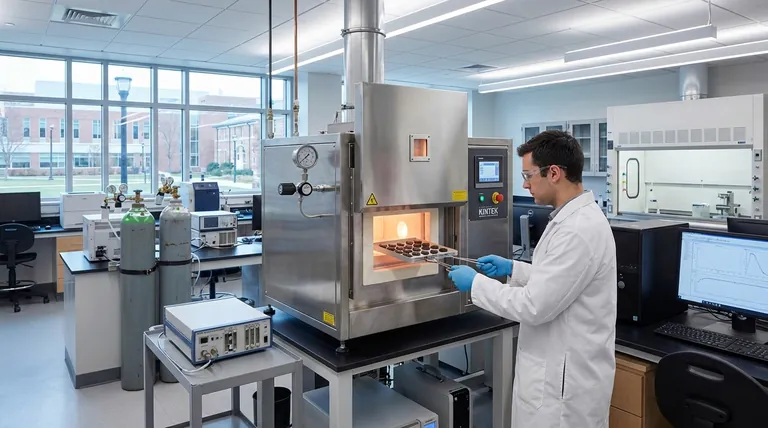

The Principle: Why Control the Atmosphere?
Modern energy materials demand a level of structural and chemical purity that is impossible to achieve in open air. The gases in our atmosphere, primarily nitrogen and oxygen, are highly reactive at the high temperatures required for material synthesis.
Preventing Unwanted Oxidation and Contamination
At high temperatures, most materials will readily react with oxygen. This oxidation can create impurities, degrade performance, and alter the fundamental properties of the material you are trying to create.
An atmosphere furnace purges the processing chamber of air and replaces it with an inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen. This creates a "clean" and non-reactive environment, protecting the material and ensuring its chemical purity.
Driving Specific Chemical Reactions
Beyond just preventing reactions, these furnaces can also be used to induce specific chemical changes. By introducing a carefully measured amount of a reactive gas, researchers can create a reducing or oxidizing atmosphere.
This control is critical for forming complex compounds, like the cathode materials in lithium-ion batteries. The furnace becomes an active participant in the chemical reaction, not just a passive heater.
Ensuring Structural Uniformity and Crystallinity
The performance of an energy material is directly tied to its crystal structure. An atmosphere furnace provides highly uniform heating, which is essential for consistent crystal growth and minimizing physical defects.
This structural integrity ensures, for example, that ions can move freely through a battery electrode or that electrons are efficiently generated in a solar cell, directly impacting efficiency and lifespan.
Key Applications in New Energy R&D
The ability to precisely manipulate the thermal and chemical environment makes these furnaces vital across the new energy landscape.
Advancing Battery Technology
For lithium-ion battery cathodes, atmosphere furnaces facilitate high-temperature solid-state reactions. Controlling the oxygen level is crucial for forming the correct crystal structure, which dictates the material's energy density, charge rate, and stability.
Enhancing Solar Cell Efficiency
In solar cell production, furnaces are used for critical steps like the doping and annealing of silicon wafers. A controlled atmosphere prevents the introduction of impurities that would disrupt the semiconductor's electronic properties, thereby improving the cell's photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Developing Fuel Cells and Hydrogen Storage
These furnaces are also used to synthesize the specialized materials required for fuel cells and hydrogen storage. This includes creating electrolyte materials with high ionic conductivity and novel alloys that can safely and efficiently store hydrogen.
Exploring Carbon Capture and Biofuels
Beyond electricity, atmosphere furnaces support research into biomass pyrolysis for creating biofuels and developing materials for carbon capture technologies, proving their versatility in the broader clean energy sector.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Atmosphere vs. Vacuum
While often discussed together, atmosphere furnaces and vacuum furnaces serve distinct purposes based on the same core principle of atmospheric control.
Atmosphere Furnaces: For Precision Chemistry
The primary strength of an atmosphere furnace is its ability to introduce and maintain a specific gas environment. It is the ideal tool when a process requires a particular inert, oxidizing, or reducing gas to guide a chemical reaction.
Vacuum Furnaces: For Ultimate Purity
A vacuum furnace works by removing virtually all atmospheric gases. It provides the cleanest possible environment and is essential when a material is so sensitive that even trace amounts of an inert gas could cause contamination or unwanted effects.
The Deciding Factor: Process Requirements
The choice between them is not about which is "better," but which is right for the task. If your goal is to leverage a specific gas for a reaction, an atmosphere furnace is necessary. If your goal is to eliminate all gaseous influence, a vacuum furnace is the correct choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal processing method depends entirely on the specific material you are creating and the properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing complex oxides (like battery cathodes): An atmosphere furnace is essential for precisely controlling the oxygen partial pressure to achieve the correct stoichiometry and crystal phase.
- If your primary focus is improving semiconductor properties (like in solar cells): A controlled atmosphere or vacuum environment is non-negotiable for annealing and doping processes to prevent performance-killing impurities.
- If your primary focus is creating ultra-pure alloys or materials highly sensitive to any gas: A vacuum furnace is often the superior choice to create the most pristine processing environment possible.
Ultimately, mastering the thermal processing environment is the key to unlocking the full potential of the next generation of energy materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Provides precise control over temperature and gas atmosphere for material synthesis. |
| Key Applications | Lithium-ion battery cathodes, solar cell doping/annealing, fuel cells, hydrogen storage. |
| Primary Benefits | Prevents oxidation, induces specific reactions, ensures structural uniformity and purity. |
| Comparison | Atmosphere furnaces use specific gases for reactions; vacuum furnaces remove gases for ultimate purity. |
Ready to elevate your new energy material R&D with tailored thermal processing solutions?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace systems designed for laboratories like yours. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With strong deep customization capabilities, we can precisely meet your unique experimental needs, whether you're developing battery materials, solar cells, or other energy innovations.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research efficiency and outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance



















