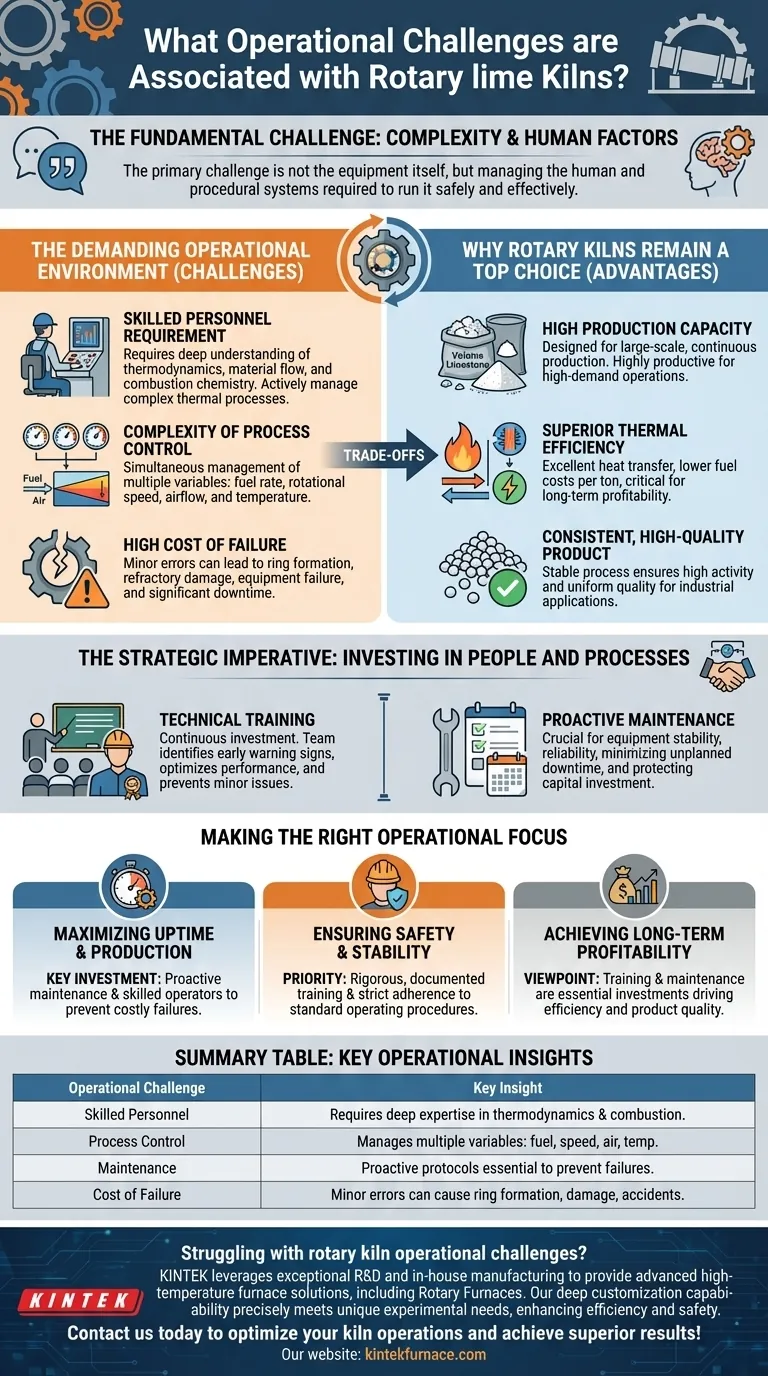
The fundamental operational challenge of rotary lime kilns lies in their complexity. Successfully running these systems requires highly skilled technical personnel, as improper operation or inadequate maintenance can quickly lead to equipment failures, production accidents, and significant downtime.
While rotary kilns offer superior production capacity and efficiency, these benefits are directly tied to a non-negotiable investment in expert operational staff and rigorous maintenance protocols. The primary challenge is not the equipment itself, but managing the human and procedural systems required to run it safely and effectively.

The Core Challenge: A Demanding Operational Environment
The advantages of a rotary kiln, such as high output and thermal efficiency, come at the cost of significant operational demands. Unlike simpler systems, they are not "set and forget" machines.
The Requirement for Skilled Personnel
Operating a rotary kiln is a technical discipline. It requires a deep understanding of thermodynamics, material flow, and combustion chemistry.
Operators are not merely monitoring gauges; they are actively managing a complex, continuous thermal process. Their skill directly impacts product quality, energy consumption, and equipment longevity.
The Complexity of Process Control
Achieving stable production involves the simultaneous management of multiple variables, including fuel feed rate, rotational speed, airflow, and internal temperature gradients.
While some modern kilns offer more precise controls, traditional fuel-fired rotary kilns demand constant adjustment. This contrasts sharply with simpler kiln designs where variables like fuel management are less of a factor.
The High Cost of Failure
The references are clear: improper operation is a direct cause of production accidents and equipment failures.
A minor operational error can lead to issues like ring formation inside the kiln, refractory damage, or inconsistent product quality. Delayed or reactive maintenance exacerbates these risks, turning small problems into major shutdowns.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Rotary Kilns Remain a Top Choice
Despite their operational challenges, rotary kilns are a cornerstone of many industries. The reasons are compelling and justify the investment in operational excellence.
Advantage: High Production Capacity
Rotary kilns are designed for large-scale, continuous production. Their ability to process large volumes of limestone in short cycles makes them highly productive and economical for high-demand operations.
Advantage: Superior Thermal Efficiency
These kilns are engineered for excellent heat transfer and energy conservation. This high thermal efficiency translates directly into lower fuel costs per ton of product, a critical factor in long-term profitability.
Advantage: Consistent, High-Quality Product
The strong controllability of a well-run rotary kiln ensures a stable process. This stability results in a final lime product with consistently high activity and uniform quality, which is essential for most industrial applications.
The Strategic Imperative: Investing in People and Processes
Mitigating the operational challenges of a rotary kiln is not about finding shortcuts; it's about making strategic investments in the two areas that guarantee stability and safety.
The Role of Technical Training
Enterprises must treat technical training as a continuous and essential investment. A well-trained team can identify early warning signs, optimize performance, and respond effectively to process deviations, preventing minor issues from escalating.
The Importance of Proactive Maintenance
A "run-to-failure" approach is incompatible with rotary kiln operation. A proactive maintenance management program is crucial for equipment stability. This ensures reliability, minimizes unplanned downtime, and protects the significant capital investment the kiln represents.
Making the Right Operational Focus
Your operational strategy should align directly with your primary business goals.
- If your primary focus is maximizing uptime and production: Your key investment must be in proactive maintenance and retaining skilled operators who can prevent costly failures.
- If your primary focus is ensuring safety and stability: The priority should be rigorous, documented training and strict adherence to standard operating procedures to mitigate the risk of accidents.
- If your primary focus is achieving long-term profitability: View operator training and maintenance management not as costs, but as essential investments that drive efficiency, reduce fuel consumption, and ensure product quality.
Mastering the operational demands of a rotary kiln is the only path to unlocking its full economic and productive potential.
Summary Table:
| Operational Challenge | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Skilled Personnel | Requires deep expertise in thermodynamics and combustion for stable operation. |
| Process Control | Involves managing multiple variables like fuel rate and temperature gradients. |
| Maintenance | Proactive protocols are essential to prevent failures and costly downtime. |
| Cost of Failure | Minor errors can lead to ring formation, refractory damage, or accidents. |
Struggling with rotary kiln operational challenges? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, tailored for diverse laboratories. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and safety. Contact us today to optimize your kiln operations and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource



















