From a purely operational standpoint, a rotary tube sintering furnace provides a suite of advantages centered on process consistency, efficiency, and control. Its core design, which involves continuously rotating the material within a heated tube, directly solves common issues like uneven heating and inconsistent product quality found in static furnaces. This dynamic processing is combined with intelligent controls to create a highly reliable and automated operational environment.
The true value of a rotary tube furnace lies in how its dynamic rotation works in synergy with precise thermal and atmospheric control. This combination moves material processing from a variable art to a repeatable, efficient science, delivering unparalleled consistency in the final product.
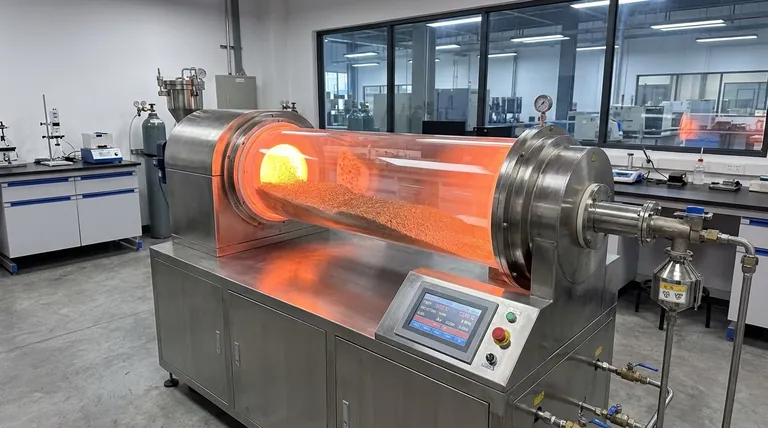

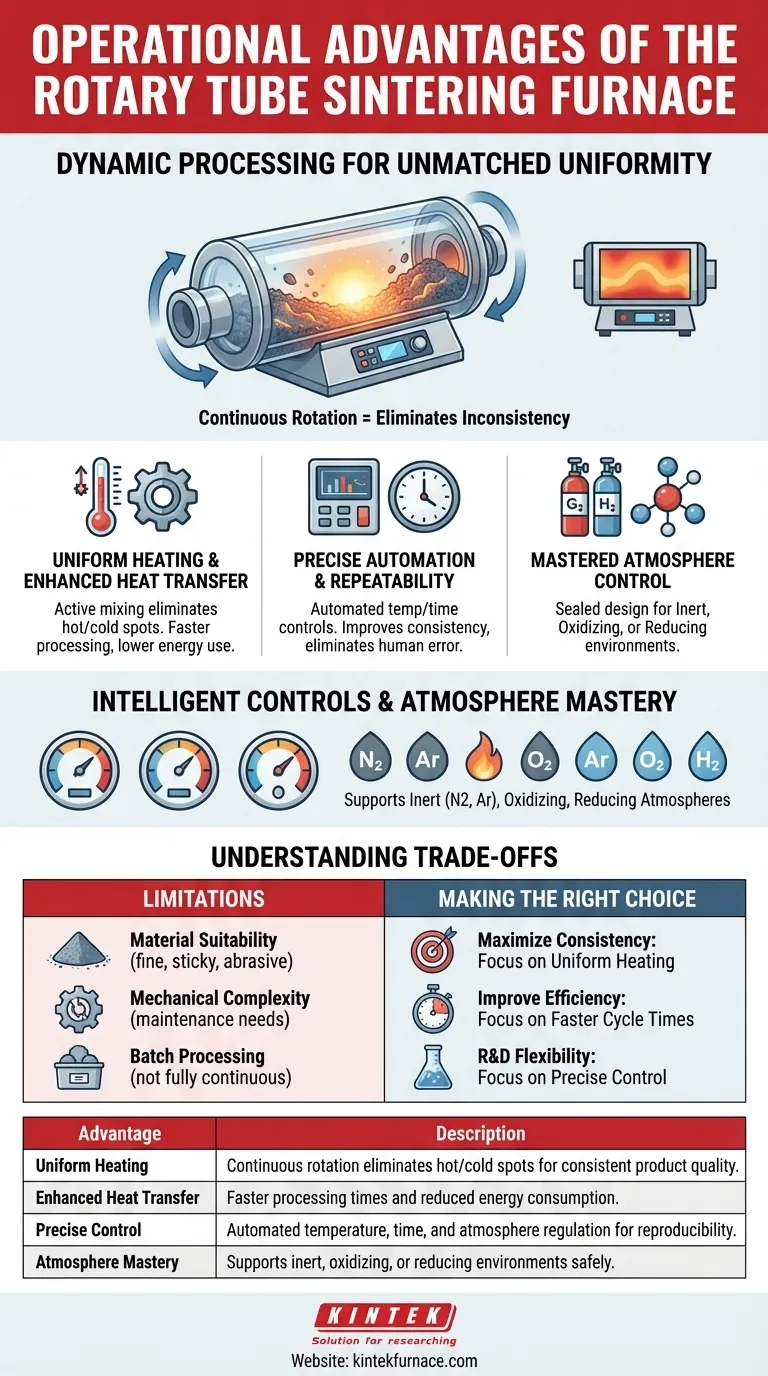
The Core Principle: Dynamic Processing for Unmatched Uniformity
The most significant operational advantage is born from the furnace's primary action: rotation. Unlike a static furnace where the material sits still, the rotary design keeps the sample in constant, gentle motion.
How Rotation Eliminates Inconsistency
By continuously tumbling the material, the furnace ensures every particle is exposed to the heat source equally. This active mixing eliminates hot and cold spots that can plague static systems.
Furthermore, this action prevents material settling or agglomeration. This guarantees that the entire batch receives the same thermal treatment, which is critical for achieving consistent density, crystal structure, and chemical properties.
The Impact on Heat Transfer Efficiency
The constant tumbling dramatically enhances heat transfer efficiency. As new surfaces are constantly exposed to the heating elements and the controlled atmosphere, the time required to bring the entire batch to the target temperature is significantly reduced.
This results in faster processing times and lower energy consumption per batch, directly improving operational throughput and cost-effectiveness.
Precision Control for Repeatable Results
Modern rotary furnaces integrate sophisticated control systems that remove guesswork and minimize the need for manual intervention, ensuring every run is identical to the last.
Intelligent Temperature and Time Automation
These systems feature high-precision temperature regulation and programmable time controls. Operators can define precise heating, soaking, and cooling profiles that the furnace executes automatically.
This automation improves process consistency and reproducibility by eliminating the potential for human error, making it invaluable for both quality-controlled production and sensitive scientific research.
Mastering the Process Atmosphere
The sealed tube design allows for complete control over the internal environment. This is a critical advantage for processes that are sensitive to oxygen or require a specific chemical reaction.
The furnace can easily maintain an inert (e.g., Nitrogen, Argon), oxidizing, or reducing atmosphere. Integrated safety controls for gas flow and pressure ensure this is done reliably and safely, widening the furnace's applicability to a vast range of materials and processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, a rotary tube furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Material Suitability
The primary consideration is the nature of your material. Extremely fine powders may become airborne, while very sticky or viscous materials may not tumble correctly. Highly abrasive materials can also cause premature wear on the tube interior.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating mechanism, including the motor and seals, introduces mechanical complexity not present in a static furnace. While modern designs are highly durable, these components represent potential points of failure and require periodic inspection and maintenance.
Batch Processing Nature
Most lab-scale and many production-scale rotary furnaces operate in a batch mode. While highly efficient for this purpose, scaling to a truly continuous, 24/7 operation requires more complex and costly automated feeding and collection systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal will determine how you value these operational advantages.
- If your primary focus is maximizing product consistency: The uniform heating provided by the rotating tube is the most critical advantage, as it directly eliminates process variability.
- If your primary focus is improving process efficiency: The enhanced heat transfer, which leads to faster cycle times and lower energy use, will provide the greatest return on investment.
- If your primary focus is research and development flexibility: The precise control over both temperature and atmosphere allows you to test a wide range of materials and processing parameters with high confidence.
Ultimately, this furnace empowers you to achieve a superior degree of control and predictability in your thermal processing workflow.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Uniform Heating | Continuous rotation eliminates hot/cold spots for consistent product quality. |
| Enhanced Heat Transfer | Faster processing times and reduced energy consumption. |
| Precise Control | Automated temperature, time, and atmosphere regulation for reproducibility. |
| Atmosphere Mastery | Supports inert, oxidizing, or reducing environments safely. |
Ready to enhance your thermal processing with a custom rotary tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can boost your lab's efficiency and consistency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules



















